It is a colorless, tasteless and odorless gaseous element found in the atmosphere, water, most rocks and minerals, and numerous organic compounds. It is essential for life, as among living organisms only a few forms of plant life can exist without it.
In the breathing process, air is drawn into the lungs, where a lot of oxygen is absorbed by the blood. It is then transported to all parts of the body, oxidizing worn-out tissues and turning them into substances that can be easily eliminated.
Oxygen also makes up about 21% of Earth's atmosphere and is able to combine with all elements of the periodic table except inert gases. Its atomic number is 8 and its symbol is O.
It is also found in large quantities in the earth's crust in its solid form, as various oxides. Furthermore, the oceans contain an abundance of oxygen in its H2O form, also known as hydrogen monoxide or water.
The gas was discovered by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm in 1772, after an experiment in which he heated different compounds containing oxygen. After these experiments the chemist called the gas "fire air".
Oxygen molecule.
Oxygen on the periodic table
The element oxygen is located in the "non-metals" section, which can be located in the groups 14, 15 and 16 of the Periodic Table.
Non-metallic elements exist, at room temperature, in two of the three states of matter: gases (oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen) and solids (carbon, phosphorus, sulfur and selenium).
Oxygen is the most abundant of all the elements, and is found in both its free (O) and combined (example: H2O) states.
In its free state that occurs in the atmosphere, for every 100 volumes of dry air there is about 21 volumes of oxygen. In its combined state, it forms eight water nodes and almost half of the rocks that make up the earth's crust.
It is also an important constituent of the compounds that form plant and animal tissue. About 66% by weight of the human body is oxygen, and it also comprises about 88% by weight of the oceans as H2O (water).
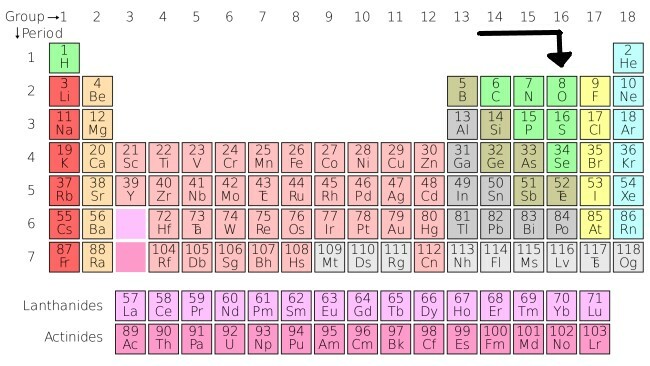
Indication of oxygen in the periodic table.
The different uses of oxygen
The main use of oxygen is in the process of human, animal and plant respiration. As it is a vital gas, it is also widely used in medicine to treat people with respiratory problems, in addition to being used in tanks as a support for astronauts and divers in action.
In industry, oxygen is widely used in steelmaking, in addition to the production of new compounds such as plastics and the creation of very hot flames for welding.
Another important use of oxygen is as a rocket fuel, when combined with hydrogen in its liquid state.
Oxygen therapy: what is it and what is it for?
Some people with breathing disorders are unable to absorb enough oxygen into the body properly. natural, so they need oxygen therapy treatment, prescribed for patients as respiratory disorders like:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- Pneumonia;
- Asthma;
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia;
- Underdeveloped lungs in newborns;
- Cardiac insufficiency;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- Sleep apnea;
- Lung disease trauma to the respiratory system.
To determine whether a person will benefit from oxygen therapy, doctors need to test the amount of oxygen in the arterial blood. Another way to check is to use an oximeter, a device that can indirectly measure oxygen levels without requiring a blood sample.
The oximeter attaches to a person's body part, the finger, for example. If the result reports low levels, it means the patient may need supplemental oxygen. Normal arterial blood oxygen levels are between 75 and 100 mmHg (millimeters of mercury).
An oxygen level of 60 mmHg or less indicates the need for supplemental oxygen (oxygen therapy). A large amount of oxygen can also be dangerous and even cause damage to lung cells, meaning a patient's oxygen level should not exceed 110 mmHg.

An oximeter device that measures the volume of oxygen in a patient's body.
Oxygen Fun Facts
- Oxygen dissolves more easily in cold water than in warm water;
- Water can be converted to hydrogen and oxygen by electrolysis;
- The oxygen that is found in air is produced by photosynthesis. Therefore, without plants, there would be very little oxygen in the air;
- In the solar system, only Earth has a high percentage of oxygen;
- Oxygen atoms make up an essential part of the proteins and DNA in our bodies;
- The process of combining oxygen with other atoms to produce compounds is called oxidation;
See also the meaning of:
- Photosynthesis;
- Carbon dioxide;
- Atmosphere;
- Greenhouse effect.

