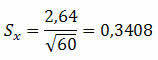Statistics is an exact science that studies the collection, organization, analysis and recording of data by samples.
Used since antiquity, when people's births and deaths were registered, it is a fundamental research method for making decisions. This is because it bases its conclusions on the studies performed.
Statistical method phases
Therefore, the phases of the statistical method are:
- problem definition: determining how data collection can solve a problem
- Planning: elaborate how to collect the data
- Data collect: gather data after planning the intended work, as well as defining the frequency of collection (continuous, periodic, occasional or indirect)
- Correction of collected data: check data to rule out any error on the part of the person who collected it
- Calculation of data: organization and counting of data
- Data presentation: assembly of supports that demonstrate the result of data collection (graphs and tables)
- Data analysis: detailed examination and interpretation of data
Allied to probability
, can be applied in the most diverse areas. Examples are the analysis of social, economic and demographic data. This is what IBGE - Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics does.The IBGE is the body that provides our country with the data needed to define the most appropriate planning model in public policies.
Curiosities
The word statistics, from Latin status + Latin pseudo prefix -isticum, relates to “state”.
In the beginning, the word was used to refer to the "political citizen". Later, it came to be used in German with the meaning of "State dataset", from which its meaning derives since the 19th century.
Get more knowledge with the contents:
- Average, Fashion and Median
- Dispersion Measures
- Standard deviation
- Variance and Standard Deviation
- Math Formulas
- Types of Graphics
- Statistics - Exercises
- Permutation