The sky looks like it's not blue
We see the blue sky due to the combination of sunlight and the elements that make up the atmosphere. This causes the blue color to spread and reach our eyes with the impression that this is the color of the sky.
The reason we look up and see everything blue is similar to the effect of an optical prism. Let's better understand how this happens?
3 facts that explain the blue of the sky
1. the color of sunlight
Well, we get the impression that sunlight is white, but it's actually a mixture of several colors. That's because white reflects all colors.
2. The mixture of colors in the atmosphere
Colors come from electromagnetic waves. Through a visible electromagnetic spectrum we can see that colors are waves that have different lengths.
They travel through the vacuum of space, where they mix with the gases, water vapor and dust that make up the atmospheric air.
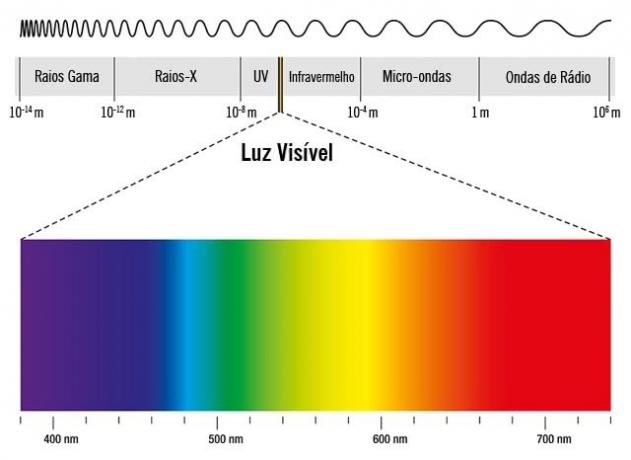
3. the length of the blue waves
In the atmosphere, the light emitted by the Sun that stands out the most is blue, because its waves are shorter, which makes them sharper.
Conclusion: the sky is blue thanks to the sun and the atmosphere
If it weren't for the mixture of colors emitted from the Sun's light together with the gases and everything that makes up the atmosphere's air, the sky would be black during the day.
Rayleigh scattering or scattering is the name of the physical phenomenon that gives us the impression that the sky is blue. It is named after the English physicist John William Strutt (Lord Rayleigh), who dedicated himself to studying the scattering of light.
You might also want to know about:
- electromagnetic spectrum
- light refraction
- Rainbow