THE Africa it is the 3rd continent in territorial extension, with 30 million km2, occupying 20.3% of the Earth's total area.
Despite concentrating countless natural resources, the African continent is one of the poorest in the world.
Africa is bathed by the Atlantic Ocean on its western coast and the Indian Ocean on its eastern side. To the north, by the Mediterranean and Red Seas and to the south, by the Antarctic Sea.
African countries
The African continent has 54 countries, 48 of which are on the continent and six are insular. The population is 910 million inhabitants.
Algeria is the largest in territorial extension with 2 381 741 km2. On the other hand, the Seychelles Islands are the smallest country on the continent at 455 km2.
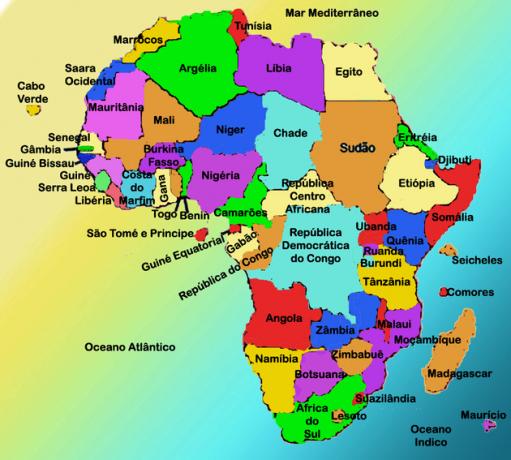
We can divide the African continent into two major regions: North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa.
North Africa or North Africa
Seven countries make up the region known as North Africa or North Africa:
- Algeria
- Egypt
- Libya
- Morocco
- Sudan
- Southern Sudan
- Tunisia
Sub-Saharan Africa
The call Sub-Saharan Africa is formed by the following countries:
- South Africa
- Angola
- benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Green
- Chad
- Congo
- Costa do Marfim
- Djibouti
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Ghana
- guinea
- Guinea Bissau
- Comoros Islands
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Kenya
- Central African Republic
- Rwanda
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
Islands
In the Atlantic Ocean are the Canary Islands, the archipelagos of São Tomé and Príncipe and Cape Verde. In the Indian Ocean, the islands of Madagascar, Comoros, Mauritius, Seychelles and Reunion are located.
Geology

The African geological base is very old, which explains the low altitudes. However, we have in East Africa, a succession of mountains, such as Kilimanjaro and the Chain (or Mountain Range) of the Atlas.
Africa occupies a single tectonic plate, unlike Europe which shares its plate with Asia (Eurasian plate).
In addition, it is mostly made up of plateaus and coastal plains, which can be immensely large, like the Niger plains.
Relief

Northern Plateau
On the northern plateau is the Saara's desert, the longest in the world with 9.2 million km2 and the Atlas Mountains, a mountain range that reaches 4000 meters in height.
Through this zone runs the Nilo river, at 6755 km, the longest in Africa and the second in the world. The Nile was the birthplace of the first civilizations in history, such as the Egyptian.
To the south of the Sahara we have the Chad Basin, with 2 382 000 km2 which is a source of fishing for the local population. There is also the Niger River, which is 4180 kilometers long.
eastern plateau
In the eastern part of the continent is the Rift Valley, the largest tectonic trench in the world, which forms a 4000 km long, narrow and deep valley. There were found traces of the first human groups.
Likewise, it is the region of the great lakes and the highest points on the continent, in which Kilimanjaro stands out with 5895 meters.
Southern Plateau
In the southern part of the continent we find the deserts of Namibia and Kalahari, called "brothers" because they are very close.
The southernmost point on the continent is the Cape of Good Hope and is surrounded by the Drakensberg Mountains.
The Congo basin, located in the continent's equatorial zone, has a huge forest, the 2nd in the world, just behind the Amazon.
Religion
From a religious point of view, Islam, Christianity and traditional African religions predominate.
We can generally divide that in North Africa the predominant religion is the Islam and in sub-Saharan Africa, the christianity and the majority. In Ethiopia, for example, you can find the oldest Christian churches on the continent.
Protestant Christianity is also present due to English, German and Dutch colonization.
African animist religions continue to be practiced by tribes and even by those who migrate to the city.
Languages
Across the continent, 2,000 languages and countless dialects are spoken. In addition to the various languages of African origin, some of the languages introduced by the colonizers are still used today: Arabic, English, French, Portuguese and Spanish.
In certain countries such as the Seychelles Islands, the colonizer's language, French, was so mixed with the local language that it is already considered another language: the criollo.
For this reason it is easy to find Africans who are true polyglots.
Population
Africa is the second most populous continent on the planet, with nearly one billion people. Demographic density is around 30 inhabitants per square kilometer, as a large part of the continent is adverse to human occupation.
The Nile valley has a population density of 500 inhabitants/km2, while deserts and forests are virtually uninhabited.
Few African countries have urban populations numerically superior to rural ones, for example: Algeria, Libya and Tunisia
The largest portion of the African population is made up of different black peoples, of which the most important groups are Bantu, Nilotic, pygmies, Bushmen.
A significant number of whites live mainly in the northern portion of the continent.
History and Colonization of Africa
The beginnings of its colonization date from the quaternary era or end of the tertiary era, and it is possible that man has his origins in this continent.
North Africa is the oldest region in the world occupied by human beings. Hominid fossils found there, in Tanzania and Kenya, are about five million years old.
The name "Africa" is generally related to the Phoenicians as "afar", which means "dust" and
In Egypt, there was the first state to be constituted in Africa, which was about 5000 years old. Later, with the objective of seeking new paths for the Indies, the Europeans will launch themselves on the African continent.
There were also great African civilizations on the continent, such as Askum (13th century) in Ethiopia and Ghana (5th to 11th century).
There have been powerful Muslim states such as Mali (13th to 15th century), Songhai (15th to 16th century), the Abomey kingdom of Benin (17th century). Finally, the Zulu confederation of Southeast Africa (19th century).
European colonization
In the 15th century, explorers from Europe conquered the coast of West Africa and from the 19th century onwards, European powers colonized the interior.
Portugal will dominate Angola, Mozambique, Guinea and strategic islands such as Tomé and Príncipe. Likewise, Portugal and other countries are going to remove around eleven million people from Africa and enslave them in their colonies.
In the 19th century, the Berlin Conference it will literally make official the imperialist advance on the European continent.
The UK will occupy a range from north to south, from Egypt to South Africa, as well as other areas it has colonized in the Gulf of Guinea. France will settle in northwest Africa, the African equator and Madagascar.
Finally, in smaller numbers, we have Germany, which settles in Togo, Tanganyika and Cameroon; and Belgium, in Belgian Congo and Rwanda.
Italy, in Libya, Ethiopia and Somalia; and Spain, will occupy part of Morocco, the current Western Sahara and enclaves in Guinea.
However, the African colonies announced their independence, especially after World War II, in a process that ended between 1960 and 1975.
After independence, there were separatist revolts and coups d'état, which culminated in brutal dictatorships.
Thus, in most cases, political independence was just a prerogative at the time, since, as a rule, the new countries maintained economic ties with their respective former metropolises.
Economy

