THE Molecular biology is one of the branches of Biology dedicated to the study of the relationships between DNA and RNA, protein synthesis and the genetic characteristics transmitted from generation to generation.
More specifically, Molecular Biology seeks to understand the mechanisms of replication, transcription and translation of genetic material.
It is a relatively new and very broad field of study, which also covers aspects of cytology, chemistry, microbiology, genetics and biochemistry.
History of Molecular Biology

The history of Molecular Biology begins with the suspicion of some type of material present in the cell nucleus.
You nucleic acids were discovered in 1869, by the researcher Johann Friedrich Miescher when analyzing the nucleus of white blood cells from wound pus. However, they were initially called nucleins.
In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick elucidated the three-dimensional structure of the DNA molecule, which consists of a double helix of nucleotides.
To develop the model, Watson and Crick used X-ray diffraction images obtained by Rosalind Franklin and the analysis of nitrogenous bases by Erwin Chargaff chromatography.
In 1958, researchers Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl demonstrated that DNA has replication semi-conservative, that is, the newly formed molecules conserve one of the chains of the molecule that the originated.
With these discoveries and the improvement of new equipment, genetic studies advanced in research on genes, from paternity tests, genetic and infectious diseases, among others. All these factors were fundamental for the growth of the area of Molecular Biology.
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
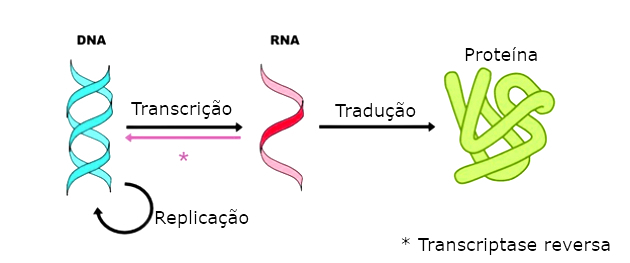
The central dogma of Molecular Biology, proposed by Francis Crick in 1958, consists in explaining how the information contained in DNA is transmitted. In summary, he explains that the flow of genetic information occurs in the following sequence: DNA → RNA → PROTEINS.
This means that DNA promotes the production of RNA (Transcription), which in turn encodes the production of proteins (Translation). At the time of discovery, it was believed that this flow could not be reversed. Today, it is known that the enzyme reverse transcriptase is capable of synthesizing DNA from RNA.
Learn more, read too:
- DNA
- RNA
- Proteins
- Protein synthesis
Molecular Biology Techniques
The main techniques used in Molecular Biology studies are:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): This technique is used to enlarge copies of DNA and generate copies of certain sequences, which allows, for example, the analysis of mutations, cloning and manipulation of genes.
- Gel Electrophoresis: This method is used to separate proteins and DNA and RNA strands, through the difference between their masses.
- Southern Blot: Through autoradiography or autofluorescence, this technique makes it possible to specify the molecular mass and verify whether a certain sequence is present in a strand of DNA.
- Northern Blot: This technique allows analyzing information, such as the location and quantity of messenger RNA, responsible for sending DNA information to the synthesis of proteins in cells.
- Western Blot: This method is used for protein analysis and combines the principles of Southern Blot and Northern Blot.
Genome Project
One of the most comprehensive and ambitious projects in Molecular Biology is the Genome Project, which aims to map the genetic code of different types of organisms.
To this end, since the 1990s, several partnerships have emerged between countries so that through Molecular Biology and its material handling techniques genetic, it was possible to unveil the peculiarities and genes present in each strand of DNA and RNA, including: animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and virus.
One of the most representative and challenging projects was the Human Genome Project. The research lasted seven years and its final results were presented in April 2003, with 99% of the human genome sequenced and 99.99% accuracy.