The periodic table is an important study tool that gathers information about all known chemical elements.
Test your knowledge with this list of 17 questions with the different approaches on the subject and solve your doubts with the resolutions commented after the feedback.
To help understand the questions, use the periodic table complete and updated.
Periodic Table Organization
question 1
(UFU) In the early nineteenth century, with the discovery and isolation of various chemical elements, it became necessary to classify them rationally, in order to carry out systematic studies. Many contributions were added until reaching the current periodic classification of chemical elements. Regarding the current periodic classification, answer:
a) How are the elements listed sequentially in the periodic table?
The periodic table is organized into sequences of chemical elements in ascending order of atomic number. This number corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.
This method of organization was proposed by Henry Moseley when he reconfigured the table proposed by Dmitri Mendeleiev.
An element can be located in the table by the family and period in which it is inserted. This distribution occurs as follows:
| groups or families | 18 vertical sequences |
| Groups of elements that have similar characteristics. |
| Periods | 7 horizontal sequences |
| Number of electronic layers that the element has. |
b) Which groups in the periodic table can be found: a halogen, an alkali metal, an alkaline earth metal, a chalcogen and a noble gas?
The classification of elements into groups is done according to properties. Elements that are in the same group have similar characteristics and for the classifications given we have to:
| Classification | Group | Family | Elements |
| halogen | 17 | 7A | F, Cl, Br, I, At and Ts |
| alkali metal | 1 | 1A | Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs and Fr |
| alkaline earth metal | 2 | 2A | Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba and Ra |
| chalcogen | 16 | 6A | O, S, Se, Te, Po and Lv |
| noble gas | 18 | 8A | He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn and Og |
question 2
(PUC-SP) Resolve the issue based on the analysis of the statements below.
I – The current modern periodic table is arranged in ascending order of atomic mass.
II - All elements that have 1 electron and 2 electrons in the valence shell are, respectively, alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, provided that the principal quantum number of this layer (n 1).
III – In the same period, the elements present the same number of levels (layers).
IV – In the same group (family), the elements have the same number of levels (layers).
It is concluded that, with respect to the current periodic table of chemical elements, they are correct:
a) I and IV (only).
b) I and II (only).
c) II and III (only).
d) II and IV (only).
e) III and IV (only).
Correct alternative: c) II and III (only).
Analyzing each alternative we have to:
I – WRONG. The elements are arranged in ascending order of atomic number.
II – CORRECT. The electrons in the valence shell define the group the element is located in.
| alkali metals | 1 electron in the valence shell |
| 3read | 2-1 |
| 11At | 2-8-1 |
| 19K | 2-8-8-1 |
| 37Rb | 2-8-18-8-1 |
| 55Cs | 2-8-18-18-8-1 |
| 87Fr | 2-8-18-32-18-8-1 |
| alkaline earth metals | 2 electrons in the valence shell |
| 4be | 2-2 |
| 12mg | 2-8-2 |
| 20Here | 2-8-8-2 |
| 38Mr | 2-8-18-8-2 |
| 56Ba | 2-8-18-18-8-2 |
| 88Frog | 2-8-18-32-18-8-2 |
The main quantum number corresponds to the shell in which the electron is located, being different from 1 because by the electronic distribution we notice that the location of the electron is from the second shell or n=2.
III – CORRECT. The location of an element in a certain period is due to the number of layers when making the electronic distribution.
| Periods | 7 horizontal sequences |
| 1st period | 1 layer: K |
| 2nd period | 2 layers: K, L |
| 3rd period | 3 layers: K, L, M |
| 4th period | 4 layers: K, L, M, N |
| 5th period | 5 layers: K, L, M, N, O |
| 6th period | 6 layers: K, L, M, N, O, P |
| 7th period | 7 layers: K, L, M, N, O, P, Q |
Example: chemical element located in the second period.
IV – WRONG. Elements belonging to the same group have similar characteristics and this is due to the fact that they have the same number of electrons in the valence shell.
Example:
| Beryllium | Magnesium |
|
2 electrons in valence layer. |
2 electrons in valence layer. |
Therefore, beryllium and magnesium are part of group 2 of the Periodic Table.
question 3
(Unitins) Regarding the modern periodic classification of elements, identify the true statement:
a) in a family, the elements generally have the same number of electrons in the last shell.
b) on the periodic table, the chemical elements are placed in descending order of atomic masses.
c) in a family, the elements have very different chemical properties.
d) in one period, the elements have similar chemical properties.
e) all representative elements belong to group B of the periodic table.
