The human body is a complex structure that allows us to carry out a number of important activities. We can walk, run, remember past events, eat, remove oxygen from the atmosphere, think, among many other activities, all thanks to the various cells, tissues, organs and systems that make up the body. human.
→ Levels of organization of the human body
We know that all animals, including humans, are multicellular, that is, they have more than one cell forming their body. These cells have different shapes and functions and form different tissues, organs and systems. When we consider cells as the first level to be studied, we have the following organization level:
cell → tissue → organ → system → organism |
Let's get to know each of these levels better:
Cells: they are the functional and structural units of most living things, with the exception of viruses. In the human body, as we know, several cells are found, as we are multicellular beings. The cells that make up our body have a membrane-bounded nucleus and also membranous organelles. eukaryotes.
Fabrics: they are formed by similar cells that perform the same function. In humans, we observe four basic types of tissue: epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue.
Bodies: they are formed by groupings of tissues that act together to perform a certain task. The heart, stomach, lungs, kidneys, esophagus, liver and spleen are some examples of organs.
Systems: they are formed by bodies that work together to perform a function. As an example of systems, we can mention the cardiovascular, the digestive, the endocrine, the reproductive, the urinary and the nervous systems.

To better understand these levels, let us imagine a muscle tissue cell (myocyte), which is joined to others to form cardiac muscle tissue. This tissue forms our heart, an organ that is part of the cardiovascular system. In this case, we have:
myocyte → cardiac striated muscle tissue → heart → cardiovascular system
Read too: Is the skin a tissue or an organ?
→ human body cells
The human body is made up of trillions of cells, each one performing a certain function. See some examples of cells and the role they play in our bodies.
adipocytes: cells that store lipids (fat).
Schwann Cells: responsible for the formation of the myelin sheath of neurons.
beta cells: cells in the pancreas that are responsible for producing insulin, a hormone related to blood glucose levels.
Sperm: male gametes.
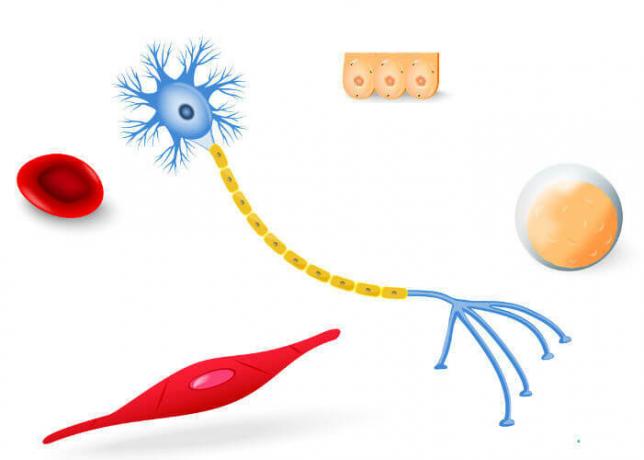
Note that the human body has different cell types.
Red blood cells, erythrocytes or red blood cells: blood cells that transport oxygen throughout the body. These are the cells found in the greatest quantity in the blood.
Hepatocytes: liver cells that synthesize proteins and bile, in addition to acting in the detoxification of various substances.
Leukocytes or white blood cells: blood cells responsible for the body's defense. There are several types of leukocytes, such as neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes and monocytes.
Myocytes or muscle fibers: cells that make up muscles.
Neurons: Nerve tissue cells that ensure the transmission of nerve impulses.
oocyte: female gamete that is also popularly known as ovum.
→ human body tissue
In the human body we find four basic types of tissue, which have their subtypes. Follow:
Read too: human body tissue
Epithelial tissue: tissue that is characterized by the presence of cells that are very close to each other, consequently presenting little substance between them (little extracellular matrix). This tissue can be divided into two basic types: lining epithelial tissue and glandular epithelial tissue.
Connective tissue: its most striking feature is the presence of a large amount of extracellular matrix. This is the type of tissue that has the greatest number of subtypes, namely:
- Connective tissue itself;
Adipose tissue;
Bone tissue;
Cartilaginous tissue;
Blood tissue.
Muscle tissue: presents cells with the ability to contract. Muscle tissue can be classified into three different types: non-striated or smooth muscle, skeletal striated muscle, and cardiac striated muscle.
Nerve tissue:it has cells capable of interpreting and transmitting nerve impulses. It is this tissue, therefore, that manages to capture information from the external and internal environment and generate responses.
Read too:Skeleton and Muscles
→ Organs of the human body
Our body has several organs, which are formed by sets of tissues. These bodies are responsible for various functions and are grouped together to form the systems. Here are some of the most important organs in our body and the role they play in our bodies.
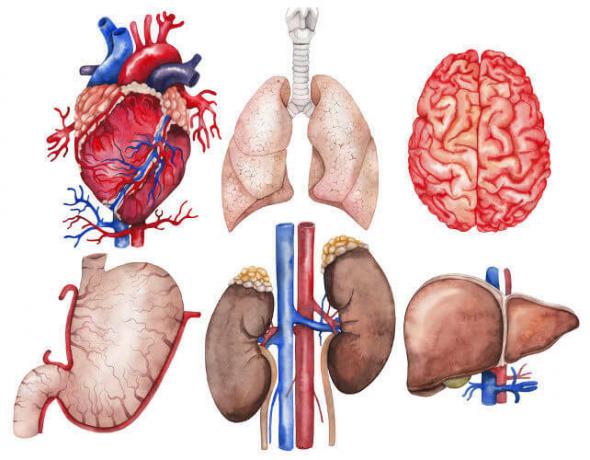
The human body has several organs, which are formed by sets of tissues.
Bladder: Urinary system organ that stores urine.
Heart: it is, without a doubt, one of the most important organs in our body, being responsible for boosting blood throughout the human body. As the blood has oxygen and nutrients, the heart makes sure that these elements reach every cell.
Stomach: it is an organ of the digestive system and therefore is related to the digestion of food. It produces gastric juice, which transforms the bolus of food into chyme.
Small intestine: where the end of the digestion process and the absorption of a large part of the nutrients takes place.
Large intestine: where water absorption and stool formation occurs.
Larynx: organ of the respiratory system that stands out for the presence of the so-called vocal folds.
Ovaries: organs found only in women and where female gametes and female sex hormones are produced.
Lungs: they have a spongy appearance and are related to oxygen uptake.
Kidneys: organs of the urinary system where urine is produced.
Testicle: organs found only in men and where male gametes and male sex hormones are produced.
→ human body systems
The human body is formed by a series of systems, which act in the most varied functions. Here are some of the main systems in the human body.

The systems of the human body are made up of sets of organs.
Cardiovascular: it is formed by the heart and blood vessels and is responsible for the circulation of blood throughout the body.
Digestive:it is formed by the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and attached glands. It is responsible for breaking down food into smaller particles.
Endocrine:it is the system formed by all the endocrine glands in the body, which are responsible for the production of hormones.
Skeletal: it is formed by the bones and guarantees, among other functions, the support of the body and the protection of Organs internal organs.
Excretor: also called the urinary system, it is formed by the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. It is responsible for the production and elimination of urine.
Muscle: it is made up of all the muscles in the body.
Nervous: it is responsible for allowing the capture of internal and external stimuli and generating responses to these stimuli.
Breeder:it is the system responsible for reproduction.
Respiratory: it is formed by the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and lungs. Ensures oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide elimination.
Integument: it is formed by the skin, hair, nails and glands. It performs various functions such as covering and protecting the body.

