We all feel hunger, thirst, smells, sounds, pains. All these sensations are produced from stimuli from a very important system in our body, the nervous system. To hear the sound of a bird singing, the ear needs to pick up the vibrations of that sound and send a nervous stimulus to the brain. There it is decoded and interpreted. So, you hear the sound. But that happens in milliseconds, let's find out how?
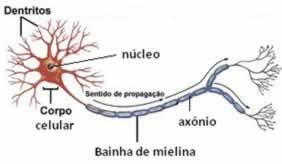
Composition of a neuron
Our nervous system is made up of nerve cells called neurons, which are composed of:
• Dendrites: small filaments that receive impulses from other neurons;
• axon: elongated and thin filament of the cell. Transmits nerve impulses;
• cell body: where is the cell nucleus;
• myelin sheath: myelin is an insulating substance produced by the axon that has the function of increasing the speed of transmission of impulses.
Between neurons there is a small space called a synapse. When the nerve impulse reaches the axon, substances (neurotransmitters) are released at the synapses. These substances cause changes in the ends of other cells, causing a new nerve impulse, passing quickly from one cell to another.
There are three types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons and association neurons.
Sensory neurons receive stimuli from the sense organs (sight, smell, hearing, taste and touch) and take them to the central nervous system to be decoded and interpreted.
Motor neurons carry central nervous system responses to muscles or other organs for execution.
Association neurons make the connections between all neurons.
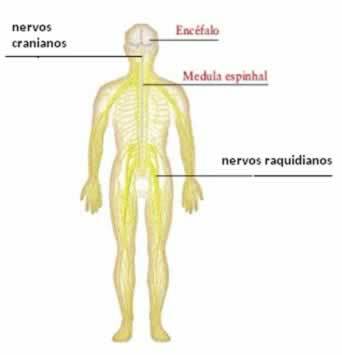
Central and peripheral nervous system
The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is located in the skull and is made up of the cerebellum, brain and medulla. The spinal cord is an extension of the brain.
The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that originate in the brain and spinal cord. This system connects the central nervous system with the rest of the body.
Take the opportunity to check out our video lesson on the subject:


