The diaphragm is the main muscle for breathing. It is responsible for separating the chest and abdominal cavities.
The diaphragm muscle is found in all mammals and some birds. In humans, the diaphragm inserts anteriorly into the sternum and ribs and posteriorly into the spine.
The diaphragm is a striated, dome-shaped, skeletal muscle. We can characterize it as the floor of the chest cavity and the roof of the abdominal cavity.
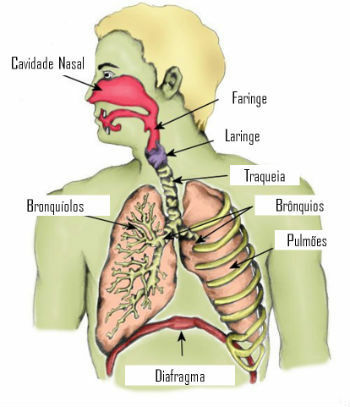
Location and shape of the diaphragm muscle
At diaphragm functions they are related to the breathing process, stabilization of the spine and aid in expelling urine, feces and vomiting.
Diaphragm movement also contributes to sneezing and coughing. The hiccup is the result of involuntary movements of the diaphragm.
The diaphragm has three openings that allow the passage of structures such as blood vessels, important nerves and structures such as the esophagus.
Learn more aboutRespiratory system.
The diaphragm and breathing
The diaphragm is the main muscle that acts in the process of lung breathing.
During the inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and lowers. This reduces intrathoracic pressure and compresses the abdominal viscera. This movement facilitates the entry of air into the lungs.
During the expiration, the reverse movement occurs. The diaphragm relaxes and rises. Thus, it increases intrathoracic pressure and expels air from the lungs.
Check issues with commented resolution inexercises on the respiratory system.