General properties are those common to all materials, regardless of their composition.
They are: mass, extension, inertia, impenetrability, divisibility, compressibility, elasticity, indestructibility and discontinuity.
Remember that matter is everything that has mass, occupies a place in space, and is made up of small particles (atoms and molecules).
We can cite wood, iron and glass as an example of matter. Check out the properties that are common to all of them below.
Pasta
It is an invariable quantity that represents the amount of matter present in a body. Regardless of where the material is, its mass will always be the same.
Remember that mass is different from weight, as weight is a vector quantity (it has modulus, direction and sense), which results from the multiplication between the mass of a body and the acceleration of gravity exerted on he.

As the acceleration of gravity on Earth is approximately 10 m/s2, so a body with a mass of 63.5 kg has a weight of 635 N.
Extension
It corresponds to the capacity of a body to occupy a place in space, in any physical state, which is measured by volume.
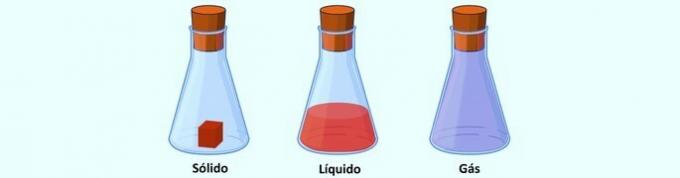
- A solid has a definite volume because its particles are tightly bound together.
- A liquid has a specific volume, but takes the form of the container in which it is placed.
- A gas fills the entire volume of the container it is in, due to its particles moving in all directions and at great speed.
Inertia
the beginning of inertia indicates that if a body is at rest or moving in a straight line, it tends to remain in that state until a force acts on it.
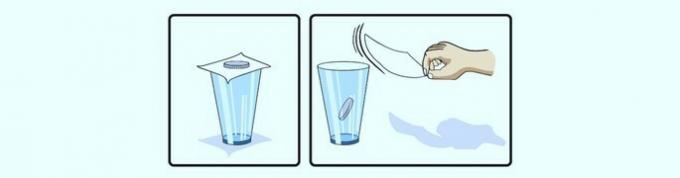
When a coin is placed on top of a piece of paper, it remains at rest. When removing the sheet, the coin moves and falls because the force of gravity acted on it.
See too: Subject: what is it, composition and examples
Impenetrability
Two bodies cannot occupy the same place in space at the same time.

When placing an object in a container of water, a quantity of the liquid is displaced, as impenetrability indicates that a body cannot be passed through. Therefore, the water and the ball cannot be in the same space at the same time.
Divisibility
The divisibility of matter allows the object, even when broken into small parts, to maintain its properties.

A loaf of bread can be broken by a physical method, such as using a knife. The slices created have the same characteristics as whole bread, but are smaller portions.
Compressibility
By applying a force, that is, exerting pressure on matter, it is possible to reduce its volume.

When a gas, such as air, is compressed, it decreases in volume. When we press the plunger of a syringe all the way, covering the hole, the point where the plunger goes shows how much the air was compressed.
Elasticity
A force applied to the material generates a deformation, but after the force ceases, the material has the ability to return to its initial state.

The deformation suffered by a spring is directly proportional to the intensity of the applied force. Therefore, the greater the force applied, the greater the length that the spring can reach.
indestructibility
Matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. This is the law of conservation of the masses.

When wood from a fire burns, a transformation of matter takes place. Combustion causes smoke to be produced by the reaction of carbon in wood with oxygen in the air.
Discontinuity
Matter has empty spaces that represent discontinuity. These pores are the spaces between molecules, which can be larger or smaller.

When we look at some rock types very closely, we can see that they are not completely uniform: they are made up of particles with empty spaces between them.
To learn more about the composition of the matter, be sure to read these texts:
- Atoms
- Simple and compound substances
- Pure substances and mixtures
General and specific properties of matter
When we want to differentiate one material from another, we use specific properties, as general properties apply to any object.
The specific properties characterize the matter and serve to identify materials according to their particularities, which can be physical, chemical, organoleptic or functional.
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Functional | Acid, base, salt and oxide. |
| Physics | Density, solubility and magnetism. |
| Chemistry | Oxidation, combustion and fermentation. |
| Organoleptic | Color, sound, flavor and odor. |
physical states of matter
Matter can take different forms in nature. These states occur according to the pressure, temperature and forces acting on the molecules of the material.
| state | Description |
|---|---|
| Solid | It has a well-defined shape and volume due to the fact that the molecules remain tightly bound together. |
| Liquid | The shape is variable and the volume is constant because the molecules exhibit less union and greater agitation. |
| Gaseous | The shape and volume are variable because the particles that make up the matter have little interaction with each other and intense movement. |
Changes in the physical state of matter
When a substance receives or loses energy, a change in physical state occurs.
| Change | Description |
|---|---|
| Fusion | Passage from solid to liquid state. |
| Vaporization | Passage from liquid to gaseous state. |
| Condensation | Passage from the gaseous state to the liquid state. |
| Solidification | Passage from liquid to solid state. |
| Sublimation | Passage from solid to gaseous state and vice versa (without going through the liquid state). |
Want to test your knowledge? So check it out: Exercises on Matter Properties, with questions for entrance exams and feedback commented by an expert!