Snake is the name given to crawling reptiles, with an elongated body and no legs. In fact, calling these animals “snakes” is more correct, as “snake” in some countries is a word used only to refer to cobras, found in Africa and Asia.

Cobra: true snake.
There are, in Brazil alone, at least 370 species of snakes, of varying sizes, shapes and colors.
Contrary to what many people think, there are few species of snakes capable of causing harm to human beings. Among them, those that most arouse fear are the venomous ones.
Venomous animals are those that produce highly concentrated venom and have, in their body, a structure capable of inoculating ("injecting") this substance: the venom. In the case of venomous snakes, they have teeth with modifications that allow this to be done.
The venomous snakes in Brazil have some common characteristics that allow them to be identified and differentiated from species that do not inoculate venom, such as pythons, salamantas, anacondas, poppies and canines.
The first feature is the presence of the loreal pit, a structure that lies between the snake's eyes and nostrils.

Venomous snakes have a loreal pit (arrow).
All venomous snakes in Brazil have this structure, only the true coral that does not.
The coral snake is an easily identifiable snake, as it has a well-known color pattern, with the presence of red, black and white rings along its entire length (sometimes yellow too, usually replacing the color White). However, there are the real corals, which are venomous; and also the fake ones. All of them are very similar, being very difficult to tell them apart.

Real or fake coral snake?
Except for true corals, all other venomous snakes have a triangular head.
In addition to the triangular head, the jararaca, urutu-cruzeiro, jararacuçu, jararacão, cortiara and caiçara; have a very interesting pattern on their skin: inverted “V”-like spots (or a phone hook).

Jararaca: venomous snake.

Urutu-cruzeiro: venomous snake.
As for rattlesnakes, in addition to the triangular head, they have a kind of rattle at the end of their tail. With this structure, such a snake produces sounds, driving away its predators.

Rattlesnake.
Finally, on the surucucus and surucutingas, these snakes have a tail with spiky scales and a smooth, tapered tip.
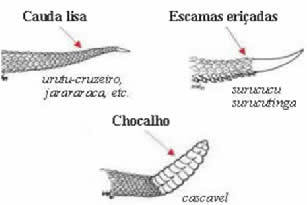
Tail of Brazil's venomous snakes.
By Mariana Araguaia
Biologist, specialist in Environmental Education
Kids School Team



