The Earth Charter is a document, proposed during Rio-92, focused on issues about a peaceful, just, sustainable global society. She proposes a change of habits to achieve a...
What is autumn? Autumn is one of the four seasons of the year and represents the transition between summer and winter. Therefore, it has features that resemble summer and...
Fatty acids are structural components of cell membrane phospholipids. They can also be found in their free form and be oxidized in certain tissues to produce energy. They are...
The stratosphere is the second largest layer of the Earth's atmosphere, situated between the troposphere and the mesosphere. It is at an altitude of 50 km from the surface and is home to the ozone layer. O...
Geology is a natural science that studies the Earth. From the Greek, the term geology is formed by the words “geo” (Earth) and “logy” (study or science). The geologist is the professional and...
Earth Day or World Planet Earth Day is celebrated on April 22nd around the world. The date represents the fight in defense of the environment, promoting reflection on the importance of...
Water is a very important natural resource for life on earth. Human beings, animals and plants need it to live and, therefore, it is the most important source of life on the planet...
The parenchyma is the tissue composed of cells that perform a specific function in the organ where they are located. In animals, the parenchyma forms the functional part of organs such as the kidneys,...
Atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds various planets and satellites in the Solar System. Each atmosphere has a different composition, most of it is quite rarefied. Is important...
Mimicry is an adaptive characteristic of animals or plants to imitate another organism to gain advantage. Among the major goals of mimicry is protection from predators. There is,...
The Earth's crust is the outermost and thinnest layer on Earth. It corresponds to about 1% of the Planet and extends to a maximum of 80 kilometers in depth. It is divided into: Crust...
The biosphere is the Earth's layer that brings together all existing ecosystems. It corresponds to the place where living beings are found. The term biosphere derives from the Greek bios, life and sfaira,...
Nitrogen (nitrogen, from the Greek "a", without and "zoe", life), which means "salt-former" or "that which forms nitrates". It is one of the most abundant elements in the Universe. On Earth it is at its greatest...
Heredity or Genetic Inheritance is the biological mechanism through which the characteristics of each living being are transmitted from one generation to another. It involves genetic processes, a...
Yeasts are types of fungi. They are unicellular organisms, which do not photosynthesize and, in general, reproduce asexually. These microorganisms multiply quickly and...
Brazil has a great diversity of birds, there are almost 2000 species, some of which are endemic (only found in the region) and others are threatened with extinction. The birds...
Living beings have general characteristics that allow them to be distinguished from non-living beings. We often hear that living things are born, grow, reproduce and die. However, there are...
Bacteriophages are viruses that specifically infect bacteria. Also called phages, these viruses adhere to the bacterium, pierce its cell wall and inject its content into the host...
Glial cells make up nervous tissue along with neurons. Glia cells, also called gliocytes or neuroglia, can be of two types: microglia or macroglia. Besides...
Many animals are considered useful to humans because they provide food or other products and have economic value, such as bees that provide honey, wax and pollen. While others are...
The rainbow is a multicolored arc, composed of seven colors, caused by the optical phenomenon that, through the refraction (scattering) of sunlight on water droplets suspended in the air, forms a...
Invertebrates are animals that do not have a spine or skull. They represent a large part of the planet's biodiversity, since they represent about 97% of all species...
The thermosphere is the largest layer in the Earth's atmosphere. This is a thermal classification and includes the ionosphere and exosphere. It is located just above the mesopause and extends to 600...
Magnetic Separation, also known as magnetization, is a method of separating solid heterogeneous mixtures. Among the mixed substances, one of them has properties...
The exosphere is the name of the outermost layer of the Earth's atmosphere from the surface, being the one that precedes outer space. It is located above the thermosphere right after the layer...
The Milky Way is among the hundreds of billions of galaxies in the Universe and where our Solar System is located. The Latin name – Milky Way – derives from the Greek word "Kiklios Galaxios",...
The Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer is an international agreement that aims to reduce the emission of products that damage the ozone layer...
What is summer? Summer is one of the four seasons of the year that begins after spring and ends with the arrival of autumn. It is marked by rising temperatures and remains for 3...
Charles Darwin (1809-1882) was an English naturalist and scientist. Author of “Origin of Species, Through Natural Selection”, he was one of the most important figures on evolutionism and...
