We live on the planet called Earth, also known as the world, and as far as we know, it is the only planet habitable of Solar system. Also known as "water planet", the Earth has very peculiar features when compared to other planets. Your position in relation to the Sun it is one of the main reasons for the existence of life and for the existence of water in its three physical states, and therefore we need to understand its place in the Universe.
Knowing the Earth is the beginning of knowing the origin of life, and understanding its structure is fundamental to understanding the dynamics of the planet, whether in its atmosphere, whether in the own Earth's crust.
Read too: Gas Planets of the Solar System: What Are They and How Are They Formed?
Planet Earth Data
Denominations: Earth, world, water planet or blue planet
Diameter: approximately 12,756.2 km
Surface area: approximately 510,072,000 km2
Mass: 5.9736 x 1024 kg
Distance from the Sun: about 149,600,000 km
Natural Satellite: Moon
Rotation period: 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds
Translation period: 365 days 5 hours and 48 minutes
Average temperature: 14°C
Land population: approximately 7,722,522,000 inhabitants
Features
Planet Earth is one of the four rocky planets that make up the Solar System, located in the Milky Way. By saying that he is a rocky planet, we are basically talking about your composition, its solid surface is formed byrocks and heavy metals, like iron. The rocky composition and the presence of heavy metals make the planet of this type present larger density. Therefore, the Earth is closer to the Sun when compared to gaseous planets.
We do not inhabit it by chance. The Earth's location in the Universe makes it possible for there to be Waterin its three physical states: liquid, solid and gas, as well as influences the presence of gases that collaborate so that its average temperature is maintained around the 14°C.
Let's understand a little bit about the Earth's atmosphere? Basically, it is composed of oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor and carbon dioxide. This is one of the main culprits for a natural phenomenon known as greenhouse effect, which allows the existence of life on the planet.
You gases present in the atmosphere, especially the carbon dioxide, have the ability to absorb the sun's rays emitted to the earth's surface. Once these are absorbed, this prevents the heat from being fully radiated back into space. The portion of absorbed solar energy is then retained in the atmosphere, allowing for a energy balance and avoiding a big thermal range (difference between the maximum temperature and the minimum temperature). So the planet can keep temperatures that allow the existence of life, unlike other planets that are in the Solar System.
The living beings that inhabit the Earth take from it everything they need to survive. You natural resources, renewable or not renovable, allow humans, animals and plants to stay alive. Throughout history, adaptation mechanisms were developed so that these resources could be harnessed. However, their excessive and irrational use has caused great damage to the planet.
The environment has been constantly degraded, compromising the lives of future generations. The search for a model of sustainable development is one of the main topics of discussion in all regions of the Earth.
→ Earth's internal structure
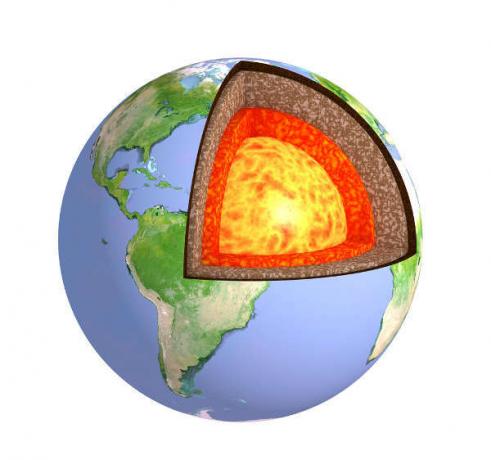
The Earth is divided into three layers: Earth's crust, mantle and core.
planet earth has shape of a sphere, presenting the regions of the poles a little flattened. This rounded shape is possible because the planet has enough mass for its gravity to exert the form of static equilibrium. In your interior, the planet has some divisions, better known asEarth layers. See what they are:
Core |
cloak |
Earth's crust |
The core is the innermost part of the planet as well as the hottest layer. Temperatures can reach 6000°C in the inner core and around 4000°C in the outer core. Its composition has the presence of iron, nickel and silicon, which remain solid (despite the high temperatures) due to the great pressure exerted on it. |
The mantle is the layer that lies above the core and below the earth's crust, therefore, an intermediate layer. Unlike the core, the mantle has pasty material, known as magmatic material. Temperatures in this region can reach 2,000 °C, and this region is also composed of iron, nickel and silicon. Magmatic material moves in what is known as convection currents. These are responsible for the movement of tectonic plates, which form the earth's lithosphere. |
The Earth's crust is the outermost part of the Earth. It lies on the mantle and is about 10 km under the oceans and between 25 km and 100 km under the continents. The earth's crust is also called the lithosphere. It is made up of minerals such as iron, magnesium and aluminum, as well as rocks. Formerly, it was believed that the lithosphere was an unbroken block of rocks, a theory that was overturned by the Plate Tectonics Theory. The earth's crust is therefore divided into several rocky plates, known as plates tectonics, which move and act on the dynamics of the earth's surface. |
See too: Why do tectonic plates move?
