Graphene is a nanomaterial composed only of carbon, in which atoms link together forming hexagonal structures.
It is the finest crystal known and its properties make it highly desirable. This material is light, conductive of electricity, rigid and waterproof.
The applicability of graphene is in several areas. The best known are: civil construction, energy, telecommunications, medicine and electronics.
Since it was discovered, graphene has remained the center of research interest. The study of applications for this material mobilizes institutions and investments of millions of euros. So scientists around the world keep trying to develop a cheaper way to produce it on a large scale.
Understanding what graphene is
Graphene is an allotropic form of carbon, where the arrangement of the atoms of this element forms a thin layer.
This allotrope is two-dimensional, that is, it has only two measurements: width and height.
To get an idea of the size of this material, the thickness of a sheet of paper corresponds to the superposition of 3 million layers of graphene.
Although it is the thinnest material isolated and identified by man, its dimension is in the order of nanometers. It is light and strong, capable of conducting electricity better than metals such as copper and silicon.
The arrangement that the carbon atoms assume in the structure of graphene, makes that very interesting and desirable characteristics can be found in it.
Graphene Applications
Many companies and research groups around the world are publishing results of work involving applications for graphene. See below the main ones.
| Potable water | Graphene-formed membranes are capable of desalinating and purifying seawater. |
|---|---|
| CO emissions2 | Graphene filters are able to reduce CO emissions2 by separating gases generated by industries and businesses that will be rejected. |
| disease detection | Much faster biomedical sensors are based on graphene and can detect diseases, viruses and other toxins. |
| Construction | Building materials such as concrete and aluminum are made lighter and stronger with the addition of graphene. |
| Beauty | Hair coloring by spraying graphene, whose duration would be around 30 washes. |
| Microdevices | Chips even smaller and stronger due to the replacement of silicon by graphene. |
| Energy | Solar cells have better flexibility, more transparency and lower production costs with the use of graphene. |
| Electronics | Batteries with better and faster energy storage can recharge in up to 15 minutes. |
| Mobility | Bikes can have firmer tires and frames weighing 350 grams using graphene. |
Graphene Structure
The structure of graphene is made up of a network of carbons linked in hexagons.
The carbon nucleus is made up of 6 protons and 6 neutrons. The 6 electrons of the atom are distributed in two layers.
At valence layer there are 4 electrons, with this shell holding up to 8. Therefore, for carbon to acquire stability, it must make 4 connections and reach the electronic configuration of a noble gas, as stated in the octet rule.
The atoms in graphene bond by covalent bonds, that is, there is the sharing of electrons.

Carbon-carbon bonds are the strongest bonds found in nature and each carbon joins the other 3 in the structure. Therefore, the hybridization of the atom is sp2, which corresponds to 2 single and one double bonds.
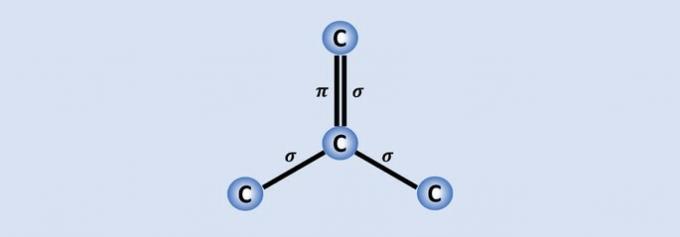
Of the 4 carbon electrons, three are shared with the neighboring atoms and one, which makes up the bond. , helps graphene, for example, to be a good conductor of electricity because it has more "freedom" in the material.
Graphene Properties

| Light | A square meter weighs just 0.77 milligrams. A graphene airgel is about 12 times lighter than air. |
|---|---|
| Flexible | It can expand up to 25% of its length. |
| Conductor | Its current density higher than copper. |
| Durable | It expands in cold and shrinks in heat. Most substances act in the opposite way. |
| Waterproof | The mesh formed by carbons does not even allow the passage of a helium atom. |
| Resistant | About 200 times stronger than steel. |
| Translucent | Absorbs only 2.3% of light. |
| Thin | A million times thinner than a human hair. Its thickness is only one atom. |
| Hard | Hardest material known, even more so than diamond. |
History and Discovery of Graphene
The term graphene was first used in 1987, but was only officially recognized in 1994 by the União de Química Pure and Applied.
This designation arose from the junction of the graphite with the suffix -ene, referring to the double bond of the substance.
Since the 1950s, Linus Pauling spoke in his classes about the existence of a thin layer of carbon, made up of hexagonal rings. Philip Russell Wallace also described some important properties of this structure years earlier.
However, only recently, in 2004, graphene was isolated by physicists Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov at the University of Manchester and can be deeply known.
They were studying graphite and using the technique of mechanical exfoliation they managed to isolate a layer of material using adhesive tape. This achievement awarded the Nobel Prize to the pair in 2010.
