O locomotive system is responsible for our locomotion, being constituted by the skeleton and by the muscles skeletal. This system is therefore made up of two systems: the skeletal system and the muscular system. Problems that affect them negatively impact our lives, triggering, for example, pain and difficulty in carrying out our daily activities.
Read too: Is the tooth a type of bone?
locomotive system
The locomotor system is made up of two components: o skeletal system it's the muscular system. These two systems work together, as the bones serve as an attachment site for the skeletal musculature of our body. Next, we'll know a little more about them:

skeletal system
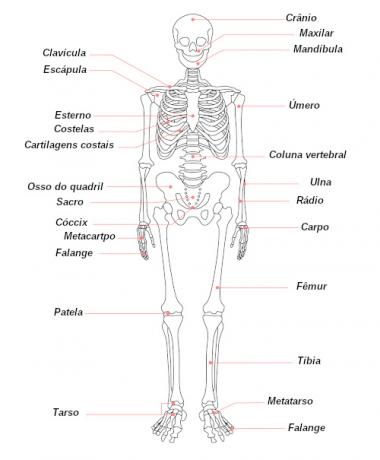
The skeletal system is formed by the human skeleton, which is composed of 206 bones. At the end of bones called long, we can also observe the presence of cartilage. The human skeleton can be divided into two regions: axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton.
O
axial skeleton it consists of 80 bones and is composed of the bones that form the head, rib cage and spine. O appendicular skeleton, in turn, is formed by the 126 bones that make up the upper and lower limbs and the shoulder and pelvic girdles. The so-called shoulder girdle ensures that the upper limbs connect to the axial skeleton, while the pelvic girdle ensures the connection of the lower limbs to this skeleton. If you want to go deeper into the topic of this topic, read: skeletal system.bone classification
The bones that make up the human skeleton can be classified according to the relationship between its length, thickness and width. the bones called long are those that have a great length: an example is the femur, the largest bone in our body. We also have the bones called the short, those with little length, with similar length, width and thickness: an example is the carpal bones, which form our wrist. Finally we have the bones boring, which are thin: they can be found forming our braincase.
joints
The bones that make up our body are joined through joints. According to the degree of movement allowed by the joints, we can classify them into mobile, semi-mobile and immobile. At movable joints they allow great movement and can be found, for example, in the shoulder and knee. At properties do not allow movement and can be found forming the skull. We still have the semi-furniture, which have a movement, but it is limited; are seen in the vertebrae of the spine.
muscular system
The muscular system is formed by the muscles that make up our body. they constitute of 40% to 50% of our body weight and act in different functions, ensuring, for example, our movement as well as the passage of food through our digestive system, the passage of urine through the urinary system and our breathing.
Read too: Muscle tissue, responsible for forming our muscles
Muscle classification
Muscles can be classified into three types: striated skeletal muscle, striated cardiac muscle, and non-striated muscle. You unstriated muscles they are found in our internal organs such as blood vessels, esophagus and bladder. They present an involuntary contraction, that is, their contraction occurs independently of our will. O striated cardiac muscle is present in our heart and also presents involuntary contraction.
You skeletal striated muscles are connected to our bones. Therefore, it is they that allow our displacement. The contraction of these muscles is voluntary, that is, it happens through our command. Skeletal striated muscles are connected to bones by tendons, which are formed by connective tissue.
Most of these muscles are connected to two bones and their contraction ensures the movement of these structures. Generally they do not work alone but together to ensure movement. In our arm, for example, for flexion to occur, the biceps must contract and the triceps relax. For arm extension, we observed the opposite, being essential that the biceps relax and the triceps contract. In these cases, we say that the muscles present antagonistic movements.

Importance of the locomotive system
The locomotor system is responsible for the movement and displacement of our body. In addition, it ensures support for soft parts of the body and protection for internal organs. Our skeleton works still guaranteeing the blood cell production and serving as a place for salt storage.
Read too: 10 fun facts about the skeleton
Problems affecting the locomotor system
The locomotor system can be affected by different factors, such as inadequate posture, poor nutrition or even the practice of physical activities incorrectly. Some of the problems that affect you are:
- Postural deviations: poor posture can lead to problems such as hyperlordosis (sharp curvature in the lower back), hyperkyphosis (sharp curvature in the thoracic region, forming the famous hump), and scoliosis (lateral curvature of the column).
- Osteoporosis: this disease is characterized by loss of bone mass, which makes bones weak and more prone to fracture. It mainly affects elderly people and, more frequently, women after menopause. Low dietary calcium intake during life may be related to this disease.
- Muscle sprain: when a muscle is overstretched and muscle fibers break. Despite being common in people who play sports, it can also occur during everyday activities, when we put our muscles to great effort.
Exercise on the locomotor system
To check what you have learned about the topic, we have prepared a crossword that you will have to answer using the knowledge acquired in this text. Prepared?

Answers:
- Is the rib cage part of the axial or appendicular skeleton? Answer: Axial
- What type of joint is found between the vertebrae? Answer: Semimobile
- Is the femur a long, short or flat bone? Answer: Long
- Example of skeletal striated muscle. Answer: Biceps
- What type of contraction is seen in the striated cardiac muscle? Answer: Involuntary
- What is the name of the biggest bone in the body? Answer: Femur
- What type of joint is found in the knee? Answer: Mobile