Correct alternative: a) in a family, the elements generally have the same number of electrons in the last shell.
a) CORRECT. Chemical elements of the same family have the same number of electrons in the last shell and this makes them have similar characteristics.
b) WRONG. Atomic masses increase as the atomic number of the element increases.
c) WRONG. The chemical properties of the elements are similar, so they are grouped in the same family.
d) WRONG. At one time, the elements have their electrons distributed in the same number of shells.
e) WRONG. The representative elements belong to group A, which corresponds to the families: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A and 8A. Elements belonging to group B are transition elements.
question 4
(Vunesp) Considering the properties of chemical elements and the periodic table, it is incorrect to state:
a) a metal is a substance that conducts electrical current, is ductile and malleable.
b) a non-metal is a substance that does not conduct electrical current, is neither ductile nor malleable.
c) a semimetal has the physical appearance of a metal, but chemical behavior similar to that of a non-metal.
d) most chemical elements are made up of non-metals.
e) the noble gases are monoatomic.
Incorrect alternative: d) most chemical elements are non-metals.
Note the classification of chemical elements on the periodic table into metals, nonmetals, and semimetals.

As we can see, most elements are metals.
a) CORRECT. Metals conduct electricity because of the electron clouds formed by free electrons, which are characteristic of their structure. They are ductile because they can turn into wires or sheets, depending on the region where pressure is applied. They are also malleable, as very thin sheets can be produced with this type of material.
b) CORRECT. Nonmetals have the opposite characteristics of metals. Instead of conductors, they are good thermal insulators and, as they are brittle, they are not molded into wires or sheets as they do not have good ductility and malleability.
c) CORRECT. Semimetals have characteristics intermediate to metals and non-metals. Being semiconductors of electricity, they have a metallic sheen but are brittle like non-metals.
d) WRONG. Most elements are classified as metals. The classes of metals present in the periodic table are: alkaline, alkaline earth, transitional internal and external.
e) CORRECT. Noble gases are monoatomic, so they are represented only by their initials.
Example:
| noble gas | chalcogen |
| Helium (He) | Oxygen (O2) |
| monoatomic: formed by an atom | diatomic: formed by two atoms |
Due to the stability of noble gases, the elements of this family have low reactivity and are also known as inert.
question 5
About the organization of the current Periodic Table, answer:
a) What are columns?
b) What are the lines?
c) What is the method used to organize the chemical elements?
Answers:
a) the columns are the groups of the Periodic Table, formerly called families, that bring together chemical elements with similar properties.
b) The lines are the periods of the Periodic Table and indicate the number of electronic layers of an atom in the ground state.
c) The chemical elements in the current Periodic Table are arranged in ascending order of atomic number, which indicates the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.
Periodic Table Families
question 1
(CESGRANRIO) Making the association between the columns below, which correspond to the element families according to the periodic table, the numerical sequence will be:
| 1. noble gases | • Group 1A |
| 2. alkali metals | • Group 2A |
| 3. alkaline earth metals | • Group 6A |
| 4. Chalcogens | • Group 7A |
| 5. Halogens | • Group 0 |
a) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
b) 2, 3, 4, 5, 1.
c) 3, 2, 5, 4, 1.
d) 3, 2, 4, 5, 1.
e) 5, 2, 4, 3, 1.
Correct alternative: b) 2, 3, 4, 5, 1.
| groups | electronic configuration |
| • Group 1A: 2. alkali metals | us1 (with n |
| • Group 2A: 3. alkaline earth metals | us2 (with n |
| • Group 6A: 4. Chalcogens | us2np4 |
| • Group 7A: 5. Halogens | us2np5 |
| • Group 0: 1. noble gases | 1s2 (He) or us2np6 (if n > 1) |
question 2
(UECE) The chemical element with Z = 54 has in its valence layer the 5s configuration2 5p6. The elements with Z = 52 and with Z = 56 belong to the families of:
a) chalcogens and alkaline earth
b) halogens and alkalis
c) halogens and alkaline earth
d) chalcogens and alkalis
Correct alternative: a) chalcogens and alkaline earths.
