urban network is the set of cities or urban centers that are territorially articulated and that they establish different relationships with each other.
Urban networks are formed by cities of different sizes and levels of development and are interconnected due to the flow of people, goods and services.
The concept of urban network can be understood as a mesh of interconnected cities, organized according to a urban hierarchy. At the top of this hierarchy are the cities that have the greatest power to influence others.
Urban networks are the result of society's transformations in the occupation of the territory and the demographic growth process.
Understanding the dynamics and processes of an urban network is important for government, social and economic management and for the development of public policies.
urban network and urban hierarchy
The hierarchy of cities or urban centers is determined by the order of importance and degree of influence exercise in a particular region of the territory. At the highest level of the urban hierarchy will be the largest and most developed cities in a country.
This development is represented by the offer of services - public and private -, by the evolution of economic activities, and by the transport and communication infrastructure.
The configuration of an urban network is what determines the hierarchy between cities and the more exchanges between them grow, the more they rise in this hierarchy. This means that the importance of cities is due to the number of connections that they do with others.
know more about urban hierarchy.
Brazilian urban hierarchy
The IBGE methodology for classifying urban centers according to the survey "Network of influence of cities", published in 2007, divides cities as follows:
metropolises
The metropolises are the 12 largest urban centers in the country, exerting a strong influence among themselves and in their regions. Metropolises are divided into three hierarchies.
- Great national metropolis: Sao Paulo
- National metropolis: Rio de Janeiro and Brasilia
- Metropolis: Belém, Fortaleza, Manaus, Salvador, Recife, Curitiba, Goiânia, Belo Horizonte and Porto Alegre
regional capital
They are cities with an area of regional influence, they are the destination of the population of other cities in the region for various activities. This classification includes 70 urban centers, divided into three levels of hierarchy.
sub-regional center
They are cities with a smaller operating area and less complex management activities. Their external relationships, in general, only happen with the national metropolises. This classification consists of 169 centers, divided into two subcategories.
zone center
Cities with elementary management functions, operating only in their area and small. In this category there are 556 cities, subdivided into two levels.
local center
Cities that have influence only within their boundaries and that provide services only to their inhabitants. These correspond to the remaining 4473 cities.
 Source: Rede Urbana - Brazil – 2007- Fonte_Instituto Geográfico e Cartográfico – IGC. São Paulo, 2003
Source: Rede Urbana - Brazil – 2007- Fonte_Instituto Geográfico e Cartográfico – IGC. São Paulo, 2003
Urban network and urbanization
The formation of an urban network is result of the urbanization process of a country, which occurs when the urban population grows more than the rural population.
As cities grow, the demand for services such as health, education, transport and energy increases. In this process, both public and private capital will be invested in order to meet these demands.
The places that receive more investments have a better offer of services and better infrastructure.
Understand better what the urbanization.
Brazilian urban network
In Brazil, urbanization began to intensify from the 1930s onwards. With the development of industry and the mechanization of the countryside, a large part of the rural population was forced to migrate to the cities in search of employment - this phenomenon is called rural exodus.
Over the following decades, economic and political dynamics in the Brazilian territory determined the spatial occupation and development of cities.
Urban centers that had more prosperous economic activities developed faster and the accumulation of capital in these regions allowed them to become richer.
As the urbanization of Brazil happened in an accelerated and unplanned way, many regional imbalances have been reproducing and intensifying over the decades.
Today, the country is configured with an urban network that concentrates on the Southeast the most developed and economically influential cities. While other regions such as the North and Northeast have more precarious conditions for the supply of goods and services and infrastructure.
know more about rural exodus.
global cities
There are also global cities, which are represented by the main economic centers in the world, such as Paris, New York, Tokyo and São Paulo.
Global cities, by exerting influence outside the borders of their countries, create urban networks on a world scale. This configuration and interconnection between urban centers at an international level was made possible by the phenomenon of globalization.
See the map of global cities:
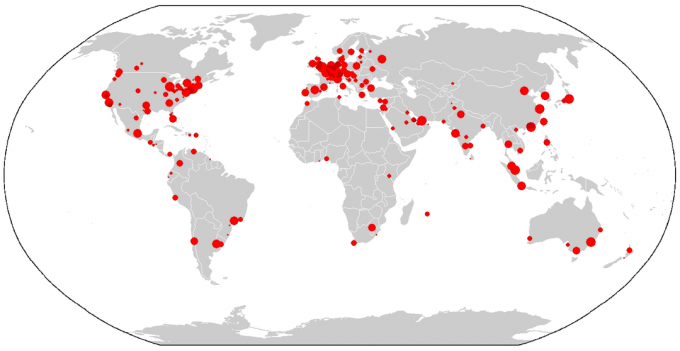 Map of global metropolises. Source: globalization and World Research Network
Map of global metropolises. Source: globalization and World Research Network
See the meaning of globalization.
Urban network and the spatial division of labor
The urban network reflects the spatial division of labor, that is, the division between functions that different cities play in a particular region of the territory.
More influential cities and higher positions in the urban hierarchy are often technological hubs and important financial centers. The more peripheral cities, on the other hand, tend to perform more primary activities, such as agriculture or livestock.
This configuration is the result of historical process of construction of cities, therefore, to understand it, it is necessary to consider the political, economic and social aspects throughout its formation.
In summary, we can conclude that the spatial division of labor portrays how economic activities are distributed in space.
See also the meanings of metropolis, City and megalopolis.
