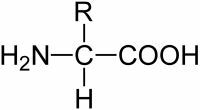
troposphere is the atmospheric layer closest to the earth's surface, averaging approximately 12 km in altitude.
In the troposphere all the weather phenomena witnessed on Earth, such as rain, lightning, cloud formation, snow, and so on. This layer also accumulates the most aggravating part of air pollution.
The thickness of the troposphere varies according to certain areas of the planet, for example, at the poles this layer is 5 km long, while at the equator it reaches up to 18 km.
The troposphere also houses the so-called anthroposphere, that is, part of the Earth where human beings live.
On average, tropospheric temperatures can vary between 40 degrees Celsius and -60 degrees Celsius, and the higher the altitude, the lower the temperature.
The boundary of the troposphere with the stratosphere is made by the tropopause, a region of thermal inversion, where the temperature of the atmosphere stops decreasing and starts to rise again.
Learn more about meaning of the stratosphere.
The composition of the troposphere consists of approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 1% other gases.
Troposphere characteristics
- Atmospheric layer closest to the Earth's surface;
- Temperatures between 40 and -60 degrees Celsius;
- Climatic and atmospheric phenomena are formed (rain, snow, hail, clouds, etc.);
- Between 5 and 20 km thick;
- Concentration of much of the air pollution.
Know more about:
- Atmosphere
- Atmosphere layers