LPG is the acronym used to represent the liquefied petroleum gas, a gaseous mixture widely used as fuel to heat food in stoves.
The use of LPG as a fuel it was proposed in 1911 and has not been replaced since then. Its use was made possible because its burning does not produce large amounts of toxic and polluting gases, such as oxides of nitrogen, sulfur and carbon, besides being a fuel that produces a good amount of heat.
Constituents of LPG
The chemical substances that are part of the chemical composition of the LPG they are Hydrocarbons of low molar mass, containing three to four carbon atoms.
Propane: a straight-chain alkane containing three carbon atoms;
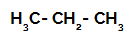
Structural formula of propane
Propene: a straight-chain alkene that contains three carbon atoms;
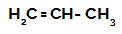
Structural formula of propylene
Butane: straight-chain alkane containing four carbon atoms;

Structural formula of butane
Isobutane: branched-chain alkane containing four carbon atoms;
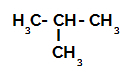
Structural formula of isobutane
Butene: a straight-chain alkene that contains four carbon atoms.

Possible structural formulas for butene
Physical characteristics of LPG
It's a homogeneous mixture;
Colorless;
Naturally odorless (odorless).
Note: It's routine to mix with LPG a quantity of sulfur-based compound so that it is possible to smell the odor in case of gas leakage from the reservoir.
Gas mixture at room temperature;
It is easy to suffer liquefaction and vaporization;
It has a higher calorific power than the Gasoline;
Its burning produces less gas emissions.
Ways to obtain LPG
O LPG can be obtained naturally from several processes, and the two most common are:
distillation of crude oil:

The oil refinery is the production site for LPG
During the process of fractional distillation of oil, the LPG is one of the separate fractions (components).
Note: Only 1% to 2% of oil can generate LPG.
Underground extraction:

Equipment used to drill and remove underground gas
When the natural gas it is extracted from a gas pocket in the subsoil, goes through the fractionation process, which generates several gases; among them, the LPG.
LPG Applications
In addition to being used in stoves for the purpose of generating fire for cooking food, the LPG presents several other uses, such as the following:
Air conditioning and sterilization of commercial environments (hotels, bakeries, hospitals, etc.);
Weld casting and cutting;
Ceramic firing and drying;
Molding and finishing of glass;
grain drying;
Burning weeds;
Rubber manufacturing;
Paper making.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-glp.htm


