O skeletal system it is made up of the bones and cartilage, which form the skeleton. This system is responsible for important functions such as support and locomotion.
the human skeleton has 206 bones, which vary in size and shape. The skeleton of fetuses is initially formed by cartilage, which is gradually replaced, giving space to the bones. In adults, cartilage is found in places where elasticity is important, such as the rib-to-sternum connections and joints.
Read too: How is blood produced?
Human skeleton
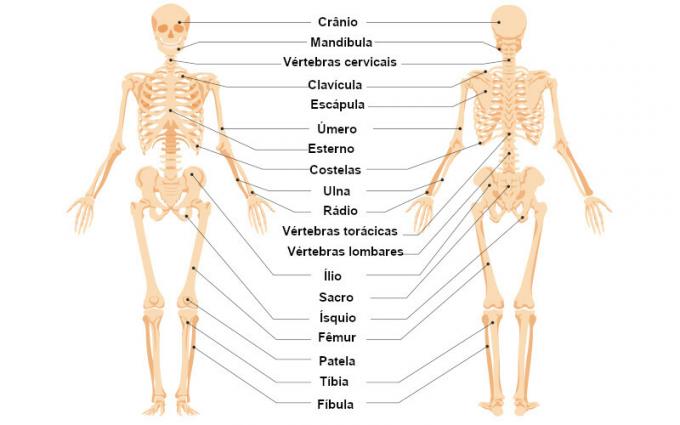
the human skeleton is formed by 206 bones, which are joined by the joints. In children, the number of bones is greater than in adults, with more than 300 bones being observed. Bones, however, do not disappear, and this reduction is observed as a consequence of fusion of certain bones.
The bones are made up of bone tissue, a type of connective tissue that, contrary to what many people think, is a living element. This fabric is formed by specialized cells
and a calcified extracellular material, which is called bone matrix. It is this matrix that makes the bone very resistant.The cells that make up bone tissue are:
- osteocytes,
- osteoblasts,
- osteoclasts.
You osteocytes they are cells that occupy gaps within the bone matrix and act to maintain the bone matrix. You osteoblasts are responsible for the production of the organic part of the bone matrix. already the osteoclasts are related to the bone remodeling process, promoting the resorption of bone tissue.
In our skeleton, we find bones with different shapes and sizes. According to their shapes, we can classify the bones into:

- long bones: bones that are longer than wide. In this type of bone, we can see distinct parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the central part of the bone, and the epiphysis is the tip. Therefore, each long bone has a diaphysis and two epiphysis. Examples: tibia and femur.
- short bones: bones that have a width proportional to their length, not presenting any dimension that stands out from the others. Examples: tarsal bones and carpal bones.
- Flat bones: are bones that are greater in width and length than thickness, giving the appearance of a blade. Examples: skull and sternum bones.
- Irregular bones: they are bones that do not fit the other classifications, not having a very defined shape. Examples: vertebrae and jaw.
Axial and appendicular skeleton
The human skeleton can be divided into two parts: the axial and appendicular skeleton.

- Axial skeleton: consisting of the skull, vertebrae, ribs and the sternum. The vertebrae form our spine, while the ribs and sternum form our rib cage. In total, we have 80 bones forming the axial skeleton.
- Appendicular skeleton: consisting of bones of the upper and lower limbs and also of the scapular and pelvic girdle. The shoulder girdle is formed by the collarbone and scapula, and the pelvic girdle is formed by the hip bones. These girdles promote the union of the limbs to the axial skeleton, the scapular being responsible for uniting the upper limbs, and the pelvic girdle responsible for uniting the lower limbs. In total, we have 126 bones forming the appendicular skeleton.
Read too: Names of theupper and lower limb bones
joints
THE region where two or more bones meet is called articulation. The joints may or may not allow movement in this region. According to the ability to move, we can classify the joints into:

- Mobile joints: as the name suggests, they allow movement of the bones. In mobile joints, there is cartilage and a capsule that contains a fluid called synovial fluid. Cartilage works by preventing friction, and the liquid works as a lubricant, thus ensuring less wear and tear caused by constant movement. Movable joints can be seen in the knee and between the pelvic girdle and femur, for example.
- Semi-mobile joints: have limited bone movement. This type of joint can be seen in the vertebrae.
- Real estate joints: as the name suggests, there is no movement between the bones. The immobile joints can be seen in the bones that make up our skull. It is noteworthy that the only mobile bone in our head is the jaw, and this movement is essential in the chewing process.
Read too: Is the tooth a type of bone?
Importance of the skeletal system
Our skeletal system plays an important role in our body, being fundamental to our support, locomotion and protection of internal organs. With regard to protection, we must highlight the role of the skull in protecting our brain, from spine in protecting the spinal cord and the rib cage in protecting the lungs and heart.
In addition to the aforementioned functions, the skeleton works as a important calcium reservoir, and the bone marrow, located inside the bones, has the function of produce the blood cells.
Exercise solved
Now that you've learned a little more about the locomotor system, let's test your knowledge of the topic. Mark V for true alternatives and F for false alternatives.
a) ( ) Bone tissue is dead tissue.
b) ( ) The human skeleton has 200 bones in the adult individual.
c) ( ) An example of a long bone is the femur.
d) ( ) The skull is part of the axial skeleton.
e) ( ) The appendicular skeleton includes our lower and upper limbs and the pelvic and shoulder girdles.
e) ( ) Bones help protect the internal organs.
f) ( ) The articulations of the bones of the skull are all mobile.
g) ( ) Vertebrae are irregular bones.
Resolution
a) (F) This alternative is incorrect, as bone tissue is living tissue.
b) (F) This alternative is incorrect, as the human skeleton has 206 bones in the adult individual.
c) (V) An example of a long bone is the femur.
d) (V) The skull is part of the axial skeleton.
e) (V) The appendicular skeleton includes our lower and upper limbs and the pelvic and shoulder girdles.
e) (V) Bones help protect the internal organs.
f) (F) This alternative is incorrect, as the articulations of the bones of the skull are immobile, the mandible being the only mobile bone.
g) (V) Vertebrae are irregular bones.