Africa is the poorest continent in the world: of the thirty poorest countries, at least 21 are African.
Extractivism and agriculture are the main activities in Africa. These are practiced at very low technological levels and, therefore, are very harmful to the environment.
Hunting, fishing and gathering natural products are still the main sources of income for most of the African population. It is worth mentioning the trade in leather and skins, ivory, wood, resins, palm oil and spices.
However, in the 21st century, due to the increase in the price of primary products, the African economy underwent a considerable increase. The region's growth rates reached up to 9% in the period 2004-2015.
Extractivism
Africa holds large mineral reserves, highlighting gold and diamonds, as well as energy sources such as oil and natural gas. It is also abundant in antimony, phosphates, manganese, cobalt and copper.
The biggest African economy is South Africa, followed by countries like Morocco and Tunisia (large exporters of phosphates, raw material for the fertilizer industry).
Also noteworthy is Algeria, rich in oil and natural gas, and a member of the OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries).
However, the exploitation of mineral wealth is practiced by European or North American companies, which are attracted by the low price of labor, electricity and raw materials.
These companies extract and produce at reduced costs, which allows them high profit margins.
Agriculture
On the other hand, agriculture on the African continent takes two forms: subsistence and commercial.
The first is rudimentary, itinerant and extensive, and the second, practiced in the old form of Plantation, system introduced by Europeans during the colonial period.
The main products of export agriculture are tropical fruits such as bananas, cashew nuts, coffee and flowers.
Livestock
Due to natural conditions that are not conducive to raising cattle, Africa has in livestock an economic activity of internal scope.
Fauna and Flora

The African fauna is very rich and has the largest animals on earth and in the savannas and steppes, populate the antelopes, zebras, giraffes, lions, leopards, elephants.
At equatorial forest we can find a wide variety of birds and monkeys.
Thanks to precipitation, the predominant vegetation is the equatorial forest. To the north and south of this strip, a region of hot and humid summers, there are savannas, which make up the most abundant vegetation type on the continent.
In the Mediterranean Sea and South Africa, the mediterranean vegetation, with bushes and grasses.
Climate
The Sahel is one of the areas where temperatures are more pleasant, with less rainfall and very pronounced dry seasons.
As for the climatic conditions, the following stand out: equatorial, tropical, desert and Mediterranean.
O equatorial climate, hot and humid all year round, it is in the mid-west region of the continent. 75% of the continent is located in the tropics. Only the north and south of the continent have a temperate climate.
O climatetropical warm with dry winters dominates the African continent as a whole and the mediterranean climate it emerges in small stretches from the northern tip and the southern tip of the continent.
Deserts occupy the rest of the territory, since rainfall is rare in the vicinity of the Tropic of Cancer, where the Sahara Desert is located, and the Kalahari Desert, found in the Tropic of Capricorn.
Curiosities
- The Nile River can be seen from space.
- The famine hits thirty African countries with extreme force, mainly those that are in the areas adjacent to the Sahara desert.
- The current political division of Africa was configured in the 60s and 70s, forming 54 independent countries.
- Africa is the only continent in the world cut by three parallels: the Equator Line, as well as the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
[RELATED-READING=2257 "Hunger in Africa"