Before the arrival of the Europeans, the Africa had rich and fabulous kingdoms.
In antiquity we have the empire of Carthage and Egypt; and in the Middle Ages, the constitution of the Empire of Mali and Ethiopia.
Through the cities of North Africa, contact and commercial exchanges were established with European countries.
Introduction
The African continent is considered the cradle of humanity, because the first archaeological evidence of the human being is there.
Before the European occupation, there was already intense trade between North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa.
These commercial transitions were carried out through caravans promoted by peoples who inhabited the southern portion of the Sahara desert. Later, other expeditions would cross the desert and take these products to Europe.
African Kingdoms
For study purposes, let's look at just a few kingdoms and empires from each of the African regions:
North Africa
- Ancient Egypt - in North Africa, one of the most fascinating civilizations in the world was created: the Egyptian. Over three thousand years old, they built impressive cities and left a legacy in science, astronomy and architecture.
- Carthaginian Empire – constituted the union of several cities in North Africa that shadowed the Roman Empire. At Punic Wars, as the disputes between the two powers are called, is one of the most remarkable events of antiquity.
east africa
- empire of ghana – century 8 to 11 – was based on the gold trade with the African kingdoms and Mediterranean cities whose merchants took them to Europe. Prosperity ends due to the depletion of mines and constant raids on caravans.
- empire of mali – century 13 to 18 – it was a crossing of caravans that came from the south and brought salt, gold, spices and leather. The empire was immensely rich and the emperor Mansa Moussa, a devout Muslim, when he made his pilgrimage to Mecca, was accompanied by more than six thousand people and countless sums of silver.

Western Africa
empire of ethiopia – 1270 -1975 – occupied the territories of Ethiopia and Eritrea. Also known as Abssinia, it managed to fend off Arab and Turkish invaders and was the only African empire to resist the European colonizer. Even the Italians were never able to completely dominate it.
South of Africa
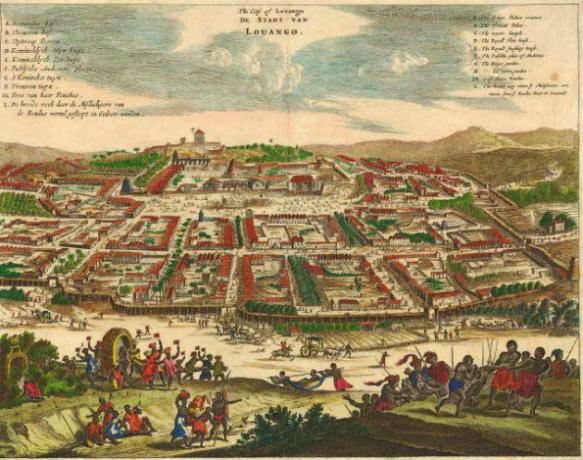
- Kingdom of Congo – 1390 – 1914 - constituted the place where today is the north of Angola, the current Congo and a part of Gabon. led by macongo, the kingdom of Congo was independent until the 18th century when it became a vassal of Portugal.
- Sultanate of Kilwa – century 10-13 – The territory was inhabited by Bantu who were conquered by Muslims. It dominated the coast of southwest Africa and its main cities included Mogadishu, Mombassa and the islands of Pemba and Zamzibar, among others.
- Zulus – 1740 – 1879. The Zulu kingdom was located in the lands where South Africa, Lesotho, Swaziland, Zimbabwe and Mozambique are located. They were the first to realize the danger of the white colonizer's permanence and they fought against the British, but they were defeated.
Islam
Muslim expansion strengthened contact between Africans and Europeans. The followers of Islam left what is now Saudi Arabia and conquered North Africa until reaching southern Europe.
O Islam it strengthened trade routes and cultural ties, trying to keep expanding into southern Africa, but they were impeded by the resistance of the peoples who inhabited it.
In parallel, leaders of conquered countries in the North, such as Egypt and Morocco, converted to Islam, which passed to Muslim rule. From North Africa, Muslims managed to reach the west, in the region known as the Maghreb.
During the second half of the 7th century, they entered the continent, crossed the Mediterranean Sea and conquered the southern portion of Europe, such as the Iberian Peninsula, where Spain and Portugal are located.
It must be understood that Christians and Muslims alternated periods of peace with war. When there were no conflicts, business flowed in both directions.
African tour
It was only in the 15th century that the Kingdom of Portugal intensified its incursions by Atlantic Ocean in search of new land and trade routes. The Portuguese arrived in India bypassing the African coast of the Atlantic in the set of conquests that became known as african tour.
The first point dominated by the Portuguese was Ceuta, in 1415. Then came Cape Bojador (1434), Rio do Ouro (1436), Cape Branco (1441), Cape Verde (1445), São Tomé (1484), Congo (1482), Mozambique (1498) and Mombasa (1498) .
Read more:
- The First Great Navigations
- European Maritime Expansion
- Conquest of Ceuta
- Africa Sharing
- African countries
- African culture
- Berlin Conference


