THE Theory of relativity was proposed by the German physicist Albert Einstein (1879-1955).
It represents the conjugation of two theories: the restricted (special) theory of relativity and the general theory of relativity.
The theory of special relativity was published in 1905 in the article "The Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".
The theory of general relativity was presented in November 1915 to the Prussian Academy of Sciences, and was officially published a few months later.
In the conjugation of these two theories, Einstein explains the situations in which Isaac Newton's physics failed.
Thus, he developed changes that revolutionized the proposals for the concepts of space, time and gravity.
Theory of Restricted Relativity
The theory of special relativity is based on two postulates:
1. All laws of nature are the same in all inertial frames of reference (non-accelerated frames of reference).
2. The propagation speed of light in a vacuum is the same in all inertial reference systems (non-accelerated reference systems).
Consequences
A consequence of the 2nd postulate is that the value of the speed of light (3 .108 m/s) is a limit for speeds. No body can move faster than light in a vacuum.
Furthermore, the fact that the speed of light is constant changed the classical ideas of space and time.
Space and time are no longer absolute and become relative.
The time measured between the same event by observers that are in relative motion to each other is different. This gives rise to the idea of time dilation.
Likewise, there is a contraction of space measured by observers in different states (rest and movement).
Moving bodies contract in the direction of this movement relative to their size when measured at rest.
Temporal dilation and contraction of space only present significant values when the values of the velocities involved are close to the velocity of light in a vacuum.
know more:
- Inertia
- Speed of light
Formula
The theory of special relativity also changed the notion of energy.
Energy can be converted into mass and mass is now considered a form of energy.
This principle is called mass-energy equivalence and can be expressed by the formula:
AND0 = mc²
Being,
AND0: resting energy
m: pasta
ç: speed of light
This relationship is easily verified in nuclear reactions, where particles and nuclei interact converting mass into energy and vice versa.
General Relativity Theory
The general theory was presented by Einstein 10 years after the restricted theory. It broadens the scope of that by extending the description of physical phenomena to accelerated (non-inertial) systems.
The basic idea of the theory is that the presence of matter bends spacetime. Thus, the greater the mass of the body, the more it will curve spacetime around it.
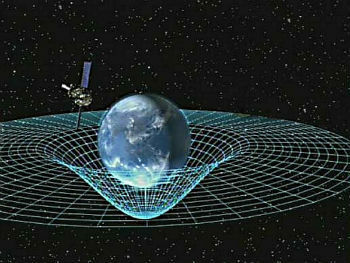
Mass curves spacetime
O Principle of Equivalence, postulates that a uniformly accelerated frame of reference is physically equivalent to a uniform gravitational field.
By including gravitational fields, the theory describes the movement of objects no longer as the action of forces, but as trajectories on the space-time surface.
From this new conception it was possible to explain the anomalous behavior of Mercury's orbit (precession of Mercury's perihelion).
The theory predicted that light should also follow the space-time surface curvature generated by intense gravitational fields. What was later proven.
It was also predicted that the measurement of time would also be influenced by gravitational fields. The more intense the field, the slower time would pass.
This prediction was also confirmed. Making the Global Positioning Satellite System (GPS) work properly requires corrections.
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein he was born in the city of Ulm, Germany, in 1879 and died in 1955, in the United States.
The German physicist and mathematician received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921 for work developed at the quantum physics and in the study of photoelectric effects.
Son of a Jewish family and, fearing persecution by the Nazis in Germany, he moved to the United States.

Einstein revolutionized the sciences with his theories
Read too:
- Atomic bomb
- gravitational waves
- Origin of the Universe
- Black Hole
- Stephen Hawking
- Big Bang Theory