Given the atomic numbers, we performed the electronic distribution and found the following results:
| 54X and | 52You | 56Ba |
|
8 electrons in valence layer |
6 electrons in valence layer |
2 electrons in valence layer |
| Noble Gases: 8A family | Chalcogens: 6A family | Alkaline Earth: family 2A |
question 3
(F. Ibero-Americana-SP) The Periodic Table group that is characterized by the predominance of artificial elements is the following:
a) lanthanides
b) noble gases
c) transition metals
d) alkaline earth metals
e) actinides
Correct alternative: e) actinides.
Artificial elements are those that do not exist in nature and that have been synthesized in the laboratory through nuclear reactions.
They are also called transuranic elements, as these radioactive elements have an atomic number greater than 92, which corresponds to uranium.
In general, these elements are short-lived, lasting up to fractions of a second.
According to this information we have to:
The elements found in nature are: lanthanides, noble gases, transition metals and alkaline earth metals. With the exception of technetium and promethium, which are artificial.
The predominance of artificial elements is actinides, classified as internal transition metals and inserted in the periodic table below the lanthanides. From that series, only actinium, thorium, protactinium and uranium are natural.
question 4
(U. Catholic Church of Salvador-BA) The X species2- with 8 electrons in the outermost shell (valence shell) it can be from element X, which, in the Periodic Table, belongs to the group:
a) 7A
b) 6A
c) 2A
d) 1A
e) 8A
Correct alternative: b) 6A.
According to the octet rule, for an element to acquire stability, it assumes the electronic configuration of a noble gas, which has 8 electrons in the valence shell.
Charge 2- on species X2- indicates that the element has gained 2 electrons.
The electron configuration of the species having 8 electrons in the outermost shell is ns2np6.
Upon losing two electrons, the element returns to its ground state with ns electron configuration2np4.
The 6 electrons in the valence shell are characteristic of chalcogens, elements of the 6A family.
For example:
| Element: oxygen | electronic configuration |
| 8O | 1s22s22p4 |
| species O2- | 1s22s22p6 |
Learn more about Periodic Table Families.
Chemical elements
question 1
(CESGRANRIO) Given the elements of atomic numbers 3, 9, 11, 12, 20, 37, 38, 47, 55, 56 and 75, the option that only contains alkali metals is:
a) 3, 11, 37 and 55
b) 3, 9, 37 and 55
c) 9, 11, 38 and 55
d) 12, 20, 38 and 56
e) 12, 37, 47 and 75
Correct alternative: a) 3, 11, 37 and 55
Alkali metals correspond to the chemical elements that end the electronic distribution with an electron in the s sublevel.
Making the electronic distribution of the given atomic numbers, we have the following alkali metals:
| Z = 3 | Z = 11 | Z = 37 | Z = 55 |
| Lithium | Sodium | Rubidium | Cesium |
The other atomic numbers correspond to elements of the following groups:
Alkaline earth metals: terminate electronic distribution at sublevel s2.
| Z = 12 | Z = 38 | Z = 56 |
| Magnesium | Strontium | Barium |
Transition metals: terminate electronic distribution at sublevel d.
| Z = 30 | Z = 47 | Z = 75 |
| Zinc | Silver | Rhenium |
Halogens: terminate electronic distribution at sublevel p5.
| Z = 9 |
question 2
(Unirio) “The artificial heart placed in Eloi began to be developed four years ago in the United States and is already used by around 500 people. The set, called the Heartmate, is made up of three main pieces. The most important is a four-pound round bag, 12 centimeters in diameter and 3 centimeters thick, made of titanium — a silver-white metal, light and strong.” Veja Magazine, July 1999.
Among the metals below, the one that has, in the last layer, a number of electrons equal to that of titanium is:
a) C
b) In
c) Ga
d) Mg
e) Xe
Correct alternative: d) Mg.
| Titanium | electronic configuration | Layer distribution |
| 22You | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2 | 2, 8, 10, 2 |
From the electronic distribution of titanium, we see that this element has 2 electrons in the last shell.
| Element | electronic configuration | Layer distribution |
| 6Ç | 1s2 2s2 2p2 | 2, 4 |
| 11At | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 | 2, 8, 1 |
| 31Ga | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d104p1 | 2, 8, 18, 3 |
| 12mg | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 | 2, 8, 2 |
| 54X and | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8 |
The element that also has 2 electrons in the last shell is magnesium.
question 3
(UFPA) Consider a certain chemical element whose most energetic sublevel is 5s2. Its atomic number and the group in which it is located on the Periodic Table are, respectively:
a) 20; 1A
b) 20; 2A
c) 38; 2A
d) 38; 1A
e) 39; 2A
Correct alternative: c) 38; 2A
By doing electronic distribution, we found that:
- The chemical element is located in the family 2A, as it has the most energetic sublevel the s2
- Has atomic number 38, which corresponds to the total number of electrons distributed.