Importance of graphene for Brazil
Brazil has one of the largest reserves of natural graphite, a material that contains graphene. Graphite natural reserves reach 45% of the world's total.
Although the occurrence of graphite is observed throughout the Brazilian territory, the exploited reserves are found in Minas Gerais, Ceará and Bahia.
With abundant raw material, Brazil also invests in research in the area. The first laboratory in Latin America dedicated to research with graphene is located in Brazil, at Universidade Presbiteriana Mackenzie in São Paulo, called MackGraphe.
Graphene manufacturing
Graphene can be prepared from carbide, hydrocarbon, carbon nanotube and graphite. The latter being the most used as starting material.
The main methods of production of graphene are:
- Mechanical microexfoliation: A graphite crystal has layers of graphene stripped off using a tape, which are deposited on substrates containing silicon oxide.
- Chemical microexfoliation: carbon bonds are weakened by the addition of reagents, partially breaking the network.
- chemical vapor deposition: formation of graphene layers deposited on solid supports, such as metallic nickel surface.
Graphene price
The difficulty of synthesizing graphene on an industrial scale means that the value of this material is still very high.
Compared to graphite, its price is thousands of times higher. While 1 kg of graphite is sold for 1 dollar, the sale of 150 g of graphene is made for 15,000 dollars.
Curiosities about Graphene
- European Union project, named Graphene Flagship, earmarked around 1.3 billion euros for research related to graphene, applications and development of production on an industrial scale. About 150 institutions in 23 countries participate in this project.
- The first suitcase developed for space travel has graphene in its composition. Its launch is scheduled for 2033, when NASA plans to carry out expeditions to Mars.
- Borophene is graphene's new competitor. This material was discovered in 2015 and is considered an improved version of graphene, being even more flexible, resistant and conductive.
Graphene in Enem
In the Enem 2018 test, one of the questions of Natural Sciences and Its Technologies was about graphene. Check below the commented resolution of this issue.
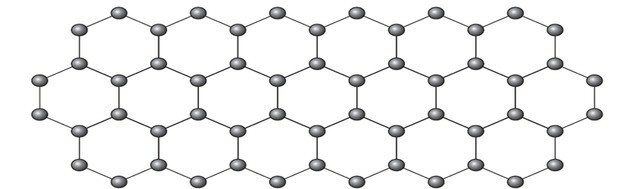
Graphene is an allotropic form of carbon consisting of a planar sheet (two-dimensional array) of compacted carbon atoms that are only one atom thick. Its structure is hexagonal, as shown in the figure.
In this arrangement, the carbon atoms have hybridization
a) sp of linear geometry.
b) sp2 of planar trigonal geometry.
c) sp3 alternated with sp-hybridized carbons of linear geometry.
d) sp3d of planar geometry.
e) sp3d2 with hexagonal planar geometry.
correct alternative:b) sp2 of planar trigonal geometry.
Carbon allotropy occurs because of its ability to form different simple substances.
Because it has 4 electrons in the valence shell, carbon is tetravalent, that is, it tends to make 4 covalent bonds. These bonds can be single, double or triple.
Depending on the bonds that carbon makes, the spatial structure of the molecule changes to the arrangement that best accommodates the atoms.
Hybridization occurs when there is a combination of orbitals, and for carbon it can be: sp, sp2 and sp3, depending on the type of calls.
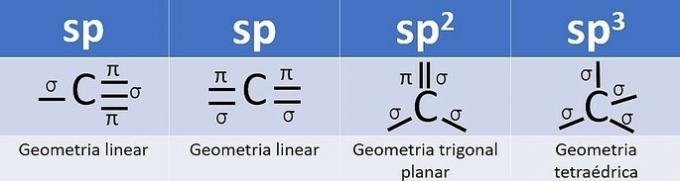
The number of hybrid orbitals is the sum of the sigma (σ) bonds that the carbon makes, as the bond does not hybridize.
- sp: 2 sigma links
- sp2: 3 sigma links
- sp3: 4 sigma links
The representation of the graphene allotrope in balls and sticks, as shown in the figure in the question, does not demonstrate the true bonds of the substance.
But if we look at a part of the image, we see that there is one carbon, representing a ball, connecting to three other carbons forming a structure like a triangle.
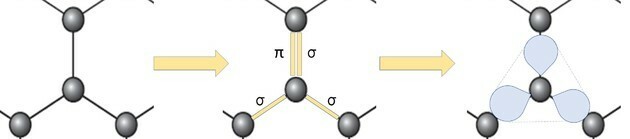
If carbon needs 4 bonds and is bonded to 3 other carbons, then one of those bonds is double.
Because it has one double and two single bonds, graphene has sp hybridization2 and, consequently, trigonal planar geometry.
The other known allotropic forms of carbon are: graphite, diamond, fullerene and nanotube. Although they are all made of carbon, allotropes have different properties, stemming from their different structures.
Read too: Chemistry in Enem and Chemistry Questions in Enem.