Planet Earth performs two main movements. In a first movement, called a translation, it traces an orbit around the Sun. It also performs a turn on its own axis, called a rotation.
Each revolution around the Sun represents a year, while each revolution around its own axis defines a day.
What is translation?
Translation is the movement performed by the Earth around the Sun. This is due to the gravitational field generated by the mass of the Sun, causing the Earth to be stuck in its orbit.
Thus, a complete turn of the Earth around the Sun takes about 365 days, 5 hours and 47 minutes. The planet moves through space at an average orbital speed of 29.78 km/s.
As the calendar year is counted only in days, every four years a leap year is held to make up for the almost six annual hours that were left out. In it, one more day (February 29) is added to the calendar.
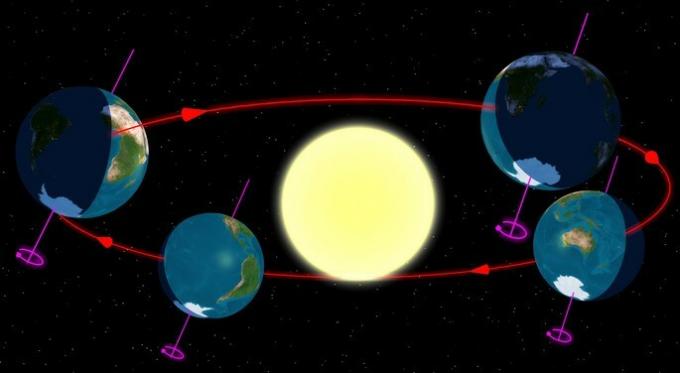
The Earth performs a trajectory very similar to a circle around the Sun, but because it is not a perfect circle, it is called an elliptical trajectory.
The average radius of the Earth's orbit is 149.6 million kilometers. However, this number varies between two moments: perihelion, when the radius is 147.1 million kilometers, and aphelion, the furthest moment, with a radius of 152.1 million kilometers.
Contrary to what some people believe, the seasons do not occur because of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. The phenomena responsible for seasonal changes are the solstices. That is, the position of each hemisphere in relation to the Sun.
It is according to the solstice that the degree of incidence of the sun's rays changes. In summer, there is greater solar incidence due to the inclination of the Earth's axis in relation to the Sun.
This is the opposite between the hemispheres. When it's summer in the southern hemisphere, it's winter in the northern hemisphere, when it's autumn in the southern hemisphere, it's spring in the northern hemisphere, and so on.
See too: Translation Movement.
What is rotation?
Rotation is the movement the Earth makes around its own axis. Each Earth spin around itself lasts 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds and 9 hundredths. Therefore, it was agreed that the day has twenty-four hours.
The Earth's axis is an imaginary line that runs through the planet from the north to the south pole. This axis has an inclination of about 23.5 degrees.

As the Earth rotates (counterclockwise), part of its surface is exposed to the Sun, being responsible for day and night.
Taking the diameter of the Equator Line as a reference, it can be stated that the rotation movement occurs at an average speed of 1674 km/h. This speed cannot be felt within the atmosphere.
See too: rotation movement.
Other Earth Movements
Although translation and rotation are the main movements that the planet performs, they are not the only ones. There are small movements that do not exert such an influence as rotation (responsible for the days and nights) and translation (responsible for the year and seasons).
The other moves are:
- Precession of the Equinoxes - movement that takes 25 800 years to complete. In it, the terrestrial axis makes a circle.
- Nutation - Influenced by the gravity of the Sun and Moon, the Earth oscillates its axis up to 700 meters and returns to its original position. Each cycle of this movement lasts 18.6 years.
- Chandler oscillation - A movement that lasts 433 days where the poles make a circular movement as an effect of the planet's mass distribution and the Earth's internal movements.
Interested? See too:
- Summer Solstice
- heliocentrism
- Planet Earth
- Solar system
- origin of the earth

