You molluscs they are animals invertebrates that have a soft body, which in some species, is protected by a shell. They are found in both terrestrial and aquatic environments, being more abundant in the marine environment. Currently, the phylum has more than 100,000 known species, being considered the second most diversified, only behind the arthropods. They are representatives of animal molluscs such as O octopus, the mussel and the snail.
Read more: Invertebrates - general characteristics, habitat and curiosities
General characteristics of molluscs
molluscs (Phylum mollusk)they are animals that have a soft body, which, in most representatives, is protected by a shell. Some species, such as slugs and octopuses, do not have shells. In squid, in turn, the shell is reduced and presents itself internally in their bodies.
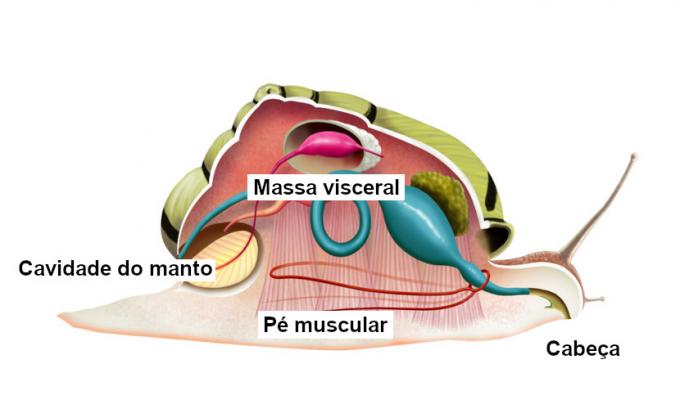
The molluscs have a body formed by three parts main:
Muscle foot: as the name implies, it is a muscular structure that helps the animal in its locomotion.
Visceral mass: it is the region of the animal's body where most of its internal organs are located.
Cloak: it is a fold of tissue that covers the visceral mass and is responsible for secreting the shell in animals that have it. It also forms a kind of chamber, called the mantle cavity, where the gills, anus and openings of Organs excretory organs are located.
Physiology of molluscs
Next, we will better understand the physiology of molluscs by knowing a little about the systems found in them.
Digestive system
The digestive system of molluscs is complete, therefore having mouth and anus. In some groups of the phylum, the presence of a structure called radula, which works as a kind of scraper tongue. Feeding varies, being observed, for example, species that feed on suspended material, species herbivores and carnivorous species.

Circulatory system
in the majority of molluscs, the circulatory system is open, that is, the hemolymph runs in the vessels, although ends up in some gaps in the animal's body. In cephalopods, the hemolymph runs exclusively inside vessels, therefore, we say that this group of molluscs has a closed circulatory system. It is noteworthy that molluscs have a heart that works in pumping the hemolymph.
Respiratory system
The respiration of molluscs is different in each group. In aquatic species, breathing by gills is observed. In terrestrial ones, the mantle cavity works as a rudimentary lung which guarantees gas exchange. In some species, breathing skin is observed.
Read too: Animal breathing - cutaneous, tracheal, phylotracheal and pulmonary
excretory system
a structure that plays a role similar to that of the kidneys.metanephrids,The excretion in molluscs is done by
Nervous and sensory system

Molluscs have a nervous system developed, with its fundamental plane consisting of a nerve ring around the esophagus, from which nerve cords depart.
The molluscs present sensory organs that vary from one species to another. Some of the typical sensory organs are the eyes and the tentacles.
Reproduction of molluscs
The molluscs present, mostly separate sexes, with the gamete-producing organs (gonads) located in the visceral mass. There are, however, hermaphrodite species, as is the case with some snails. THE fertilization can be external or internal depending on the species analyzed. In some species, the indirect development, which means that there is the presence of a larval stage in its life cycle.
Read more: African Giant Snail - a species that has spread throughout Brazil and can cause diseases
classification of molluscs
Molluscs are classified into different groups, however, our focus will be on the three main groups: gastropod, bivalvia and cephalopod.

