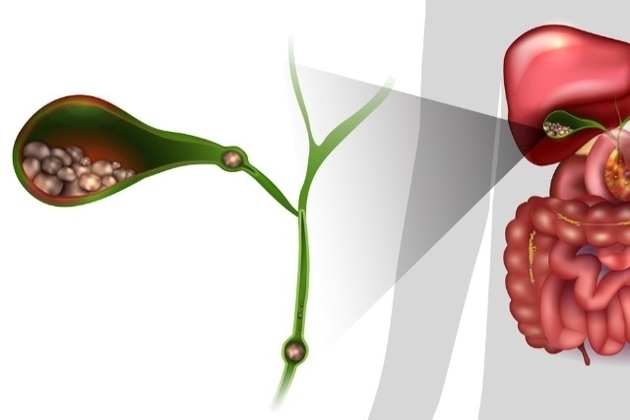
THE gallbladder it is a muscular organ that is located close to the liver and acts on the digestive system.
Its main function is to store bile, which is produced by the liver. It helps digestion in the process of dissolution and use of ingested fat, stimulating the secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK) and neutralizing acids until reaching the intestine.
Gallbladder Anatomy
The anatomy of the gallbladder is similar in shape to a pear, measuring between 7 and 10 cm in length.
It has a dark green color due to the bile it stores, approximately 50 ml. Its main components are water, sodium bicarbonate, bile salts, pigments, fats, inorganic salts and cholesterol.
The gallbladder is connected to the liver and duodenum by the biliary tract, with right and left hepatic ducts, cystic and common bile ducts.
THE bile produced by the liver travels through the hepatic duct, passes through the intestine and meets with the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder. The meeting of these two ducts forms the common bile duct.
In the duodenum, when the bolus arrives, a stimulus is provoked in the gallbladder, which contracts and releases bile, facilitating the digestion.

Gallbladder Diseases
Blockage of bile flow through the cystic duct is considered the most frequent reason for gallbladder disease. In addition, the gallbladder can present problems such as inflammation and infection.
Below are the main diseases related to the gallbladder.
cholelithiasis
One of the most common diseases, cholelithiasis is also known as gallstones or gallstones.
There is no single cause for this disease. The most common factors are genetic inheritance, diet, body weight and high cholesterol levels.
People who have gallstones do not always show symptoms, which can be confused with stomach pain, in kidneys and, in some cases, even with back pain.
The pain is usually intense and gradual. To identify gallstones, ultrasound of the abdominal region is performed.
The treatment for cholelithiasis is surgery to remove the stones and the gallbladder, because if the gallbladder ruptures, there is a possibility of inflammation and infection.

cholecystitis
Gallbladder inflammation usually occurs in people who have gallstones. It is also related to the complication of other diseases.
Its main symptoms are abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and sensitivity to touch in the abdomen region.
Cholecystitis can be acute or chronic. THE acute cholecystitis it appears suddenly, with severe pain in the upper abdomen, which can be alleviated with antibiotic medication.
THE chronic cholecystitis it is more serious and affects people who have gallstones and its treatment is emergency surgery.
sclerosing cholangitis
This disease represents the narrowing of the bile ducts due to their inflammation and scarring. The tissue formed by the healing does not allow the passage of substances that aid in the absorption of fat.
Because it is related to the activities of the liver and gallbladder, the main consequences of sclerosing cholangitis can be liver failure, cirrhosis and, in some cases, cancer.
Treatment may vary depending on the symptoms presented. For the simplest cases, it is only recommended to monitor the evolution of the disease. In more advanced cases, liver transplantation may be necessary.
Difference between gallstones and kidney stones
Gall stones and kidney stones are diseases with very similar symptoms and can be confused. See the table below for a comparison between these two diseases.
| Gallstones | kidney stone | |
|---|---|---|
| What are | These are gallstones and are located in the gallbladder or in one of its ducts. | Popularly known as a kidney stone, it can be found both in the kidneys and in other organs of the urinary system. |
| Causes | There is no specific reason, however, the most common is related to cholesterol, that is, to fats that are not dissolved by bile. | The main cause is low water intake, which generates low urine volume. |
| How to differentiate | The main characteristic is the pain in the front of the abdomen, being intense and sudden, causing nausea and vomiting. | The pain is strong and intense in the abdominal region, but located in the back. The presence of blood in the urine is also common in these cases. |
| Treatment | In most cases, surgery to remove the gallbladder is recommended. | Stones are spontaneously eliminated in the urine. |
Read too:
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- human body systems
- Organs of the human body
- Organs of the human body without which you can survive