Plate tectonics are portions of the outer layer of the earth's structure called the lithosphere, where continents and oceans are located.
These tectonic plates move over the more fluid lower layer, called the asthenosphere.
The Earth's surface layer is made up of seven main rigid rock slabs that shift position and fit together like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle.
The motion of these plates can be converging when they move against each other; divergent, when they move away or conservative, when they move vertically or parallel.
The movement of the plates are responsible for volcanoes, earthquakes and tsunamis. As well as the formation of continents and seas, the formation of mountain ranges and the entire landscape that lies on these tectonic plates.
Main Tectonic Plates
The name plate tectonics is a concept that deals with the geological history of the Earth. The main tectonic plates are:
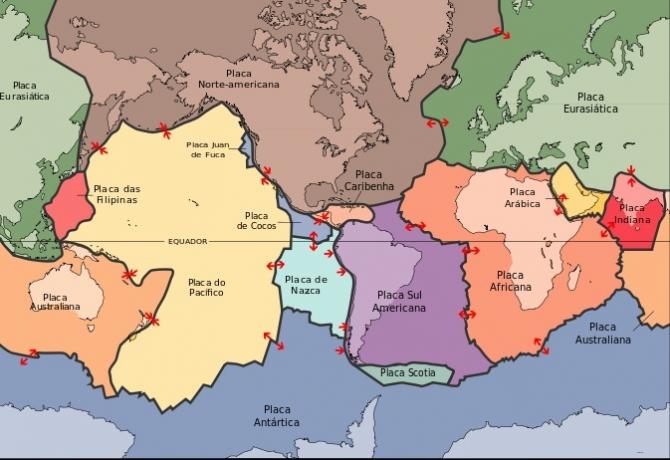
- African plate
- Antarctic Plate
- Australian Plate
- Eurasian plate
- Pacific plate
- North American plate
- South American plate
- Nazca plate
- Scotia Plate
- Caribbean Plate
- Indian plate
- Philippine plate
There are also smaller plates, called: Adriatic Plate, Anatolia Plate, Arabic Plate, Carolina Plate, East American Plate, Plate of Fat, Hellenic Plate, Indo-Australian Plate, Iranian Plate, Coconut Plate, Juan de Fuca Plate, Somali Plate, Sunda Plate and Plate of Tonga.
The Movement of Tectonic Plates
The movements of tectonic plates are responsible for a series of geographic accidents, such as: volcanoes, earthquakes and tsunamis.
The movement of the plates was also responsible for the formation of continents and the definition of the Earth map, as it is known.
Some clues such as the similarity between the Atlantic coasts of the African and South American continents and fossils of different species common on both sides lead to believe that the planet was once formed by a single continent, called Pangea, there are about 225 million of years.
The movements of tectonic plates can be observed across their boundaries and are classified as:
- Divergents (which define the construction zone of the crust),
- Convergents (defined in the crust destruction zone) and
- Conservatives (where the transform faults are).
Divergent movements of tectonic plates
It occurs when the plates trace the movement away from each other causing the “birth” of a new oceanic crust.
The movement is plotted in the horizontal direction. This limit is defined in three stages, the first being the opening of a crack that occurs with the fracture of the crust, the invasion of water and formation of saline lakes. At this stage, there is intense volcanic activity.
In the second stage, fragmentation is total and two continents are formed effectively separated by an ocean. Volcanic activity persists through the rise of magma.
The permanence of magma activity defines the arrival of the third stage, called ocean formation. The main example of the divergent boundary in its three stages is in the Atlantic Ocean, which separates Europe, Africa and America.
The division of continents originated 180 million years ago at an average speed of 1 centimeter per year.
Convergent movements of tectonic plates
This is the definition for the collision movement of one plate on another. There are three types of convergence between tectonic plates: continental-continental, oceanic-oceanic, and oceanic-continental.
Convergent motion between continental plates creates an area called the metamorphic zone, which is responsible for modern folding, earthquakes and volcanic activity.
Convergence between oceanic plates creates a subduction zone, in which one plate tends to slide under the other, creating a pit.
In these places are found the greatest depths of the oceans, such as the Marianas Trench, which is almost 11 kilometers deep.
On the other hand, oceanic-continental convergence occurs when these two types of plates collide. The denser oceanic plate dips below the continental plate creating a subduction zone, while the continental plate rises, forming large mountain ranges.
For example, the Andes Mountains were formed from the convergent movement between the Nazca Plate (oceanic) and the South American Plate (continental). This type of geological formation is known as modern folds.
Know about the San Andreas Fault.
Conservative movements of tectonic plates
Conservative movement occurs in fault areas, where the plates slide in relation to each other, vertically or horizontally and in a parallel way, without divergence or convergence.
The friction caused by these boundaries generates the so-called earthquake zone. In these places, the so-called shallow focus earthquakes occur, which have a great intensity.
Complement your research by reading the texts:
- Continental Drift
- pangea