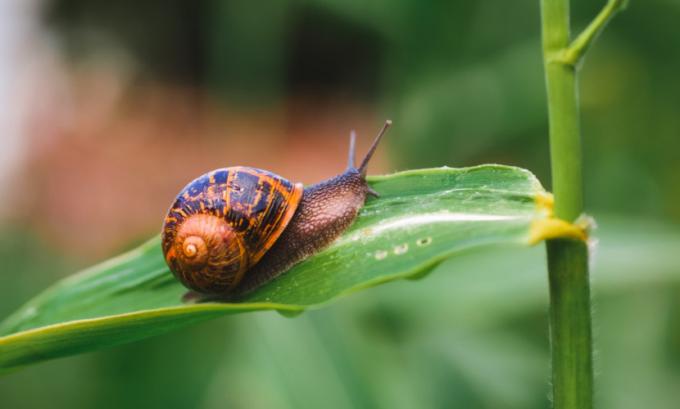
Gastropoda (gastropods): represent the largest group of molluscs, with species occurring in the marine, freshwater and terrestrial environment. They stand out for having a single spiral shell, in which the animal can hide when it feels threatened. In some species, the shell, however, is not present, this being the case with slugs. The radula is generally used to feed these animals, being used as a scraper, a cutter, a brush, among other ways. Slugs, snails and snails are part of this group.
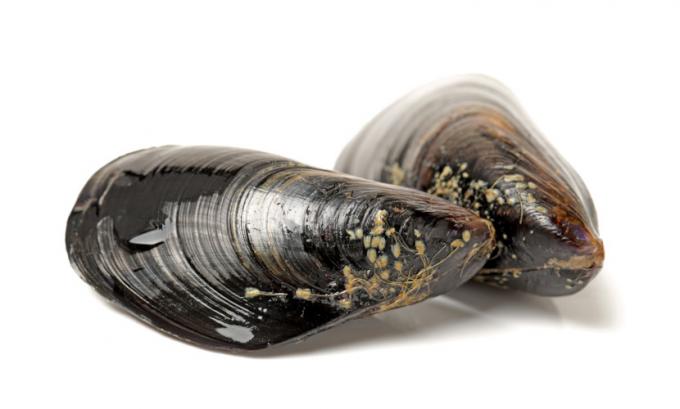
bivalvia (bivalves): they are exclusively aquatic molluscs. As the name implies, bivalves have a shell formed by two articulated halves. Powerful muscles ensure the halves remain closed. In these animals, the gills present in the mantle cavity help both in gas exchange and in feeding. This structure participates in food because it contains mucus, which coats it and ensures that particles are captured. The water enters the bivalve's body through a siphon, passes through the gills and leaves the animal's body through another siphon. Shellfish, mussels, oysters and scallops are part of this group.
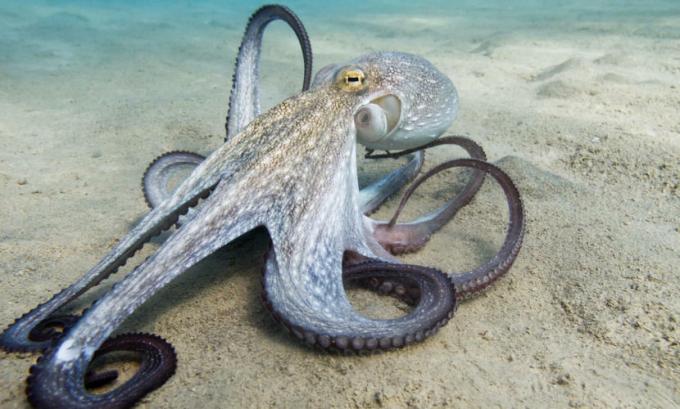
Cephalopod (cephalopods): are marine molluscs that have tentacles that depart from their head. These animals use their tentacles to get their food and also to move. Squids are cephalopods that move by releasing a stream of water through a siphon. Octopuses, in turn, have a crawling habit, using a mechanism similar to that of squid to escape predators. In addition, these animals are able to cast paint that darkens the water and makes it difficult for the predator to see. In cephalopods, the shells, in general, are reduced or absent. In octopuses, for example, the shells are not present, while in squid they are internal and tiny. The nautilus, on the other hand, has an external shell. To learn more about these groups, read: classification of molluscs.



