THE organic agriculture, also called organic, is a type of alternative agriculture that aims to offer healthy products, prioritizing food quality.
It is carried out through specific techniques that counteract the use of pesticides and fertilizers at all stages of the process.
The terminology originated in the 1920s, emphasizing the importance of producing healthy foods that provide health benefits. Thus, it presented as a fundamental issue the non-use of pesticides.
These conditions aroused awareness in the population for the consumption of healthier foods.

Main Characteristics of Organic Agriculture
Organic agriculture diversifies the products cultivated in order to ensure environmental balance, especially the soil.
In addition, it uses low environmental impact techniques with a focus on sustainability and conservation of natural resources.
While mechanized agriculture focuses on high production and uses toxic products in the plantations to speed up the cultivation process.
In summary, the main characteristics of organic agriculture are:
- Enables soil conservation and fertility, ensuring environmental balance;
- Minimizes impact on the environment;
- Optimizes the use of natural resources, ensuring ecological sustainability;
- Adds value to Organic Foods;
- Eliminates the use of pesticides.
Advantages of Organic Agriculture
The main advantages of organic agriculture are:
- Preservation of natural resources;
- Production of healthy and higher quality food;
- Sustainability and low environmental impact;
- Maintenance of biodiversity;
- Use of natural fertilizers (compost, mine farming, etc.);
- Crop rotation (polyculture);
- Healthy and nutrient-rich soil;
- Use of renewable energy.
Disadvantages of Organic Agriculture
The main disadvantages of organic agriculture are:
- More expensive and time-consuming;
- Lower production compared to traditional agriculture;
- Environmental impact with the use of pesticides and pesticides of organic origin;
- More expensive products than conventional ones.
Conventional Agriculture x Organic Agriculture
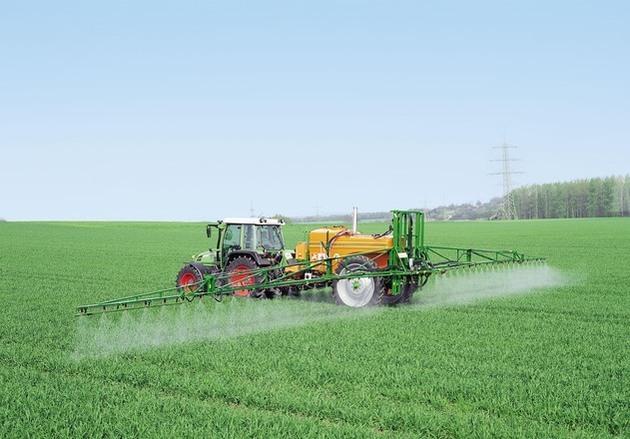

Conventional agriculture is primarily focused on high production. It is characterized by the use of modern techniques and equipment with the use of a variety of inputs, such as pesticides and fertilizers, which make it possible to accelerate the cultivation process.
In conventional agriculture there is also no concern with the nutritional quality of food. On the other hand, organic agriculture prioritizes the offer of healthy products. It uses specific techniques (natural fertilizers, composting, mine farming, polyculture) that are based on the non-use of pesticides.
The conventional agricultural production system, by abusively using pesticides, causes damage to the environment in terms of contamination of air, soil, water and living beings. Furthermore, the products generated affect the health and well-being of the population.
Meanwhile, the organic system minimizes the impact on the environment and guarantees ecological sustainability.
The consumption of foods with pesticide residues causes adverse effects on human health, of acute and chronic magnitude.
Chronic effects can occur months, years and even decades after exposure and consumption, manifesting itself in various diseases such as cancer, congenital malformations, endocrine disorders, neurological and mental.
Organic Agriculture in Brazil
In the 70s, the first alternative agriculture movements emerged that positioned themselves contrary to the project for the modernization of traditional agriculture promoted by the public policies of the government. This movement became known as the Green Revolution.
These movements aimed to bring about profound changes in the traditional process of agricultural work, as well as in the impact on the environment and human health.
THE family farming emerged in the Brazilian context from the 90's, to offer an answer to the settlers, tenants, small producers and rural workers who participated in social movements rural areas.

It is characterized by the use of manual cultivation techniques compatible with the local reality, ensuring the cultural integrity of rural communities. And by presenting a similar methodology, this family production system was closely intertwined with organic agriculture.
The development of organic agriculture in the family model represents the base of the economy of 90% of the Brazilian municipalities, being responsible for the income of 40% of the economically active population in the country.
Family farming in Brazil is the 8th largest food producer in the world, ensuring a prominent position in the agribusiness worldwide.
In Brazil, activities pertaining to the development of organic agriculture were approved by Law 10,831, of December 23, 2003. However, its regulation took place on December 27, 2007 with the publication of Decree No. 6,323.
Learn more about the subject, read also:
- agricultural systems
- subsistence farming