Alcohol is the name given to the oxygenated organic function (group) that has one or more hydroxyls (OH) bonded to a saturated carbon atom (only single bonds). Below we have the general structural formula of an alcohol:
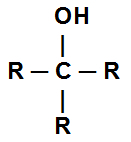
General structural formula of an alcohol
Each R can be a Hydrogen or any branch.

Cleaning products have an alcohol in their composition
An alcohol can be classified and named according to the amount and position of the hydroxyl(s) present(s) in the chain.
a) According to the number of hydroxyls that the alcohol structure presents:
Mono alcohol: alcohol that has only one hydroxyl in its structure, as in the model below:
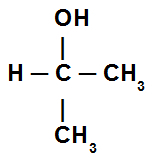
Alcohol: alcohol that has two hydroxyls in its structure, as in the model below:

Trialcohol: alcohol that has three hydroxyls in its structure, as in the model below:
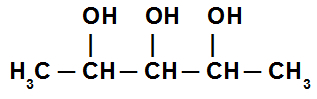
Polyalcohol: alcohol that has four or more hydroxyls in its structure, as in the model below:

b) Regarding the type of bonds existing between the carbon atoms:
Saturated alcohol: it is the alcohol that has only single bonds between the carbon atoms in the chain. See an example:
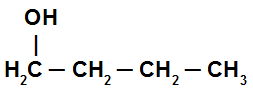
Structure of an alcohol with simple bonds between carbons
Unsaturated alcohol: is the alcohol that has at least one double bond or a triple bond between two carbon atoms in the chain, as long as none of these carbons is linked to a hydroxyl group. See an example:
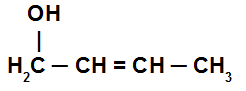
Structure of an alcohol with a double bond between carbons
c) In relation to the position of the hydroxyl in an alcohol
Primary alcohol: it is the alcohol whose hydroxyl is directly linked to a primary carbon (a carbon that links only to another carbon atom). See an example:
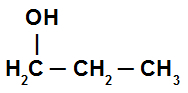
Alcohol with hydroxyl linked to a primary carbon
Secondary alcohol: is the alcohol whose hydroxyl is directly linked to a secondary carbon (a carbon that links to two other carbon atoms). See an example:
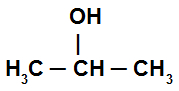
Alcohol with hydroxyl linked to a secondary carbon
Tertiary alcohol: is the alcohol whose hydroxyl is directly linked to a tertiary carbon (carbon that binds to three other carbon atoms). See an example:

Alcohol with hydroxyl linked to a tertiary carbon
d) Nomenclature
THEnomenclature IUPAC of an alcohol must follow the rule expressed below:
Prefix + infix + ol
of the type number of
carbon bonding
Let's follow some examples of application of the rule:
Example1: Ethanol
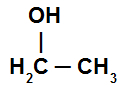
Ethanol structural formula
Alcohol has a normal chain, two carbon atoms (prefix et) and only single bonds between the carbons (prefix an). For the nomenclature, just join the prefix (et), the infix (an) and 'ol'. Thus, the name of this compound is:
Ethanol
Example 2: Propan-1,2-diol
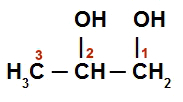
Structural formula of Propan-1,2-diol
Alcohol has a normal chain with three carbon atoms (prop prefix), only single bonds between carbons (infix an) and two hydroxyl groups (diol as suffix). As it has more than two carbons, it is necessary to number the chain so that the position (1 and 2) of the hydroxyls is informed in the name. Thus, the name of the compound is:
Propan-1,2-diol
Example 3: 3-methyl-butan-2-ol
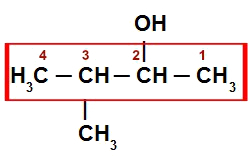
Structural formula of 3-methyl-butan-2-ol
like this alcohol presents branched chain, the first step is to locate the main chain (it must have the carbon attached to the OH group and as many carbons as possible). In this case, it will be the horizontal sequence from left to right, which has four carbons. (prefix but). Your numbering should start on the right, the part that is closest to the OH group.
The main chain has a methyl radical (CH3) on carbon 3 and just simple bonds between carbons (infix an). The hydroxyl (suffix ol) it is located on carbon 2. So, your name is:
3-methyl-butan-2-ol
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-um-alcool.htm

