The stem is the part of the plant with the function of sustaining and conducting substances.
Stems can have a variety of shapes. Therefore, they are classified as aerial, subterranean and aquatic.
aerial stems
Aerial stems can be of the following types:
Stem

The trunk is a type of erect aerial stem, one of the most common that exists.
It has a cylindrical structure that may have branches. It is most common to be found in medium to large plants.
It is the type of stem characteristic of large trees.
Stem

The stem is a type of aerial and erect stem. It has a soft and fragile structure, with a greenish color.
The most typical example of stem occurs in the stem of cabbage and some herbs
thatch

The culm is an aerial stem and its main characteristic is the presence of nodes and internodes visible throughout its extension.
The internodes form buds that can be hollow, like bamboo, or filled, like sugarcane.
Stipe

The stem is an erect, rigid and long stem. In general, it does not branch and leaves always appear at its apex.
Palm trees are the classic examples of stem-type plants.
Rhizophores

The rhizophore is a type of aerial stem whose main characteristic is the geotropism positive, growing towards the ground, in the same direction as gravity.
This condition favors the emergence of adventitious roots, which are important for the development of plants in the mangrove.
underground stems
Stems can also develop underground and present the following types:
rhizomes

Rhizomes are underground stems that grow horizontally and can branch out.
They have buds, from which sprouts arise to give rise to new plants.
Rhizomes are found in banana trees, ginger and ferns.
tubers
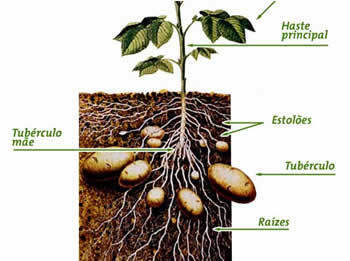
The tubers are underground stems that accumulate energy reserve substances.
Therefore, tubers are often edible. Example: potatoes, yams, yams.
Buds are also found on the surface of the tubers, which can give rise to new plants.
Bulbs

Bulbs are underground stems and leaves that can store reserve substances.
In this case, the stem has a flattened shape, being called a plate. While its leaves are succulent and store substances.
Examples of bulbs are onion and garlic.
aquatic stems

Aquatic stems are those that develop inside the water, presenting different structures for air storage, allowing the plant to float.
Examples of aquatic stems are found in water lilies, water hyacinth and elodea.
Know more:
- stems
- Types of flowers and their functions
- Types of fruits
- Root types
- Sheets
shoot adaptations
The stems also present some types of adaptations that help the plants to establish themselves in different environments.
cladodes

Cladodes assist in carrying out photosynthesis and water storage. It is common in dry climate plants such as cacti.
They consist of green aerial stems and arise from plants that shed their leaves to prevent water loss.
In this case, the cladodes assume the appearance of a leaf.
tendrils

Tendrils are spiral-shaped branches that help support and fix climbing plants on a given support.
They are found in vines and passion fruit.
thorns

Thorns are tough, sharp structures that do not carry out photosynthesis.
They serve as plant protection and are difficult to remove.
We find thorns, for example, in orange, lemon and cactus trees.
Read too:
- plant parts
- vegetable kingdom
- Botany: the study of plants