- It is located in the fifth period, as the electronic distribution was carried out up to the fifth layer.
Checking this information in the Periodic Table, we can confirm that it is the element strontium.
question 4
(UFC) An x atom has one more proton than a y atom. Based on this information, determine the correct statement.
a) If y is alkaline earth, x is alkali metal.
b) If y is a noble gas, x is a halogen.
c) If y is a transition metal, x is a noble gas.
d) If y is a noble gas, x is an alkali metal.
e) x is located in the same period before atom y in the periodic table.
Correct alternative: d) If y is a noble gas, x is an alkali metal.
The periodic table is arranged in ascending order of atomic number.
If Y has atomic number z and X has one more proton than it, it means that these two elements are in the same period and X is subsequent to Y.
Example:
| Element | subsequent element |
| zY | z + 1X |
| 11At | 12mg |
The two elements are in the 3rd period and magnesium has one more proton than sodium.
According to this reasoning we have to:
a) WRONG. An alkali metal comes before an alkaline earth metal on the periodic table. The correct statement would be: If y is alkali metal, x is alkaline earth.
b) WRONG. A halogen comes before the noble gas on the periodic table. The correct statement would be: If y is halogen, x is noble gas.
c) WRONG. Transition metals and noble gases are separated by other chemical elements and therefore are not sequential.
d) CORRECT. Noble gases are the last group on the periodic table and alkali metals the first, so they are sequential.
Example:
| noble gas | alkali metal |
| zY | z + 1X |
| 2he | 3read |
Lithium, an alkali metal, has one more proton than helium, which is a noble gas.
e) WRONG. X is in the same period as Y but after it, not earlier as the alternative states.
question 5
From the atomic number of a chemical element it is possible to know:
a) the number of neutrons in the nucleus
b) the number of electrons in the electrosphere
c) the core mass
Answer: b) the number of electrons in the electrosphere
An atom in the ground state is electrically neutral. So, knowing the atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons (positively charged particles), we know the number of electrons (negatively charged particles) in the electrosphere.
For example, iron has atomic number 26, so in the ground state it has 26 electrons around the nucleus.
Learn more about chemical elements it's the atomic number.
Periodic and aperiodic properties
question 1
(UFSM) Judge whether the statements related to the periodic properties of the elements are true (T) or false (F).
( ) Depends on the atomic masses of the elements.
( ) They are repeated at more or less regular intervals in relation to the increase in atomic numbers.
( ) Are similar in the same group of elements.
( ) Are similar in the same period of elements.
( ) In the same group, the numerical values of the periodic properties always increase when there is an increase in the atomic number of elements.
The correct sequence is:
a) V - F - V - F - F
b) V - F - F - V - V
c) F - V - V - F - F
d) F - V - F - V - V
e) V - F - F - V - F
Correct alternative: c) F - V - V - F - F
(FALSE) Depend on the atomic masses of the elements.
According to Moseley's law of periodicity, many physical and chemical properties of chemical elements vary by atomic number.
(TRUE) They are repeated at more or less regular intervals in relation to the increase in atomic numbers.
Properties such as atomic radius, atomic volume, density, melting point, and boiling are examples of properties that recur regularly in the periodic table.
(TRUE) Are similar in the same group of elements.
The periodic table groups have been arranged with elements that have similar properties.
(FALSE) Are similar in the same period of elements.
Properties are similar in families, not periods. In periods, the elements are distributed by the number of electronic layers.
(FALSE) In the same group, the numerical values of the periodic properties always increase when there is an increase in the atomic number of elements.
Properties can increase or decrease depending on the atomic number. An example of this is electronegativity, which decreases as the atomic number increases in a given group.
Read too: Periodic Properties
question 2
(FAESP) The aperiodic properties of the elements are:
a) density, atomic volume and atomic mass.
b) melting point, electronegativity and specific heat.
c) atomic volume, atomic mass and melting point.
d) atomic mass, specific heat and melting point.
e) atomic mass and specific heat.
Correct alternative: e) atomic mass and specific heat.
