porifers (Phylum Porifera) are invertebrates who live exclusively in the aquatic environment. As the name of the phylum indicates, they have a body full of pores, where the water enters the body of the animal.
the porifers, also called sponges, are filter feeders, extracting from the water the nutrients necessary for their survival. Currently, about 8000 species of sponges are known, which occur both in the marine environment and at the freshwater and feature a rich variety of colors, shapes and sizes.
Read too: Molluscs - animals that have a soft body
Porifera characteristics
Porifers (Latin: porus= pore and iron= possessor) are invertebrate animals, aquatic and who have a body full of small pores. Also known as sponges, these animals live fixed in the substrate, thus not showing any type of movement. Porifers can be found alone or forming colonies and live mainly in a marine environment, but there are also freshwater sponges.
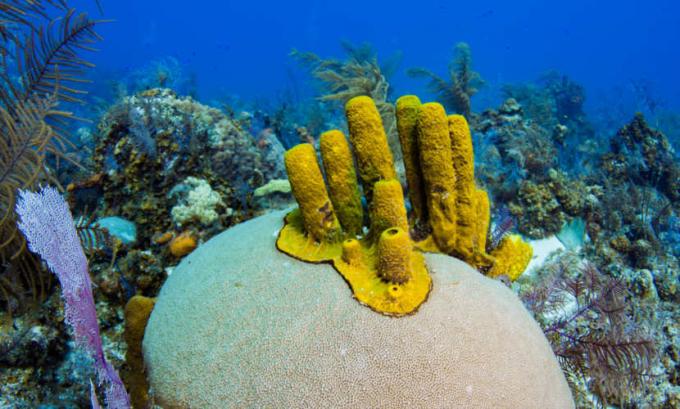

THE organization of the poriferous body is very simple, not being observed the presence of organs or systems. They usually have a cylindrical body with a central cavity, called the spongiocele or atrium, and an opening located at the top of the animal, called the kiss.
The sponge body wall is formed by two layers of cells which are separated by the mesoyl. The outer surface (pinacoderm) is formed by flat cells called pinacocytes, where the cells called porocytes, which form the pores, which allow water to enter the animal's body and reach the atrium.
The innermost layer of the sponge's body wall faces the atrium. In this layer, the so-called choanocytes or collar cells, flagellated cells that play the role of capturing food. These cells, when hitting their scourges, create a stream of water and, using their collar, capture food particles, which are engulfed by phagocytosis.

O mesoyl, in turn, is a layer of the sponge wall that has a gelatinous consistency and where the skeletal material and cells known as amoebocytes, which are cells with various functions, among which we can mention:
transport of nutrients to other cells,
gamete formation,
secretion of skeletal material.
The skeletal material of some sponges consists of flexible fibers made from spongine, and in others, in spikes which can be formed from silica or limestone.
Physiology of sponges
Sponges have no systems, so many of their physiological processes are relatively simple.
→ Digestion: it is of the intracellular type, that is, it occurs inside the cells. They get their food through filtration, removing food particles that are in the water that enters your body through your pores.
→ exchangesgaseous: are performed through diffusion in the cells of the animal's body.
→ Excretion:It also occurs in every cell, with metabolic waste being released into the water.
Read too: Cnidarians - animals with the body a little more complex than the porifers
How do porifers reproduce?
Porifers reproduce both asexually and sexually. THE asexual reproduction can occur in different ways and can be observed, for example, when small fragments of sponges are broken and give rise to a new individual by regeneration. We can also observe the reproduction by budding, in which a small sprout appears in the animal's body, later detaching itself and giving rise to a new individual. In some cases, this sprout may remain attached to the organism that generated it.
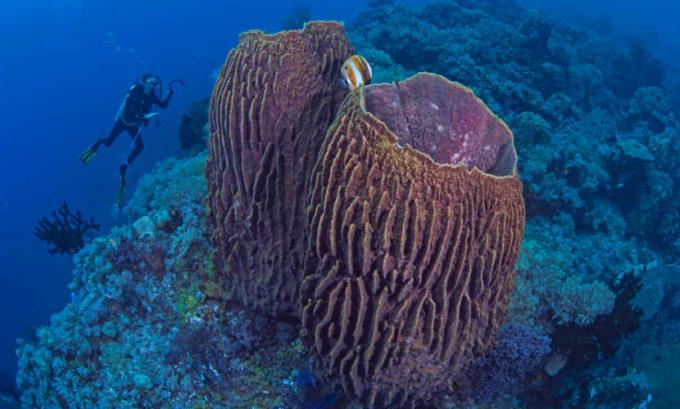

THE repsexual productionit is also seen in these animals. In sponges, there are no structures responsible for the production of gametes. These cells are formed from choanocytes and amoebocytes. The male gamete is released into the water and reach the female gametes, which are usually retained within the body of the sponge. Fertilization then occurs, giving rise to a flagellate larva that has the ability to move. This larva is carried by the currents, until it fixes itself in the substrate, originating a new sponge.
It is worth noting that most sponges are hermaphrodite, therefore presenting both sexes. However, they exhibit sequential hermaphroditism, presenting themselves initially as one sex and later as another.
The importance of sponges
Sponges are as important for the environment as for man. In the environment, they are important for establishing relationships with microorganisms and per participate in food chain. They are also used as shelter by various aquatic species.
For man, sponges are also very important. In the past, they were widely used as bath sponges. Today, however, one of its main uses is in pharmaceutical industry due to the presence of compounds that can be used as medicines.