Carboxylic acids are compounds that have a carboxyl group at the beginning or end of the molecule.
The carboxyl is represented by COOH and represents the union of the carbonyl group (C=O) and the hydroxyl (OH).

Nomenclature
The nomenclature of acids follows the following order:
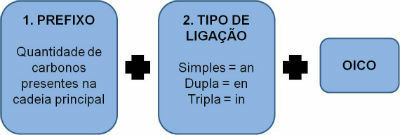
Initially, you must write the prefix, considering the number of carbons in the chain. After that, it is necessary to check the existing links and give them the correct name. Finally, the term oic is added.
The chain's unsaturations and branches must be numbered.
The numbering always starts from the end closest to the functional group, in this case the carboxyl group.
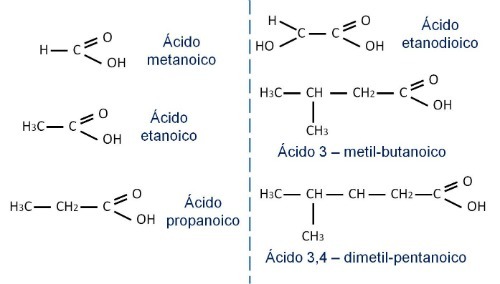
Check out some carboxylic acid nomenclatures:
Know more:
- Organic Functions
- Oxygenated Functions
- Organic chemistry
Examples
The two best known carboxylic acids are methanoic acid and ethanoic acid.
methaneic acid
Methanic acid or formic acid received this name because it was first extracted from the distillation of ants. The acid is injected by the red ants and causes itching and swelling at the bitten site.
It is a colorless, liquid, and strong-smelling acid.
Methanic acid can be obtained from the reaction of carbon monoxide and caustic soda.
A feature that differentiates them from other carboxylic acids is the presence of the aldehyde functional group. As a result, it can be easily oxidized, releasing carbon dioxide and water.
Ethanoic acid
O ethanoic acid or acetic acid is the main component of vinegar.
It is a colorless liquid, with a strong smell and a sour taste.
In addition to food use, acetic acid is also used in industries to produce substances that compose paints, solvents and dyes.
carboxylic acid salts
The carboxylic acid reacts with bases, producing the salts of carboxylic acids and water. The name of this reaction is salification.
In the presence of water, these salts suffer hydrolysis and they can regenerate the carboxylic acid and base that gave rise to them.
Carboxylic acid salts are used to make soaps.
Discover other oxygenated organic functions:
- alcohols
- Aldehydes
- Ketones
- esters
- ethers
- Phenol