Sanitary Landfill it is a place where solid waste discarded by man is dumped. The implementation of this system aims to reduce the impact of garbage in the world, especially the contamination of soil, water and air.
slurry
O slurry is a dark, viscous, smelly liquid that releases methane gas (CH4), one of the main causes of the greenhouse effect, being more harmful to global warming than carbon dioxide (CO2).
The sanitary landfill system makes it possible to capture leachate and gases released by garbage, since they are toxic residues that contaminate the soil, air and water courses.
One of the alternatives has been the use of methane to produce biogas, a biofuel from organic materials. In summary, biogas is an alternative source of clean (renewable) energy produced by organic waste (biomass).
In sanitary landfills there is a mechanism to capture the gases released by the fermentation and decomposition of organic matter.
Thus, the biogas it is produced by combustion that takes place through equipment called an “anaerobic biodigester”.
Structure and System of a Sanitary Landfill
The landfill is built on large tracts of land and away from urban centers.
They are usually surrounded by green areas or native vegetation. In São Paulo, to avoid illegal dumping of garbage, the landfill should be around 50 meters wide with native vegetation.
First, a large hole is made that should not exceed two meters from the water table and then, a polyethylene blanket and a layer of small stones are placed, through which the liquids and gases released by the garbage will pass.
In addition, concrete gutters and vertical tubes are installed through which the gases rise, from which some are collected and others released into the atmosphere.
It is important to emphasize that landfills have a certain amount of garbage that can be deposited. After that time, the landfill ends its activities in that location. For this reason, energy sources that use biomass (organic matter) are increasingly being implemented.
How Does a Sanitary Landfill Work?
After the implementation of the waterproofing, gas capture, leachate and covering system, the landfill works according to the scheme below:
 Sanitary Landfill Structure
Sanitary Landfill Structure
Advantages and disadvantages
Benefits
- Less environmental impact;
- Reduction of methane release into the atmosphere;
- Conversion of gases into renewable energy sources;
- Power generation with gas engines.
Disadvantages
- Construction that requires large tracts of land;
- Environmental impacts: environmental pollution such as liquid and gas leaks; contamination of groundwater and aquifers; risks to wild animals;
- Limit on the amount of garbage layers;
- Presence of rats, flies and disease transmission;
- High economic cost in implementation and maintenance.
Difference between Landfill, Sanitary Landfill and Controlled Landfill
Dumping ground
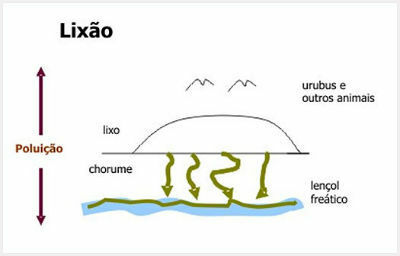
The dump or uncontrolled landfills is an open space destined for the disposal of garbage without a system for the treatment of garbage.
The big problem with landfills is the proliferation of insects, such as flies, rats, scorpions and cockroaches transmitters of many diseases, in addition to bad smell, air pollution, soil and bed sheet contamination water tables.
The accumulation of waste in landfills is often the cause of floods. In Brazil, more than 90% of garbage is dumped in dumps.
Sanitary Landfill

Sanitary landfills are spaces for the disposal of garbage that, in turn, undergo treatment and later they are covered with layers of sand in order to avoid odors, fires and the proliferation of animals disease transmitters.
Even with these precautions, the landfill can cause many environmental problems. However, it is a more sustainable alternative than a dump or controlled landfill.
Controlled Landfill
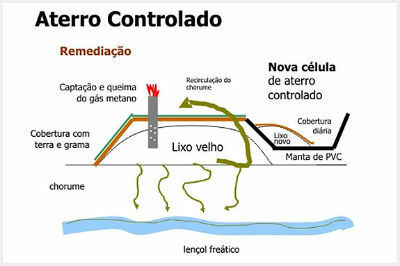
The controlled landfill is an intermediate location between the dump and the landfill. It already has a system for capturing leachate and gases, however, not as advanced as the landfill. In summary, the controlled landfill is a cell adjacent to the dump, that is, it represents a quick alternative that minimizes environmental impacts.
Waste Treatment and Collection
Landfills are systems that, due to their disadvantages, are not fully appropriate and effective.
In this case, waste treatment reduces environmental pollution in the short term, but it should be accompanied by a selective collection of waste and recycling in order to reduce the proliferation of garbage for the man.
Nowadays, selective collection, waste separation systems, have several collectors and recyclers cooperatives. Remember that there are specific landfills for industrial and hospital waste.
In the social sphere, this initiative has shown good results as it generates jobs and makes environmental awareness projects possible for the population.
Recycling and Selective Collection
Both recycling and selective collection have been one of the most important alternatives for the destination of waste produced by man.
So, the selective collect it is a system for separating this waste, which is divided into several garbage containers. That is, for each type of material, there is a specific location, which are separated by colors:
- Blue: to papers and cardboards;
- Green: to glasses;
- Red: for plastics;
- Yellow: for metals;
- Brown: for organic waste;
- Black: for woods;
- Gray: for non-recycled materials;
- White: intended for hospital waste;
- Orange: for hazardous waste;
- Purple: for radioactive waste.
After separating the waste, many materials can be recycled, that is, reused through the production of new ones.
In short, selective collection is the separation of materials and the recycling it is the transformation of raw materials that can be reused. Both processes contribute to the reduction of waste on the planet.
Understand more about the Types of Garbage.


