O esophagus it is an organ that has a cylindrical shape, formed by muscle tissue, is about 25 cm long and 3 cm in diameter.
It is an organ that makes up the digestive system, being responsible for connecting the pharynx to the stomach and taking the ingested food to the stomach.
esophageal anatomy
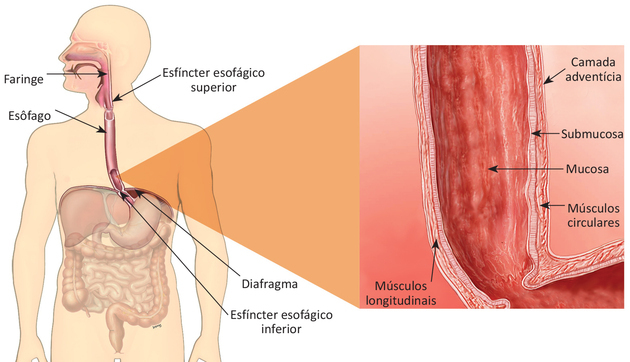
Located in the trunk of the body, the esophagus is classified in three ways:
- cervical esophagus: represents the beginning of the organ, which makes the direct connection with the trachea and is about 4 cm long;
- thoracic esophagus: represents the largest region of the esophagus, measuring approximately 18 cm, being located behind the left bronchus;
- Abdominal esophagus: is a region of about 3 cm that connects directly with the diaphragm, which in turn attaches to the stomach.
To perform its function, the esophagus has an upper and a lower part.
THE upper esophagus it has a muscle called the upper esophageal sphincter, responsible for opening the necessary space, loosening the esophagus for the passage of food or liquids.
THE lower esophagus connects with the stomach and receives the name of gastroesophageal junction. In this area, there is the presence of the lower esophageal sphincter, which helps control the passage of food to the stomach. This action prevents stomach heat and digestive enzymes from reaching the esophagus.
The esophagus is made up of several layers that form its wall. Are they:
mucous
The mucosa corresponds to the layer that lines the inside of the esophagus. It is divided as follows:
- Epithelium: is the innermost layer of the esophagus and is formed by cells called squamous cells.
- own blade: is the layer of connective tissue formed under the epithelium.
- Muscularis musoca: represents the thin layer of muscle that is located under the lamina propria.
submucosa
The submucosa represents the layer of connective tissue that lies beneath the mucosa, containing blood vessels and nerves. It is in this layer that the esophagus has glands that secrete mucus.
Muscularis own
THE muscularis proper is a layer of muscle that works by contracting so that ingested food is pushed out of the throat, down the esophagus and into the stomach.
Adventitia
The adventitia corresponds to the outermost layer of the esophagus, being formed by a connective tissue.
Also read about:
- epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscle tissue
- human body tissue
esophageal diseases
Below are the most common diseases related to the esophagus.
esophageal cancer
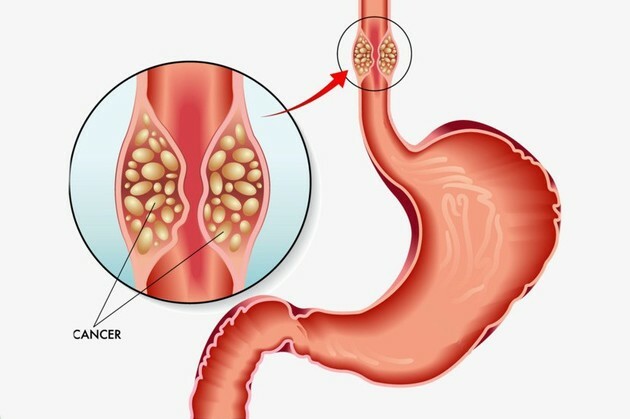
Esophageal cancer is the development of cancer cells in the esophageal wall. The most likely causes for this disease are related to tobacco and alcohol use and esophageal disorders.
The main symptoms are difficulty in eating food, weight loss and pain at the site. Diagnosis is made through an endoscopy exam. Treatment may involve surgery and chemotherapy, as well as complementary therapies to help relieve symptoms.
Inflammation of the esophagus

Inflammation of the esophagus corresponds to esophagitis. The most common factors related to esophagitis are infections, gastritis and gastric reflux. The most common symptom is constant heartburn, bad breath, bitter taste in the mouth and sore throat.
After confirming the diagnosis, treatment is based on medication combined with a specific diet and lifestyle changes.
Gastroesophageal reflux
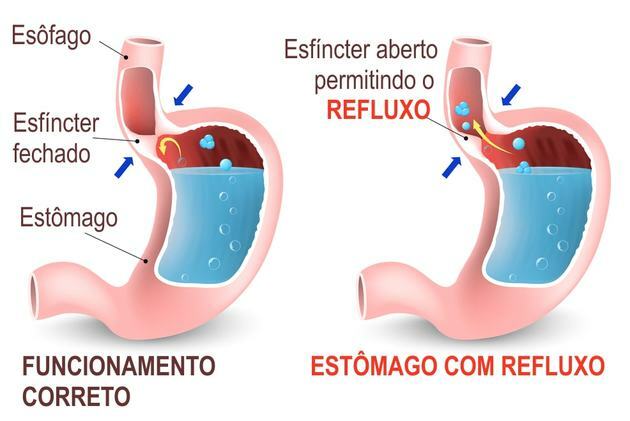
Gastroesophageal reflux is when food returns to the esophagus because the sphincter located between the stomach and esophagus remains open. The main symptoms are heartburn, sore throat and bitterness in the mouth.
The treatment for reflux consists of educational measures, such as avoiding drinking liquids during meals, drinks with a high caffeine content and even the use of medication.
Barrett's Esophagus
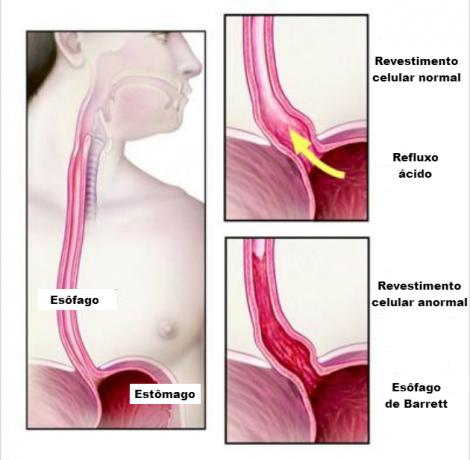
Barrett's esophagus is a disease that results from the complication of gastroesophageal reflux, causing exposure of the esophageal mucosa to gastric contents.
As a result, the esophagus undergoes changes in the type of cell that forms this region, which is an attempt by the body to protect against acidity.
People with this disease are more likely to develop esophageal cancer. The symptoms are similar to those of other esophageal disorders, namely heartburn, poor digestion, burning sensation, pain and sore throat.
Treatment requires medical follow-up, in which the use of medication and restricted and controlled diet is indicated.
Discomfort in the esophagus

The esophagus can be uncomfortable, causing burning, heartburn, poor digestion, pain, and inflammation.
THE burning in the esophagus it is very common and can be related to the ingestion of certain types of food and even the posture the person is eating. The burning sensation occurs in the stomach area and goes up to the throat.
THE heartburn and poor digestion can be considered as some of the symptoms of esophageal related diseases such as cancer and esophagitis.
Read more about this topic:
- Digestive system
- Digestion
- Gastroenterology
- Organs of the human body
- Organs of the human body without which you can survive
- Exercises on the Respiratory System


