The human body is made up of an enormous amount of cells. Cells are considered the smallest part of living organisms, being, therefore, structural and functional elements.
The human body is multicellular (multiple cells). It consists of 10 trillion cells that work in an integrated way, where each one has a specific function, namely: nutrition, protection, energy production and reproduction.
Cell Structure
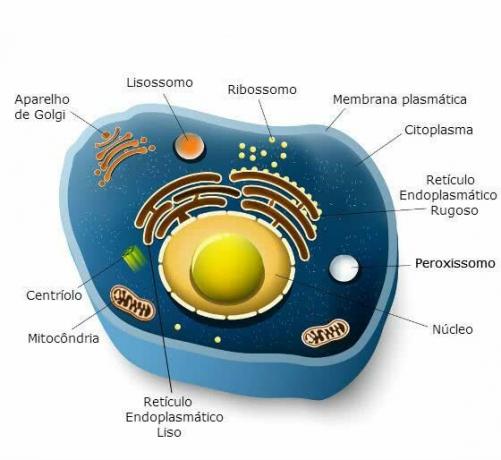 Cell Structure.
Cell Structure.
The typical cell is made up of the following parts:
- Cell Core: surrounded by the nuclear membrane, the nucleus contains the genetic material of the cells (DNA).
- Cytoplasm: the cytoplasm carries the cellular content where each organelle has a vital function. It consists of hyaloplasm, fluid and viscous substance, region called cytosol and a kind of skeleton that gives shape and supports the organelles, the cytoskeleton.
- Plasma membrane: thin and flexible membrane with selective permeability (regulates the passage and exchange of substances) that surrounds the cells.
- Cell Organelles: the organelles are like small organs, each one has a specific function, among respiration, nutrition and cell excretion. Are they: mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi complex, lysosomes, peroxisomes, centrioles and vacuoles. You ribosomes they are not considered organelles as they do not have membranes.
Types of Cells in the Human Body
The human body is made up of different types of cells; there are approximately 130 types that are distinguished by their specific forms and functions.
The grouping of cells forms the tissues. The most numerous cells in the human body are epithelial cells, those that surround the body and organs.
Know more about:
- Human Body
- Human Body Tissues
- Organs of the Human Body
- Cell
Among the cells that are part of the human body we have:
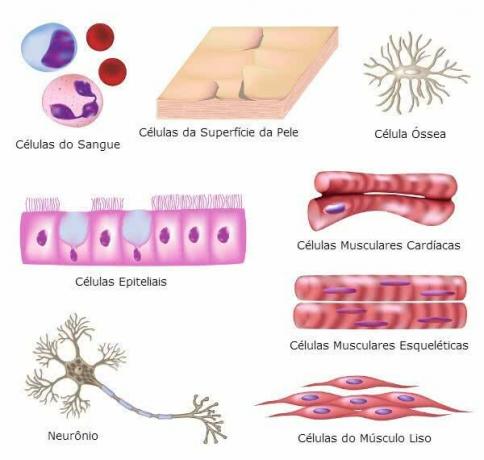 Different types of cells in the human body.
Different types of cells in the human body.
Brain Cells
Composed of millions of cells, the brain is made up of several types of them, namely:
- The microglia: nervous system defense.
- The dendritic cell: immune cells that carry antigens.
- O neuron: message transmission.
- The Schwann cell: production of myelin that aids in the production of nerve impulses.
You neurons they need a lot of oxygen to function, so they are the first cells in the body to die.
Learn more about Nervous Impulse Transmission and the Synapses.
blood cells
Human blood is made up of different types of cells, each with its function, the most important being:
- the red blood cells called red blood cells or erythrocytes (transport of oxygen);
- you leukocytes or White blood cells (they act on the body's immune system as it fights and eliminates microorganisms);
- you thrombocytes or platelets (Blood coagulation).
Read too:
- Blood
- Red Cells
- Leukocytes
- platelets
bone cell
You bones are formed by cells called:
- osteocytes (secretion of substances);
- osteoclasts (large cells with multiple nuclei responsible for bone tissue resorption and remodeling);
- osteoblasts (synthesis of organic components).
Muscle Cells
Muscle cells may have several nuclei, the most important being the sarcomere cells (muscle contraction) and the fibroblasts (protein synthesis).
Epithelial cells
Epithelial cells are present in the types of epithelia covering the body externally in the skin, and internally in various agencies. They are cells that have different shapes that can be flat, cubic or columnar.
Corneal epithelial cells are the last cells in the human body to die, as they need less oxygen to carry out their functions.
sex cells
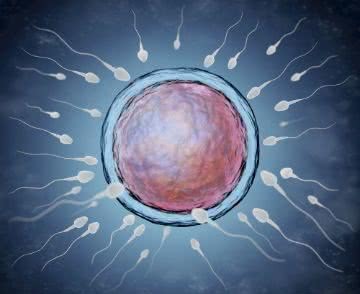 Illustration of sperm swimming to fertilize an egg. Compare the difference in sizes.
Illustration of sperm swimming to fertilize an egg. Compare the difference in sizes.
The biggest human cell is the egg, female sexual gamete. Women are born with all their eggs, which begin to mature at the time of puberty, the sign of which is the first menstruation.
The release of eggs at ovulation ceases with menopause. On the other hand, the smallest cells are the sperm, which in men are produced from puberty and continue throughout life, although it decreases in older age.
See too:
- cell types
- 8 "Superpowers" of the Human Body Cells.
- 15 Curiosities about the Human Body