THE Atlantic forest is a biome composed of a set of forests and ecosystems which corresponds to 15% of the Brazilian territory.
Since 1500, this area has been suffering from deforestation, fires and environmental degradation.
That is why, currently, the vegetation corresponds to only 7% of the original forest, with medium and large trees, constituting a dense and closed forest.
Atlantic Forest Characteristics
Considered one of the richest biomes on the planet, that is, with greater biodiversity, the Atlantic Forest is the second largest forest in Brazil, consisting of plateaus and mountains.
Its area covers the east, southeast and south coast of Brazil and, in addition, a part of Paraguay and Argentina.
Among the Brazilian states, it is present in 17 of them: Alagoas, Bahia, Ceará, Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Paraíba, Paraná, Pernambuco, Piauí, Sergipe, Rio Grande do Norte, Rio Grande do Sul, São Paulo, Espírito Santo, Rio de Janeiro and Santa Catherine.
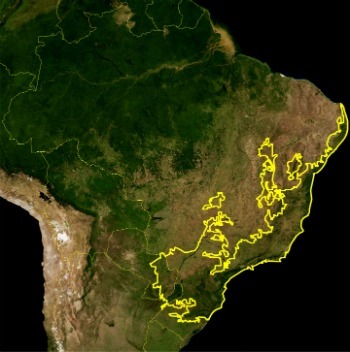 Map of Brazil indicating the location of the Atlantic Forest
Map of Brazil indicating the location of the Atlantic Forest
At forests that make up the Atlantic Forest are:
- Dense Ombrophilous Forest
- Open Ombrophilous Forest
- Mixed Ombrophilous Forest
- Deciduous Seasonal Forest
- Seasonal Semideciduous Forest
Also add the following ecosystems:
- mangroves
- Restings
- Altitude Fields
Flora
According to data from the Ministry of the Environment, in the Atlantic Forest there are approximately 20,000 plant species corresponding to more than 35% of the species existing in Brazil.
Studies show a great diversity of trees per hectare, greater than that found in the Peruvian Amazon. This can represent the greatest tree diversity per unit area in the world!

There are bromeliads, begonias, orchids, ipe, palm trees, quaresmeira, pau-brasil, vines, bryophytes, jacaranda, peroba, jambo, jequitibá-rosa, imbaúba, cedar, tapiriria, andira, pineapple and fig trees.
According to current research, 200 Brazilian plant species are threatened with extinction, 117 of which belong to this biome.
Fauna
Likewise, the fauna is very rich. According to studies carried out, the Atlantic Forest is home to 849 species of birds, 370 species of amphibians, 200 species of reptiles, 270 of mammals and about 350 species of fish.
Many of these animals are at risk of extinction: Golden Lion tamarin, howler, giant anteater, deer, skunk, agouti, giant armadillo, mono-carvoeiro, little hyacinth macaw, otter, coati, tapir, jaguar, ocelot, capybara, etc.
Read:
- Atlantic Forest Animals
- Endangered Animals in Brazil
- Amazon rainforest
Climate
The Atlantic Forest climate is predominantly tropical wet, influenced by the humid air masses coming from the Atlantic Ocean.
Also features other microclimates along the forest, since the large trees that make up the vegetation generate shade and moisture.
In addition to the humid coastal tropical climate, present in the northeastern region, the Atlantic Forest also encompasses climates altitude tropical, in the southeast region, and the humid subtropical, in the southern region.
Its average temperatures and air humidity are high throughout the year and rainfall is regular and well distributed.
Population
It is important to note that in the Atlantic Forest region there are approximately 70% of the Brazilian population, which represents more than 120 million people.
As well as natural diversity, there is a great cultural diversity and traditional peoples.
These communities are the indigenous, at maroons, at caiçara and riverside communities who live a deep relationship with nature.
Depending on it for their livelihood, they use their resources sustainably for food, crafts, among other purposes.
read
- What is a biome?
- Vegetation Types
- Brazilian Biomes
Learn more about the Atlantic Forest and Brazilian biomes:
Test your knowledge with Exercises on Brazilian Biomes.



