O menstrual cycle refers to the period between the first day of menstruation and the first day of the next period.
During the period of the menstrual cycle, the body undergoes changes that prepare it for a possible pregnancy.
The first menstruation is called menarche and in the first two or three years it is normal for the cycles to be a little irregular. Over time, they become more regular and tend to stabilize until they reach 40-45 years of age.
From this age on, cycles become irregular again until menopause, when a woman stops menstruating.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
There are two main phases of the menstrual cycle that differ from each other, the follicular phase and the luteal phase. It is still possible to recognize a third phase, the ovulatory, characterized by the moment of ovulation.

The duration of the menstrual cycle is around 28 days, although there are shorter cycles of 21 days and longer ones of up to 35 days, also considered normal.
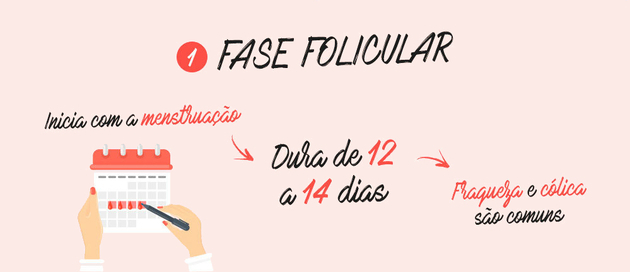
1. Follicular Phase
The first phase is called the follicular phase, which lasts approximately 14 days, ranging from 9 to 23 days. This phase gets its name because the ovarian follicles are in the process of development.
But what are ovarian follicles? They are found in the ovaries and harbor immature eggs that will be gradually released throughout a woman's reproductive life.
The follicular phase starts on the first day of bleeding until the egg is released, the ovulation phase. Menstruation, the bleeding period, lasts an average of 5 days, although it can range from 3 to 7 days.
In the first days of the follicular phase, there is a great production of the hormone FSH (stimulating follicle), responsible for stimulating the ovaries to produce mature eggs.
With the maturation of the follicles, there is also a high production of the estrogen hormone, resulting in the thickening of the endometrium and vessel formation, conditions that make the uterus ready to receive the fertilized egg and start the pregnancy.
At the end of the phase, the main follicle continues its development and growth, secreting estrogen faster and faster, leading to the estradiol peak around the tenth day.
In general, the main follicle continues its development and increases in size. Estrogen secretion remains elevated, ensuring that the egg is ready to be released.
Another feature is the change that occurs in the mucus in the cervix, which becomes thin and watery. All these changes consist of preparing the uterus for the possible arrival of sperm and consequent fertilization.
2. Ovulatory Phase
The ovulatory phase consists of the release of the mature egg that is ready to be fertilized, which goes to the fallopian tubes or fallopian tubes and goes to the uterus. This process consists of ovulation.

The day of ovulation varies depending on the length of the cycle. In many cases, it occurs in the 14th day of the cycle. However, this is not a rule and most women ovulate on different days of their cycle.
The egg has a short lifespan, around 24 hours. For pregnancy to occur it is necessary to maintain sexual intercourse during the woman's fertile period. Sperm can remain viable for up to 5 days in the female body.
For this reason, it should be considered that sexual intercourse without the use of contraceptive methods and up to 5 days before ovulation could result in pregnancy.
3. Luteal or Luteal Phase
The luteal phase begins with the formation of the corpus luteum, it comprises the period from ovulation to the first day of the next period.

The formation of the corpus luteum or yellow body occurs after ovulation due to the transformation of the walls of the ovarian follicles that transform into a secretory structure of the hormone progesterone, the most active in this phase.
In general, the luteal phase lasts around 12 to 16 days. The corpus luteum may degrade or remain active, indicating possible pregnancy.
Progesterone promotes a greater lining of the endometrium, preparing the uterus to receive the fertilized egg and fixing the zygote.
If nidation does occur, it initiates the production of hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), known as the pregnancy hormone, keeping the corpus luteum active.
If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates and a new cycle begins with the onset of menstruation.
Learn more about female reproductive system
Menstrual Calendar
The menstrual calendar or table is a method used to predict the likely day of ovulation, that is, the most fertile period for a woman.
For example, if the menstrual cycle is 28 days, ovulation occurs on the 14th day after the first day of bleeding.
However, considering the lifespan of sperm, it is necessary to consider a few days before ovulation as a high probability for the risk of pregnancy.
Sexual intercourse should be avoided five days before and five days after the probable day of ovulation. On the other days of the cycle, the chances of getting pregnant are smaller.
It is noteworthy that this method is not safe to prevent an unwanted pregnancy and also does not prevent against Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
Also read about:
- Pregnancy
- How does human fertilization occur?



