You seas and oceans of the world correspond to the liquid masses of planet Earth that bathe the continents, alongside rivers, lakes and lakes.
However, they are made up of large amounts of salt water and cover about 71% of the Earth's surface.
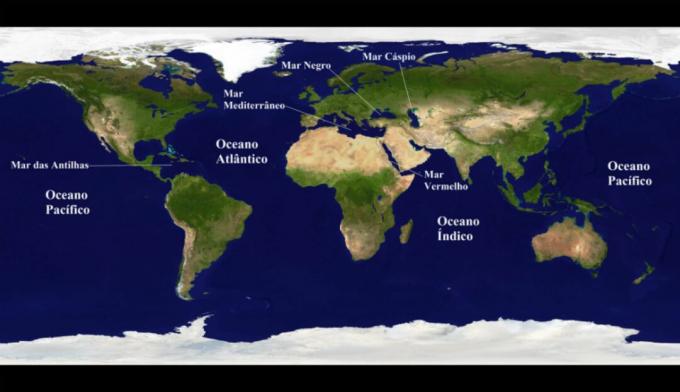 Oceans and Some Seas of the World
Oceans and Some Seas of the World
Difference between Sea and Ocean
Oceanography is the name for the study of the seas and oceans, which, in turn, contribute to the climate balance and maintenance of the planet's biodiversity.
The essential difference between seas and oceans lies in the extent they have, since the seas are smaller than the oceans and, therefore, are part of them.
Furthermore, the seas are closed, while the oceans are open and have greater depth.
Types of Seas
Depending on the location and geographical characteristics of the seas, they are classified into:
- Open or Coastal Seas: They have great connections with the ocean, for example, the Antilles Sea.
- Closed or Isolated Seas: they have a small connection with the ocean (through channels) and are located in the interior of continents, for example, the Dead Sea.
- Inland or Continental Seas: have almost no connection with the oceans (made through straits), for example, the Mediterranean Sea.
Seas of the World
According to the “International Hydrographic Organization”, there are about 60 seas in the world (including gulfs and bays), of which the most important are:
- Red Sea: located between Africa and Asia, the Red Sea is considered a gulf (extensive bay) with great biodiversity, with an area of approximately 450,000 km².
- Baltic Sea: located in northeastern Europe, the Baltic Sea has an area of approximately 420,000 km².
- Caspian Sea: considered the largest salt lake in the world, with an area of 371,000 km², the Caspian Sea is located in southeastern Europe.
- Dead Sea: located in the Middle East, the Dead Sea has an area of approximately 650 km², and receives this name since it has a high amount of salt, which makes the proliferation of species impossible.
- Black Sea: located between Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus, the Black Sea has an area of 436,000 km², and gets its name due to the large amount of mineral salts in its waters, which alter the coloring.
- Mediterranean Sea: Considered the largest continental inland sea in the world, the Mediterranean Sea is located between Africa, Europe and Asia, with a total area of approximately 2.5 million km².
- Antilles Sea: Also called the “Caribbean Sea” or “Caribbean Sea”, the Antilles Sea is located between Central and South America, and has an approximate area of 2.7 million km².
- Aral Sea: located in Central Asia, the Aral Sea (in Portuguese, “Mar de Ilhas”) has an approximate area of 68 thousand km² and has more than 1500 islands.
- Bering Sea: With an area of approximately 2 million km², the Bering Sea is located between Alaska and Siberia. It is named after the Danish navigator and explorer Vitus Jonassen Bering (1680-1741).
Seven seas
The expression "Seven Seas" appeared in Antiquity, when ancient peoples believed that the world was divided by seven of them: Adriatic, Arabic, Caspian, Mediterranean, Black, Red and the Gulf region Persian.
Currently this classification has been modified with the seven seas being the oceans: North Pacific, South Pacific, North Atlantic, South Atlantic, Indian, Arctic and Antarctic.
Oceans of the World
There are basically three oceans on planet Earth, namely:
- Pacific Ocean: considered the largest and deepest ocean on the planet, the Pacific, located between Asia, America and Oceania, has a total area of 180 million km² and a depth of approximately 10,000m.
- Atlantic Ocean: with an area of 106 million km² and a maximum depth of 7,750m, the Atlantic is located between the Americas, Europe and Africa and has the largest trade flows (export and import).
- Indian Ocean: considered the smallest ocean in the world, with about 74 million km², the Indian Ocean is located between Africa, Asia and Oceania.
Some scholars still consider the Oceans:
Arctic glacial ocean, to the north, with about 14 million km²;
Antarctic Glacial Ocean, to the south, with an approximate area of 22 million km².
Pollution of Seas and Oceans
Increasingly, the planet's water masses are suffering from climate change resulting from especially of human actions that, little by little, are substantially modifying the natural configuration of the planet.
Like global warming, the volume of water in the oceans and seas has increased in recent years, resulting from the melting of glaciers. Some seas have suffered from the process of desertification, which affects some areas of the planet.
In addition, biological, physical and chemical pollutions, caused by excess waste as well as environmental disasters in the seas (for example, oil spill), has led to the death of several species, and consequently, to the imbalance environmental.
Environmentalists warn of the importance of preserving the planet's water, which is essential for the survival of many animal and plant species.
Read about the aquatic ecosystems.

