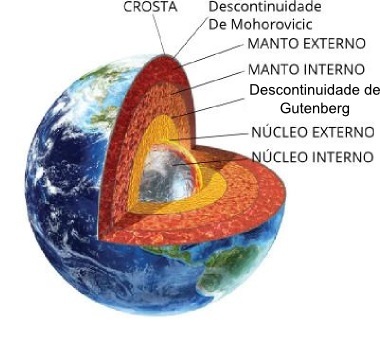
THE Earth is divided into three layers — crust, mantle and core — thanks to transformations that have taken place over billions of years. These layers act interdependently with each other, and changes in one affect the others, demonstrating that our planet is not a single, static block of rock.
Read too: Rocky Planets - Planets formed mainly by rocks and metals
What are the Earth's layers?
For scholars in the field (geologists and related scientists), the Earth it has several layers from the surface to its deepest interior. However, for didactic purposes, the division crust-mantle-core it is the most accepted and widespread, and it is also the easiest to understand. From this classical division, subdivisions can occur, such as terrestrial and oceanic crust, lower and upper mantle, inner and outer core.
Let's look at the main features of the Earth's layers.

Crust
The crust is the Earth's surface layer, also known as lithosphere. It is known for being the rock layer where we step and carry out our daily activities. It houses the
biomes, animals, mountain ranges, among others, being the most important for humans.It can be subdivided into:
Earth's crust;
oceanic crust.
The first can be called the continental crust, being the area of occurrence of continents and the oldest, with rocky blocks that are more than 3.5 billion years old. Its thickness varies between 5 and 80 kilometers, with a high concentration of silicon and aluminum (sial).
Already the oceanic crust is "thinner" than the previous and more recent. The thickness varies from 5 to 15 kilometers, being the place of seas and oceans. Its composition houses silicon and magnesium (sima) and all the biodiversity navy.
cloak
The cloak is considered to intermediate layer between the crust and the core, with a thickness between 100 and 2900 kilometers. Like the crust, it also has subdivisions, namely:
upper mantle;
lower mantle.
The upper mantle is located below the lithosphere, at a depth that reaches 700 kilometers. It is in this layer that we find the slimy part of the earth structure, known as magma, which can reach 2000 ºC. Its viscosity is responsible for the movement (floating) of the tectonic plates in the lithosphere, which results in the appearance of:
mountain ranges;
volcanic eruptions;
earthquakes;
tsunamis; etc.

The lower mantle is located between 700 and 2900 kilometers deep, close to the planet's core. It is estimated to be solid, composed of iron, magnesium and silicon silicate.
See too: Why do volcanoes erupt?
Core
THE Earth's innermost layer it is subdivided into outer and inner core. The depth ranges from 2900 to 6700 kilometers. Studies show that this layer is basically composed of nickel and iron (nife), with temperatures that can reach 5000 ºC.
The outer core is liquid (viscous) and surrounds the inner core, which is solid. Both are responsible for the Earth's magnetic field, which helps us direct the Cardinal points on compasses, for example.
To understand the high temperatures in the planet's inner layers, it is necessary to consider the geothermal degree. According to this degree, every 30 meters of depth, it is estimated that the temperature increases by 1 ºC.
solved exercises
Question 1 (PUC-MG) - The plate tectonics theory explains how the Earth's internal dynamics are responsible for the structure of the lithosphere, and it is INCORRECT to state that:
A) the lithosphere is the rigid part that makes up the earth's crust and is segmented into plates that float in various directions over the mantle.
B) the movement of the plates can be convergent or divergent, bringing them closer or further apart, or even sliding them in relation to each other.
C) tectonics is responsible for phenomena such as the formation of mountain ranges, drift from continents, expansion of the ocean floor, volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
D) continental and oceanic plates have a similar basic mineralogical composition, since these plates make up the earth's crust.
Resolution
Alternative D. Oceanic plates make up the oceanic crust and have a different composition from continental plates.
Question 2 (Unesc 2019) – With the development of the theory of plate tectonics, phenomena such as the formation of mountain ranges and submarine trenches were better understood. Thus, it is known that the Andes Mountains is located in a region of the earth's crust that
A) coincides with divergent tectonic plate boundaries.
B) is located in an area of expansion of the ocean floor.
C) presents an area failed by the formation of an oceanic ridge.
D) presents an area of collision of tectonic plates.
Resolution
Alternative D. All mountain ranges on the planet are in tectonic plate collision areas.