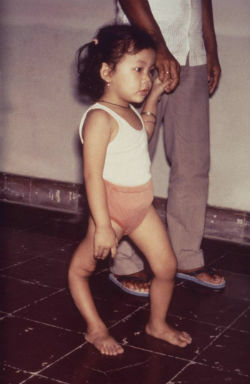Giardiasis, Giardiosis or lambliosis is a protozoan disease. The scientific name of the causative etiological agent is Giardia lamblia.
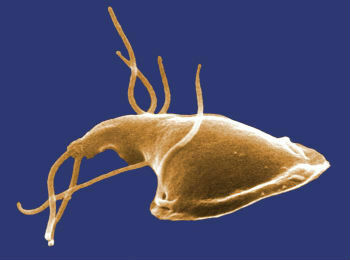 Giardia lamblia, protozoan causing giardiasis
Giardia lamblia, protozoan causing giardiasis
Its main characteristic is the involvement of the small intestine, causing intense diarrhea.
Although it is more common in children, it can also affect adults. Giardiasis usually occurs in temperate countries.
Diagnosis is made by examining the stool, and if left untreated, it can lead to dehydration and anemia in the patient.
Streaming
Giardiasis is transmitted through food and water contaminated with protozoan cysts.
Therefore, the places where the sanitation (sewage, treated water, etc.) is non-existent or precarious, the chance of the disease spreading is much greater. For this reason, in more developed countries the number of infected people is lower.
The protozoan is found in the feces of carriers of the disease and, therefore, can be transmitted through direct or indirect contact with the feces of those infected.
Interestingly, giardiasis can also be transmitted through unprotected anal sexual contact (without using condoms).
Did you know?
This parasite is resistant to chlorine. Therefore, water treated with chlorine may have protozoan cysts.
Symptoms
Once infected with the protozoan, symptoms usually appear within two weeks. The main symptoms of giardiasis are:
- low fever
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Gases
- Heartburn
- Nausea
- Weakness
- malaise
- Appetite and weight loss
- Irritability
- Yellowish and strong smelling stools
Note: In some cases, the patient may have lactose intolerance.
Canine Giardiasis
Giardiasis can also affect domestic animals such as dogs. Transmission and symptoms are similar to those in humans.
That is, it occurs when dogs ingest protozoan cysts through contaminated water or food. In addition to dogs, it can lodge with other hosts such as cats, rodents, cattle, etc.
The Vector and the Biological Cycle
THE Giargia lamblia it is an intestinal parasite that has a life cycle. This unicellular flagellate protozoan affects humans from the moment mature cysts are ingested.
The vector that causes the disease can present itself in two ways: cysts and trophozoites (adult stage of the protozoan). They are resistant and do not die from the acids released by the stomach. Thus, they reach the small intestine.
The incubation period for the protozoan is approximately one to four weeks. To better understand the vector's biological cycle, check the diagram below:
 Giardia Life Cycle
Giardia Life Cycle
Treatment
For the treatment of giardiasis, a good diet, rich in nutrients, is recommended. Lighter foods are indicated.
In addition, fluid intake is essential, due to severe diarrhea that can cause dehydration in the patient. Medicines are indicated by experts to kill the protozoan.
If left untreated, in the worst case it can lead to the death of infected individuals.
Prevention
To prevent giardiasis, we should wash our hands well before meals, as well as the foods we are going to consume (fruits, vegetables and greens). Cooking food is also a form of disease prevention.
Therefore, prophylaxis is done with care with hygiene. Also, experts recommend drinking drinking water.
Continue your research and read more about the topic:
- Protozoa
- Amebiasis
- Diseases Caused by Protozoa