The human body is formed by hundreds of muscles that help us movements, stability of the skeleton and fill of the body, since they connect the bones with the nervous system.
In other words, muscles are tissues in the human body, responsible for the contraction and distension of cells that originate the movements.
From this, the property of muscle contraction (contractility) occurs through electrical impulses emitted by the central nervous system through the nerves, so that allows the entry of sodium into the muscle, the exit of potassium, the release of calcium and the sliding of molecules proteins from myosin and actin, thus performing the movement of muscle contraction. Myology is the science that studies muscles.
Also read the article about the Muscle System.
Types of Muscles
Depending on their composition, shape, structure and function, the muscles of the human body are divided into:
Smooth or non-striated muscle (smooth muscle): Muscle with slow and involuntary contraction, controlled by the vegetative nervous system, for example, the muscle of the internal organs (stomach, liver, intestine), skin, blood vessels, excretory system (peristaltic movements), among others.
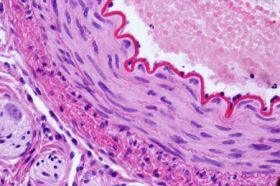 Cross Section of an Artery with the Intermediate Layer of Smooth Muscle
Cross Section of an Artery with the Intermediate Layer of Smooth Muscle
Skeletal Striated Muscle (Skeletal Muscle): Located together with the skeleton and connected through the tendons, this type of muscle is controlled by the central nervous system and characterized by strong and voluntary movements, for example, the muscles of the lower and upper limbs: the arms, hands, legs and the feet.
 Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle
Striated Cardiac Muscle (Cardiac Muscle): Located in the heart (myocardium), this type of muscle is controlled by the vegetative nervous system and characterized by vigorous and involuntary contractions.
 Cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle
Also, depending on your localization the muscles can be:
- surface muscles: Located just below the epithelial tissue, for example, the muscles of the face and neck.
- deep muscles: located inside the human body, for example, in organs.
Main Muscles of the Human Body
The largest muscle in the human body is the thigh, with a length of up to half a meter. On the other hand, the smallest muscle is the one located between the vertebrae, measuring about 1 cm.
The strongest muscle in the human body is the mouth, called the "Masseter", responsible for chewing, speech and movement. In turn, the weakest muscle is the eyelid, responsible for eye movement.
The human muscular system has about 600 muscles, grouped into:
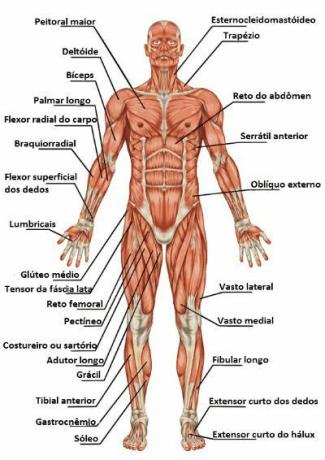
Head and Neck Muscles
- Occipitofrontal muscle (skull)
- Temporoparietal muscle (skull)
- Orbicularis oculi muscle (eye)
- Procerus (nose)
- nasal (nose)
- Buccinator muscle (mouth)
- Orbicularis oculi muscle (mouth)
- Masseter muscle (jaws)
- Temporal muscle (jaws)
- Genioglossal muscle (tongue)
- Stapedius muscle (ear)
- Eardrum tensor muscle (ear)
- Platysma (cervical)
- Sternocleidomastoid (cervical)
- Long muscle of the neck (anterior vertebral)
- Scalene anterior muscle (lateral vertebral)
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle (pharynx)
- Cricothyroid (larynx)
Muscles of the Chest and Abdomen
- Splenios (back)
- Erector of the spine (back)
- Intercostals (chest)
- Transverse of the abdomen
- anus lifter
- Sphincters of the anus
Upper Limb Muscles
- Trapezius (vertebral column)
- Pectoralis major (thoracic cavity)
- Minor pectoral (thoracic cavity)
- Deltoid (shoulder)
- Coracobrachialis (anterior arm)
- Biceps brachii (anterior arm)
- Brachial (anterior arm)
- Triceps brachii (posterior arm)
- Round pronator (forearm)
- Brachioradialis (forearm)
- tenar (hand)
- Hypothenate (hand)
- Lubricals (hand)
Lower Limb Muscles
- Greater psoas muscle (pelvis)
- Gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus (pelvis) muscles
- piriform muscle (pelvis)
- Sartorius muscle (thigh)
- pectineal muscle (thigh)
- bicep muscle of the thigh
- Peroneus long and peroneus short (thigh) muscles
- Triceps surae muscle (thigh)
- Anterior tibial muscle (leg)
- Short extensor muscle of the toes (foot)
- Abductor hallux muscle (foot)
- Plantar interosseous muscles (foot)
Bodybuilding is the sport that, through activities such as lifting weights (weight lifting), strengthen the muscles of the body, thus increasing muscle mass.