The aperiodic properties are repeated at regular intervals.
Atomic mass is the measure of the atom's weight in atomic mass units, which corresponds to of the carbon-12 mass.
Specific heat determines the amount of heat needed to increase the temperature by 1 °C of 1 g of the element.
These two properties are unrelated to the element's position on the periodic table.
The other properties are classified as periodic as they increase or decrease with the atomic number. Are they:
- Density: represents the quotient between the mass and volume of an element.
- Atomic volume: represents the volume of a set of atoms and influences the distance between them.
- Melting point: temperature at which the transition from solid to liquid occurs.
- Electronegativity: the atom's ability to attract to itself the electronic pair it shares in a covalent bond.
Read too: electronegativity and Electronic Affinity
question 3
(PUC-PR) Among the following diagrams related to the periodic table, which ones are correct?
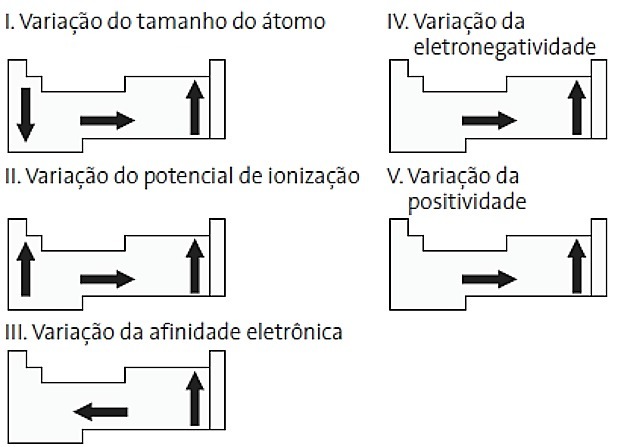
a) II and V
b) II and III
c) I and V
d) II and IV
e) III and IV
Correct alternative: d) II and IV.
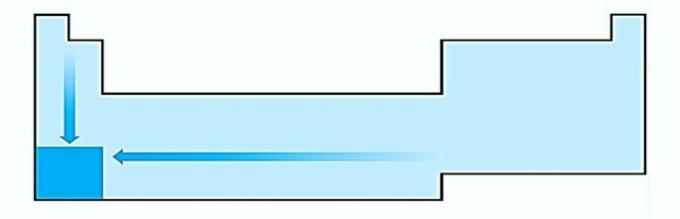
I. WRONG. Atom size variation is measured by the average distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron. The largest atoms are located at the bottom of the table, so the increase occurs according to the atomic number and the correct representation is:
II. CORRECT The energy required to rip an electron off an isolated atom in the gaseous state is called the ionization potential. It increases as shown in the statement diagram.
III. WRONG. Electronic affinity expresses the energy released when a neutral atom in the gaseous state receives an electron, which is a very important property of non-metals. The highest electronic affinities are observed in halogens and oxygen.
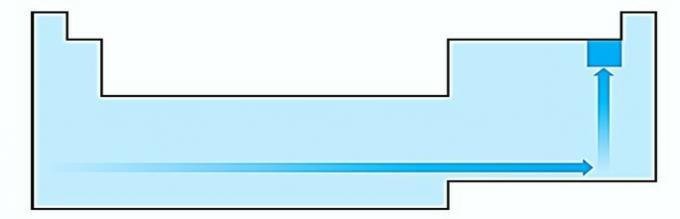
IV. CORRECT Electronegativity is related to ionization potential and electron affinity. As such, halogens are the most electronegative elements on the periodic table.
V. WRONG. Electropositivity occurs in the opposite direction to electronegativity. It represents the atom's ability to give up electrons.
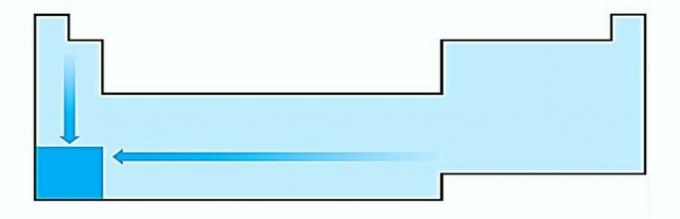
Therefore, alkali metals have the highest electropositivity.
Keep testing your knowledge with the lists:
- Exercises on chemical bonds
- Exercises on electronic distribution
- Exercises on atomic models
- Exercises on thermochemistry