The nephron is the basic functional unit of the kidney, responsible for the formation of urine.
Each human kidney has approximately 1,200,000 nephrons.
The function of the nephron is to filter the elements of blood plasma and eliminate unwanted excreta through the urine.
Nephron Anatomy and Histology
The nephron consists of the following parts:
renal corpuscle: at one end of the nephron, the renal or glomerular capsule is located, where the capillary glomerulus is located inside.
The renal capsule is a layer of epithelial cells that surrounds the glomerulus. The capillary glomerulus is a ball of blood capillaries. The renal capsule and glomerulus together form the renal corpuscle.
nephric tubule: the renal capsule connects to the nephric tube. It has three distinct regions: the proximal convoluted tubule, the nephric or Henle loop and the distal convoluted tubule, which flows into the collecting duct.
Collector Duct: responsible for conducting the urine produced to the ureter.
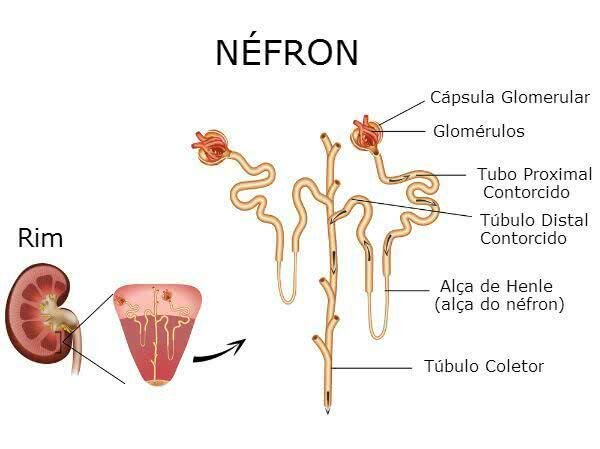
constitution of the nephron
Urine Production
Urine is produced through three processes: filtration, resorption and secretion.
Blood reaches the kidney via the renal artery and enters the capillaries of the glomerulus under high pressure.
This forces filtration in the glomerulus, with fluid outflowing into the renal capsule, forming the glomerular filtrate.
This filtrate contains water, urea, vitamins, amino acids, uric acid, salts, etc.
During the course of the glomerular filtrate through the proximal convoluted tubule, there is reabsorption of useful substances by the capillaries of the nephron. Along this path, more than 99% of the filtered water in the glomerulus is reabsorbed.
In this way, water, glucose, amino acids, vitamins and most of the salts from the glomerular filtrate return to the blood.
In the nephral loop, water is reabsorbed from the glomerular filtrate to the capillaries.
In the convoluted distal tubule, unwanted excreta from blood capillaries are removed and discharged into the urine. Examples of these excreta are uric acid and ammonia. Finally, urine is released into the collecting duct and forwarded to the ureters.
Learn more about Urinary system and Kidneys.
Curiosities
The number of nephrons between species:
Cattle - 4 million
Pork - 1.25 million
Dog – 500 thousand
250 thousand cat
Test your knowledge with Urinary System Exercises.