Capacitors are electronic components that store electrical charges to be used whenever electrical resistance makes it difficult for current to pass.
Capacitance (C), which is the storage capacity of a capacitor, is measured in Farad (F), which is done using the following formula:
C = Q/V
Where,
Ç: capacitance
Q: electrical charges
V: tension
The capacitor has two terminals: a positive, which is larger, and a negative, which is smaller. It is made up of metal plates (armor) and a dielectric material that separates them. Dielectrics are insulating materials that can become conductive, such as cellulose, ceramics, Teflon and glass.
There are different types of capacitors: ceramic, electrolytic, mica, oil and paper, polyester, SDM, tantalum, variable.
Association of Trainers
THE capacitor association it can happen in series, in parallel or mixed.
At serial association, the positive plates of the capacitors connect to their negative plates. Therefore, the association charge is constant (Q = constant).
At
parallel association, the negative plates of the capacitors connect to each other, just as the positive plates connect to the positive plates.In this case, the electrical voltage, also called the electrical potential difference, is constant (V = constant).
At mixed association, capacitors are connected in two ways, in series and in parallel.
read Resistors and Physics Formulas.
Solved Exercises
1. (FURG-RS) All capacitors shown in the figures below have the same capacitance. Choose the association whose equivalent capacitance is equal to that of a single capacitor:
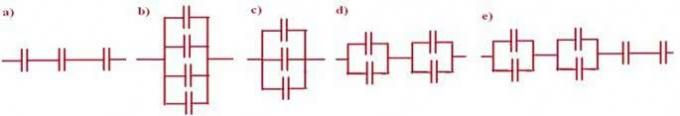
Alternative d.
2. (PUC-MG) If we double the charge accumulated on the plates of a capacitor, the potential difference between its plates will be:
a) unchanged.
b) multiplied by four.
c) multiplied by two.
d) divided by four.
e) divided by two.
Alternative c: multiplied by two.
3. (PUC-SP) The charge of a capacitor increases by 6.10-5C when the potential difference between its terminals increases from 50V to 60V. This capacitor has the capacity:
a) 12.10-6F
b) 10.10-6F
c) 6.10-6F
d) 2.10-6F
e) 1.10-6F
Alternative c: 6.10-6F