Pluto is a dwarf planet that is located 5.9 billion kilometers away from the Sun. It is noteworthy that Pluto is no longer considered a planet in the solar system since 2006. This year,...
The Proterozoic eon is the younger of the two divisions of Pre-Cambrian time, the oldest being Archean. The Proterozoic extended from 2,500 to 542 million years ago. Features The...
According to the classification, the types of existing rivers are influenced by factors such as relief, drainage system, runoff and water color. Remember that rivers are courses...
Fractional Dissolution is a method of separating solid heterogeneous mixtures that is carried out in parts, that is, in a fractional form. It is used when there are substances in the mixtures...
The ionosphere is one of the layers of the atmosphere characteristic for suffering ionization from solar radiation. Thus, it is very active and its size decreases with the energy it absorbs from the Sun. THE...
The seasons are spring, summer, autumn and winter. They arise because of the Earth's movements and everything happens in an organized way in nature. Our life is also influenced...
Social insects are those that live organized in groups, interacting with each other, in a harmonious ecological relationship called society. The best known social insects are the bees, the...
The habitat is where an animal lives and the niche is how it lives there. These are two concepts with different meanings, although they are often confused. In short, the habitat is the place...
Galaxies are clusters of stars, planets, gas and dust bound together by the force of gravity and enough energy to form stars and planets. Types of Galaxies There are three types...
The blue macaw is a completely blue bird of the parrot family, as well as hyacinth macaws, parrots, parakeets, among others. It is an endemic species from northeastern Brazil, or...
Thermal Pollution occurs due to changes in the temperature of the air and water used mainly by hydroelectric, thermoelectric and nuclear power plants. It is the least known type of pollution because...
The integumentary system varies greatly from animal to animal. In most animals, there is a layer or more of epithelial cells constituting the integument, called the epidermis, a nutritious layer...
Soil salinization is a process of accumulation of mineral salts (Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, etc.) in the soil. This increased concentration of salts harms the properties of the soil and...
World Environment Day is celebrated on June 5th. It was created on the occasion of the Stockholm Conference, organized by the United Nations (UN) in 1972. What is the Day...
Society is a type of harmonious ecological relationship between animals, which involves the organization of individuals of the same species, division of labor and cooperation between them. It is very common...
The Triassic Period, in geological time, is the first period of the Mesozoic Era and began 252 million years ago, at the end of the Permian Period. This period ended at 201 million years, being...
Meteorites are chunks of rock and metal from asteroids and other planetary bodies that survive their journey through the atmosphere and fall to Earth's ground. The Space Agency observations...
The volcano is one of the geological structures which represent a type of mountain, usually cone-shaped, which has an opening in the earth's crust. The process of volcanism, arising from...
Chagas disease is a disease caused by a protozoan. It is transmitted through the feces of the insect, a type of bed bug, which contains the parasite. Painting of Triatoma brasiliensis, a species...
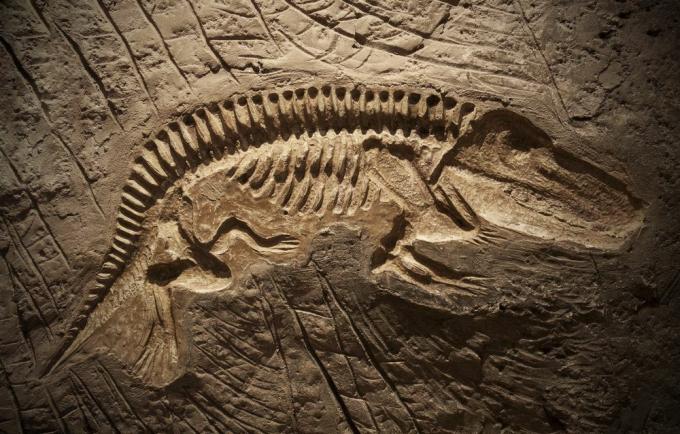
Fossilization represents the various processes of transformation of very old remains or remains, called fossils. Fossils can be of plant or animal origin, for example,...
Competition is a disharmonious or negative ecological relationship, in which the interaction occurs between individuals looking for the same resource, usually when there is a shortage of this resource...