Amoebiasis, also called amoebic dysentery or amoebic dysentery, is a parasitic disease caused by protozoa. The scientific name of the causative agent of amoebiasis is Entamoeba histolytica.
Its main characteristic is the alteration of the usual actions of the intestine, causing intense diarrhea that may be accompanied by blood.
Anyone, of any age group, can acquire this parasite. Diagnosis of the disease can be made by examination of the stool, endoscopy, proctoscopy or computed tomography.
Although less common, a blood test can detect the presence of antibodies against the parasite.
Learn more about Protozoa.
Streaming
Transmission of amoebiasis occurs through ingestion of cysts from the amoeba found in contaminated water or food. The cysts that cause amoebiasis are usually found in the feces of those infected and in the soil.
Although rare, the disease can be transmitted through sexual contact without proper protection.
Note that most cases occur in less favored countries, where hygiene conditions are more precarious, which facilitates the proliferation of the protozoan.
Biological Cycle
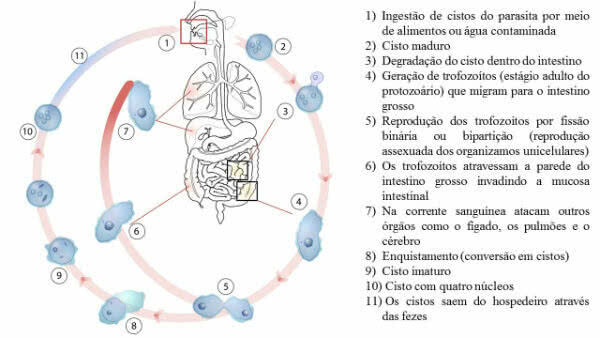 Parasite Biological Cycle
Parasite Biological Cycle
The life cycle of the protozoan that causes amoebiasis begins when the individual ingests the cysts. These pass through the stomach until they reach the small intestine. Interesting to note that they are very resistant as they survive stomach acids.
From there, they migrate to the large intestine, where they become attached to the intestinal mucosa. They feed on intestinal cells, beneficial bacteria present in the intestines and fecal clump, at the same time they create colonies.
Importantly, the incubation period of the protozoan varies a lot, that is, it can be days, months or years.
If left untreated, amoebiasis can lead to intestinal ulcers. In the worst case, it affects other organs in the human body, for example, the lungs, liver, spleen and even the brain.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of amoebiasis are:
- Fever
- Chills
- strong diarrhea
- intestinal cramps
- pain to evacuate
- Excess gas
- blood in feces
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weakness
Treatment
The treatment of the disease is done through the use of drugs that fight the protozoan, in addition to symptoms such as fever, nausea, etc. Two weeks are usually sufficient for recovery from the illness.
In addition, a diet rich in nutrients and fluid intake is recommended, due to dehydration caused by excessive diarrhea.
In the most extreme cases, surgery can be done if the cysts reach other organs.
Prevention
Preventing amoebiasis starts with better hygiene and sanitation (water and sewage treatment).
Therefore, it is recommended to wash your hands well before meals and after using the bathroom. You should also sanitize food (fruits, vegetables, vegetables) before consuming them. In addition, experts recommend taking potable water.
The use of protection (condoms) in oral-anal sex is also a way to prevent amoebiasis.
Giardiasis and Amebiasis
Although both diseases are caused by protozoa and transmitted by contaminated water and food, giardiasis is caused by the flagellate protozoan Giardia lamblia.
Learn more about others Diseases Caused by Protozoa.