Monocotyledons are angiosperm plants that have only one cotyledon in the seed. Cotyledons are the modified embryonic leaves that the plant presents.
During the early stages of its development, the cotyledon is responsible for transferring nutrients to the plants.
The group of monocots corresponds to about 2% of the total number of angiosperms, which are represented by flowers such as orchids and lilies, in addition to grasses, coconut trees and banana trees.
Characteristics of Monocots
See below the characteristics and examples of monocots in each part of the plant.
flower

The main characteristic of monocotyledonous flowers is that they are trimers, that is, they have three petals or multiples of three.
An example that helps to understand the division of petals of monocots are orchids and lilies.
You may also be interested in:
- Types of flowers and their functions
- germination
Seed
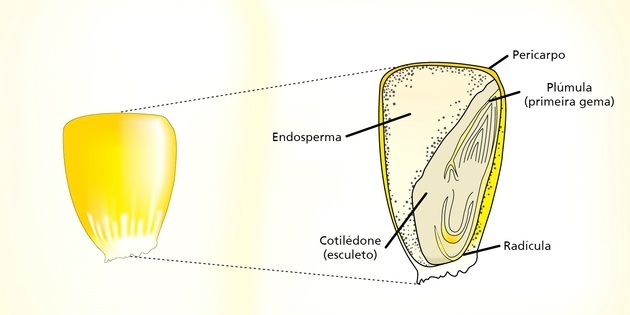
The seeds of monocotyledonous plants are characterized by having only one cotyledon. This means that embryo nutrition takes place from a single region.
To visualize and understand the cotyledon of monocots, look at the white part of the corn grain.
Read too:
- botany
- gymnosperms
Sheets

The leaves of monocots are parallel to each other, as their ribs are parallel to each other.
To visualize the leaves of monocotyledons, observe as an example the sugar cane and the banana tree.
Also read about:
- Sheets
- vegetable hormones
Source

The root of the monocotyledonous plant has the characteristic of being fasciculate, which is also called hair. This type of root forms a set of fine roots that originate from a single point.
Corn stalk is an example of a monocotyledonous plant with this type of root.
Complete your study and also read:
- Root types
- plant parts
Stalk

The main characteristic of angiosperm stems is the disorganized distribution of vessels. Their vascular bundles are randomly arranged.
Another characteristic of the stem of monocots is that the growth of branches is rare.
To understand what the stalk of monocotyledonous plants looks like, see coconut and palm trees as an example.
You may also be interested in:
- Stalk
- Stem Types
- Angiosperms
Monocots and Dicots
Angiosperm plants are divided into monocots and dicots.
See the main differences between monocotyledons and dicots:
Features |
Monocots | Dicots |
|---|---|---|
| Seed | 1 cotyledon | 2 cotyledons |
| flower | trimeral flowers | Dimer, tetramer or pentamer flowers |
| Sheets | Parallellinerves | Leaves with reticulated or feather-shaped ribs (reticulinervia or peninervia) |
| Source | fasciculated | Pivoting or axial |
| Examples | Grass, sugar cane, corn, rice, coconut trees, palm trees | Eucalyptus; avocado; Strawberry; Apple; pear; bean; pea; castor bean; rosewood; potato |