The liver is the largest gland in the human body, with both endocrine and exocrine activity.
The liver is located in the abdominal region, on the right side, below the diaphragm. It has a shape that resembles a trapeze, with rounded angles. Its weight is approximately 1500g. The color is reddish-brown.
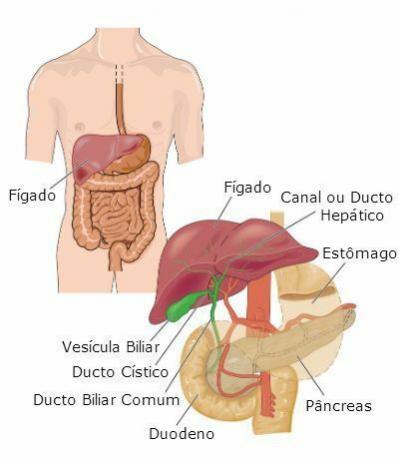
liver location
It is a structure attached to the digestive system, formed by millions of cells that clump together in plaques and are called hepatocytes.
The liver is an organ with the capacity to regenerate, if we remove half of the liver, in a few months it will return to normal size.
Anatomically, the liver has four lobes: the direct and largest, the left, the square and the caudate.
Roles
The liver can perform over 500 functions in the human body. Among the functions of the liver, the following stand out:
- Storage and release of glucose;
- Secrete the bile that was stored in the vesicle. THE bile it is sent to the intestine, where it helps to dissolve and use fat;
- Lipid metabolism;
- Conversion of ammonia to urea;
- Synthesis of most plasma proteins
- Destruction of worn red blood cells;
- Storage of vitamins and minerals;
- Filtering of impurities.
Learn more about Glands of the Human Body.
Liver Diseases
In general, liver disease is accompanied by the following symptoms: jaundice (yellow skin), dark urine, abdominal swelling, bleeding, itching and tiredness.
The main liver diseases are liver cirrhosis and viral hepatitis.
THE hepatical cirrhosis it consists in the transformation of the original cells of the liver tissue by a fibrous tissue. As a result, the organ does not perform its functions normally.
THE viral hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by infection with one of the five hepatitis viruses. Hepatitis can be type A, B and C.
Know more:
- Endocrine System
- Organs of the Human Body

