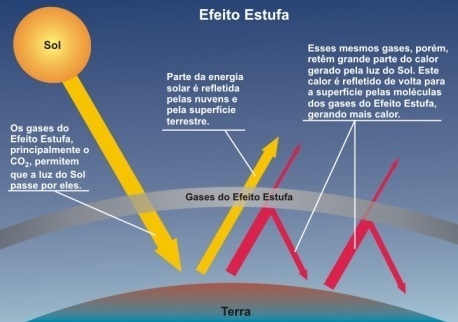
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon caused by the concentration of gases in the atmosphere, which form a layer that allows the passage of sunlight and the absorption of heat.
This process is responsible for keeping the Earth at a suitable temperature, ensuring the necessary heat. Without it, our planet would certainly be very cold and the survival of living beings would be affected.
How does the greenhouse effect occur?
When the sun's rays reach the Earth's surface, due to the layer of greenhouse gases, around 50% of them are retained in the atmosphere. The other part reaches the earth's surface, heating it and radiating heat.
Greenhouse gases can be compared to insulators, as they absorb part of the energy radiated by the Earth.
What happens is that in recent decades the release of greenhouse gases, due to human activities, has increased considerably.
With this accumulation of gases, more heat is being retained in the atmosphere, resulting in an increase in temperature. This situation gives rise to global warming.
To get an idea, the greenhouse effect can be compared to what happens inside a parked vehicle, with the windows closed and directly receiving sunlight. Although the glass allows the passage of sunlight, it prevents heat from escaping, increasing the temperature inside.
Also know about:
- Thermal Inversion
- Environmental impacts
Greenhouse gases
The main greenhouse gases are:
- Steam (H2O): found in suspension in the atmosphere.
- Carbon monoxide (CO): colorless, flammable, odorless, toxic gas produced by burning under low oxygen conditions and by the high temperature of coal or other materials rich in carbon, such as petroleum derivatives.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): expelled by the burning of fuels used in motor vehicles based on oil and gas, the burning of mineral coal in industries, and the burning of forests.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC): compound formed by carbon, chlorine and fluorine, from aerosols and the refrigeration system.
- Nitrogen Oxide (NxOx): set of compounds formed by the combination of oxygen and nitrogen. It is used in internal combustion engines, furnaces, stoves, boilers, incinerators, the chemical industry and the explosives industry.
- sulfur dioxide (ONLY2): it is a dense, colorless, non-flammable, highly toxic gas, formed by oxygen and sulfur. It is used in industry, mainly in the production of sulfuric acid and is also expelled by volcanoes.
- Methane(CH4): colorless gas, odorless and if inhaled it is toxic. It is expelled by cattle, that is, in the digestion of herbivorous animals, decomposition of organic waste, fuel extraction, among others.
What are the causes of the greenhouse effect?
As we have seen, the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, but it is intensified due to the increasing burning of fossil fuels that represent the basis of industrialization and many human activities.
Forest fires to transform their areas into plantations, cattle raising and pastures also contribute to the increase in the greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
The consequence of the intensification of the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere is the global warming.
According to scientific researches, the Earth's average temperature, in the last hundred years, has increased by about 0.5ºC. If the current rate of air pollution remains in the same proportion, it is estimated that between the years 2025 and 2050, the temperature will increase by 2.5 to 5ºC.
The consequences of the greenhouse effect will be as follows:
- Melting of large ice masses in the polar regions, causing sea level rise. This could lead to the submergence of coastal cities, forcing the migration of people.
- Increase in cases of natural disasters such as floods, storms and hurricanes.
- Species extinction.
- desertification of natural areas.
- Most frequent episodes of drought.
- Climate change could also affect food production, as many productive areas could be affected.
Another problem associated with the presence of polluting gases in the atmosphere is the acid rain. It results from the exaggerated amount of products from burning fossil fuels released into the atmosphere as a result of human activities.
Learn more about the relationships and differences between the Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming.
How to avoid the greenhouse effect?
To warn about the situation of the greenhouse effect and global warming, several countries, including Brazil, signed the Kyoto Protocol, in 1997.
Before that, in 1987 the Montreal Protocol. The main purpose is to reduce the emission of products that damage the ozone layer.
Some tips for individual and collective actions also contribute to reducing the greenhouse effect, they are:- Take short journeys on foot or by bicycle;
- Give preference to public transport;
- Use recyclable products;
- Save electricity;
- Carry out selective collection;
- Reduce beef and pork consumption;
- Compost organic material.
To learn more, read also:
- Air pollution
- Ozone layer
- Paris Agreement
- Hole in the ozone layer



