Have you ever tried washing dishes using only water?─ It doesn't work, does it?!Why can't water alone remove grease and dirt?That it happens because the composition of these materials is very different from the composition of water, which makes it difficult for them to mix.
We say that water molecules are polar, that is, they have parts that are charged: one part is positive and the other is negative.Fats and oils are apolar, which means that its molecules have no charge.Thus, the polar molecules of water cannot penetrate the fat molecules and drag them along. It is for this same reason that oil does not mix with water, as shown in the following figure:

Water and oil do not mix because water is polar and oil is non-polar
Another problem is that the water molecules form a kind of “skin” or “film” that makes it even more difficult for it to penetrate the dirt. This thin layer is called the water surface tension. Its formation occurs because the positive part of one water molecule attracts the negative part of another water molecule, and so on.
In this way, the molecules are very close together, especially the surface molecules, forming the film we talked about. The following illustration shows how water molecules (symbolized by the blue balls) attract each other and create surface tension:
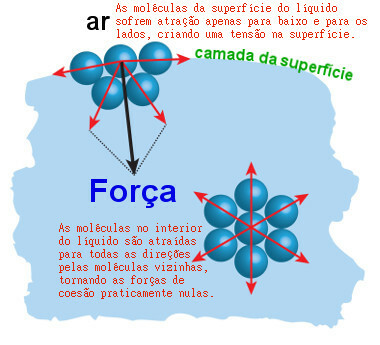
Surface tension is a "film" formed by the attraction forces between surface water molecules
Proof that water actually has this "film" is shown in the image below, in which an insect can walk on top of water:

Insect on water due to intense surface tension
So, to be able to clean the grease and dirt, we need to use soap.But how does soap work? How does it clean?
Basically, the soap is able to “break” this “film” of water, allowing it to penetrate the materials and remove the dirt. That's why soap is often called a surfactant or surfactant, because he decreases the surface tension of the water. It's as if the soap made the water “wetter”, you know?!
But how does he get it?To understand, look at the image below that shows the structure of a soap:
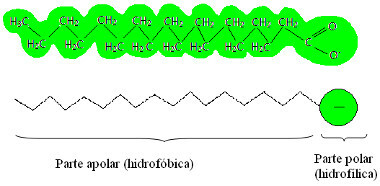
Typical structure of a soap
See that the soap has a part that is non-polar (as well as the fat and oil)and another part that is polar (just like water).In this way, the non-polar part of the soap molecule interacts with the non-polar molecules of fats and oils,and the polar part interacts with the polar molecules of water.
Soap molecules distribute themselves and form micelles, as the following figure shows:
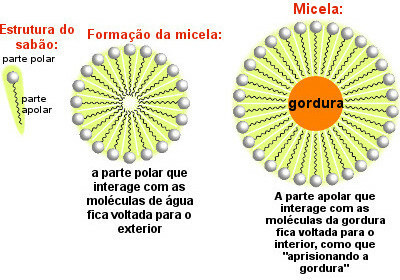
Soap Mixen Wrapping Grease
Note that the non-polar part of the soap molecules surrounds the fat particle, which is dragged along by the water that is in contact with the polar part of the soap facing outwards. Thus, the micelles formed by the soap help to remove the greasy dirt.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry