The thymus is a gland that participates in the regulation of the body's immune defense. It is considered a primary lymphoid organ.

thymus location
The thymus is located in the chest, between the lungs and the front of the heart.
It changes size with different stages of life. From birth to adolescence, the thymus reaches up to 40 grams.
From there, it starts to decrease in size until the elderly phase. However, even with its decrease, the functions are not lost.
Occupation
The main function of the thymus is to T lymphocyte maturation.
You lymphocytes immatures are produced in the bone marrow and migrate to the thymus, where they mature and become T lymphocytes. From the thymus, they enter the bloodstream and reach the lymphoid tissues.
The thymus only releases T lymphocytes after recognizing that they will not react against proteins or antigens natural parts of the body. So he performs a T lymphocyte selection to be released into the bloodstream.
This function of the thymus ensures the correct functioning of the
immune system. When there are few T lymphocytes in the body, the chances of acquiring diseases increase.The thymus is also responsible for thymosin hormone production, which stimulates the maturation of T lymphocytes.
Anatomy and Histology
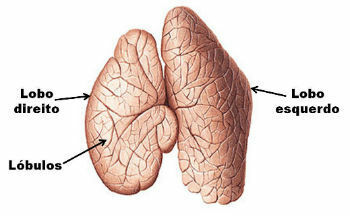
parts of the thymus
The thymus is divided into two joined lobes and numerous lobes of different shapes and sizes. The two wolves usually vary in size and shape. It is common for the right lobe to be smaller than the left lobe.
The thymus is covered by a capsule of connective tissue.
Each lobe of the thymus has two parts:
- Cortex: Peripheral region with a large number of lymphocytes. It is the area of intense lymphocyte production;
- Marrow: Central region with few mature lymphocytes.
The cells that make up the thymus are largely lymphocytes, but there are also reticular cells and macrophages.
Lymphocytes that are not selected by the thymus die and are destroyed by macrophages.
Histologically, it is possible to observe Hassall's bodies, which are clusters of epithelial cells organized around a central point.
Read too:
- Glands of the human body
- endocrine glands
- Organs of the human body
- Lymphatic system
- endocrine system
Curiosities
- The term thymus is derived from the Greek Thymus and it means vital energy.
- In the past, it was believed that a person's soul was stored inside the thymus.
- The thymus was the last of the important organs for the body to have its functions unveiled.