Macroeconomics is an area of study of Economic Sciences, responsible for analyze factors in the economic system of a particular region or country.
The analysis made by macroeconomics is global, disregarding the particularities or individual behaviors. the greek prefix macro it is relative to everything that is big, wide and wide.
The main objectives of macroeconomic studies are: the development of economic growth, the generation of jobs, reducing inflation, building advantageous international trade and stabilizing prices.
Among the points that are studied by macroeconomics is the income and products produced by a territory (Internal Product Gross - GDP), as well as the levels of prices, employment and unemployment, the exchange rate and interest, the currency, among others factors.
Learn more about the meaning of GDP.
The macroeconomic structure is divided into five main parts:
- Goods and Services Market: determines the level of production and prices in the analyzed region;
- Labor Market: determines the wage rate and employment level;
- Monetary Market: studies the value of the currency and the interest rate, based on its offer by the Central Bank;
- Securities Market: study of economic agents with higher and lower expenses in relation to final income;
- Foreign Exchange Market: related to the volume of imports and the outflow of financial capital;
The concept of macroeconomics emerged and began to be discussed in the early 1930s. This study was developed from the Great Depression of 1929.
the British economist John Maynard Keynes he is considered the first great author on macroeconomics, standing out for his book “General Theory of Employment, Interest and Currency”, published in 1936.
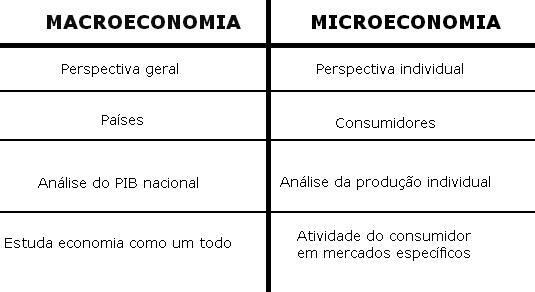
Macroeconomics and Microeconomics
Macroeconomics studies the economic values of a society or large group, not considering the particularities of its members, but all as a single entity.
Microeconomics (or Price Theory) is the study of individual and particular economic behavior, such as workers, companies and families, for example.
See more about the meaning of economy.
Differences between Macroeconomics and Microeconomics
Learn more about meaning of microeconomics.

