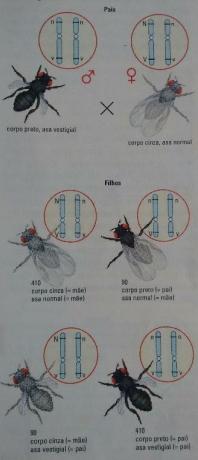
Fertilization or Fertilization is one of the stages of sexual reproduction, in which the sex cells or gametesunite originating the zygote or egg cell. The zygote goes through many cell divisions giving rise to an embryo, which will develop into a new being.
Fertilization Characteristics
 Representation of the male (sperm) and female (egg) human gametes.
Representation of the male (sperm) and female (egg) human gametes.
Most living beings perform sexual reproduction, which means they produce gametes or sex cells.
The female gametes of animals are named eggs and the males are the sperm. In plants, the females are oospheres and the males, anterozoids.
Also read about:
- male reproductive system
- female reproductive system
Monoic and Dioic
In the species of animals and plants, whose sexes are separated (have female or male sex organs), gametes are produced by different individuals, which are called dioic.
Examples: human, dog. in species monoecious, also called hermaphrodites, individuals have both male and female organs, so they produce both gametes. Example: earthworms.
Gametes and Heredity
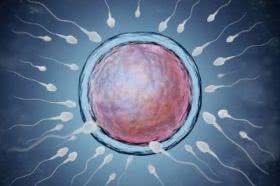 Human fertilization. A sperm will be able to fertilize the egg.
Human fertilization. A sperm will be able to fertilize the egg.
sex cells carry genetic information, bring with them the characteristics that will be passed from one generation to another, through the mechanism of heredity.
At the time of reproduction, when the sex cells are mature, they are released and fuse forming the zygote or egg cell, the first cell of the new being. This process is called Fertilization or Fertilization.
See too: Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
Types of Fertilization
self-fertilization
in species monoic, especially in plants, the male gametes can fertilize the females of the same individual. In that case there is no gamete exchange between different individuals, the call occurs self-fertilization.
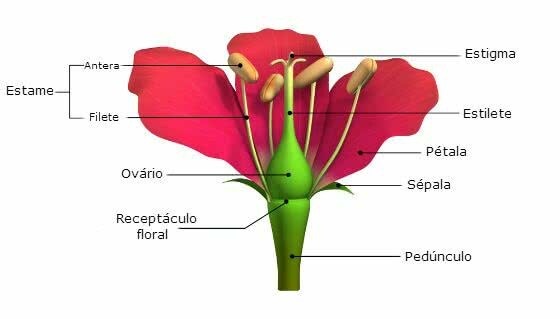 Schematic of a hermaphrodite flower, showing the female (style and stigma) and male (stamen) organs on the same flower.
Schematic of a hermaphrodite flower, showing the female (style and stigma) and male (stamen) organs on the same flower.
Plants have some biochemical mechanisms to prevent self-fertilization and allow the union of characters from different organisms.
Some create barriers between male and female organs, for example these organs mature at different times.
Cross fertilization
 Earthworms, hermaphrodite or monoecious animals, during copulation. In this case, there will be cross-fertilization.
Earthworms, hermaphrodite or monoecious animals, during copulation. In this case, there will be cross-fertilization.
In most living beings, be dioic (with separate sexes) or monoic, there is exchange of gametes between different individuals. Gametes meet and fuse in a process called cross-fertilization.
In cross-fertilization, the characteristics of different individuals are mixed and this increases the genetic variability, which is an advantage as it makes the descendants stronger. The union of gametes can happen in two different ways: it can be internal or external.
know more about Internal and external fertilization