→ Earth's outer structure
The Earth is made up of outer layers that are intrinsically linked to the planet dynamics. Our planet is alive not only biologically but is constantly moving geologically and physically. There are three important components of your external structure:
Atmosphere |
Biosphere |
Hydrosphere |
The atmosphere is the gaseous layer that surrounds the Earth. The main gases present in this layer are oxygen, nitrogen and carbon dioxide. Its main functions are: to maintain the Earth's average temperature and prevent rock fragments from space from reaching its surface. |
The biosphere is the layer of life on Earth, corresponding, therefore, to all ecosystems on the planet, considering not only living beings but also the entire environment inhabited by them. It is one of the most complex layers, as it results from various biological, chemical and physical phenomena. |
The hydrosphere is the Earth's layer that comprises all the liquid part, such as oceans, seas and continental waters (rivers, lakes and underground reserves). This layer is extremely important for the maintenance of life, as we are not able to survive without water. |
Know more:Why do volcanoes erupt?
How did Planet Earth originate?
The planets, as well as the Earth, originated billions of years ago, yet their formation and that of the Solar System is controversial. No theory in this sense has been 100% accepted by astronomy. The most convincing was drawn up in 1644 by René Descartes, and became known as Solar Nebula Theory.
Thattheory, reformulated in 1796 by Pierre-Simon de Laplace, believes that the origin of the sun and planets is due to collapse of a cloud, which, when rotating at great speed, ended up contracting and “exploding”. In the explosion, the higher density central concentration gave rise to the Sun. The remaining particles from the center, and which spread out, then gave rise to the planets.
At denser particles, with less volatile substances, they became more close to the sun, forming then the rocky planets. Already the most volatile substances were dragged tofurther away, forming the gaseous planets.
Know more: What is panspermia?
Planet Earth in the Universe
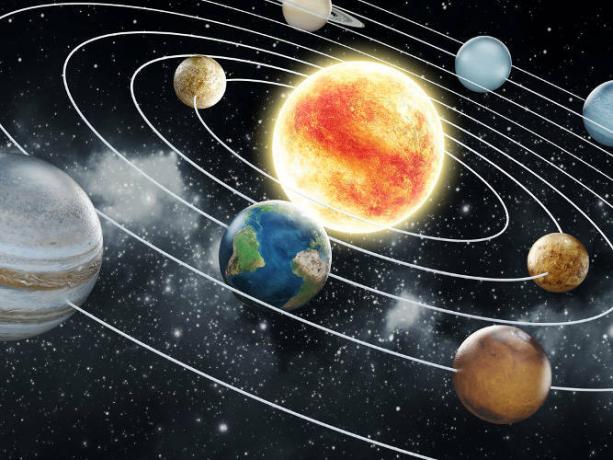
Planet Earth makes up the Solar System along with seven other planets, all of which are classified as rocky or gaseous.
In relation to the Sun, planet Earth is the third in distancing. Prior to it are Mercury and Venus, and posterior to it are Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Between rocky or terrestrial planets, the Earth is the biggest one, both in density and in diameter.
The planet has a natural satellite, theMoon, possibly formed due to the collision between the planet and another celestial body. THE rotation of the satellite is synchronized with that of the planet, and its existence is associated with the tides (changes in sea level).
The Earth is not a celestial body of its own light and it is not static. The planet is constantly carrying out various movements, such as:
Rotation: it is the movement performed by the Earth around its own axis, and is responsible for the existence of day and night.
Translation: is the movement performed by the Earth around the Sun, and is responsible for the existence of the seasons.
Precession: is the movement in which there is displacement of the Earth's axis.
Nutation: is the oscillating motion of the Earth's axis with respect to the average position of its orbit.
Lookalso: Earth Movements: Characteristics and Effects
Curiosities about planet Earth
The circumference of the Earth was calculated by Eratosthenes over two thousand years ago. Eratosthenes was an ancient Greek geographer, mathematician, grammarian, poet and astronomer.
The Earth's rotational motion has been decreasing by approximately 17 milliseconds every 100 years. Although practically imperceptible, in the long term, this decrease will lead to an increase in the length of the day.
The movement of the tectonic plates that form the earth's crust causes phenomena such as earthquakes and tsunamis, and is also related to the existence of volcanoes.
In a year, there are about 50,000 earthquakes on Earth, of which approximately 100 are capable of causing great damage.
According to the American Air Force, about 2,783 satellites currently orbit the Earth.
Take the opportunity to check out our video lesson on the subject:
