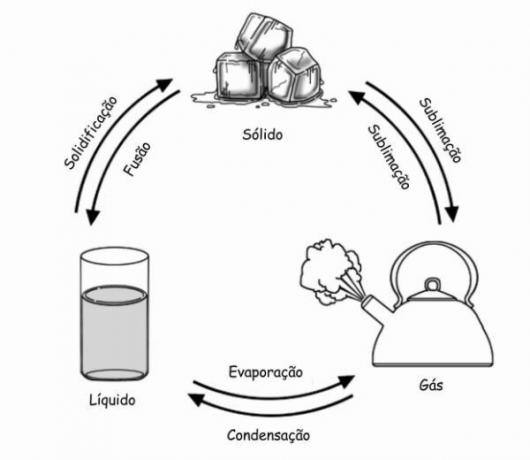
Condensation or liquefaction is the chemical process of transforming matter from a gaseous state to a liquid. In short, it consists of the inverse of vaporization, when matter from the liquid state is transformed into gas.
Condensation occurs when steam or gas reaches a temperature below its boiling point. In the case of water vapor, for example, condensation starts when the temperature is below 100 degrees Celsius. Thus, the gaseous state of water is transformed into liquid droplets.
At boiling, water molecules gain energy (due to heat) and agitate, causing them to separate and change shape to a gaseous (vapor) state. When losing heat, molecules also lose energy and decrease the degree of agitation. As they become slower, the molecules attract each other again. Thus, they reorganize themselves in the form of the liquid state.
Condensation is part of one of the five processes of transformation of matter, as well as the Sublimation, Evaporation, Solidification and the Fusion.
See also: meaning of Vaporization and Boiling.
In the figurative sense of the word, condensation can also represent the act or effect of summarizing certain content to the essential, be it a text, an idea, a story and so on.
pulmonary condensation
It is an indicative sign of respiratory diseases in the pulmonary system, when the alveolar air present in the lungs is replaced by a liquid state, which can damage the place where it is concentrated.
Also known as pulmonary consolidation, this type of condensation can be caused as consequence of pneumonia, edema, pulmonary hemorrhages or due to aspiration of an object foreign to the body.


